Month: November 2024
No Time for Menopause: Empowering Women to Thrive Through the Transition

Let’s face it: menopause isn’t exactly a topic most of us bring up at brunch or during office water-cooler chats. It’s often shrouded in silence, yet it’s an inevitable phase for half the population. But here’s the thing—there’s no reason menopause should be a time of dread. Women today are busier, more empowered, and achieving more than ever. From running businesses to managing families, there’s simply no time to let menopause slow you down.
So, how do you navigate menopause while staying at the top of your game? This article dives into everything you need to know about menopause—what it is, its symptoms, and how to take control of your life during this transition. It’s time to shift the narrative: menopause isn’t a roadblock; it’s a new chapter of power and potential.
What is Menopause?
First, let’s break it down. Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman’s menstrual cycles. It officially occurs 12 months after your last period, typically between the ages of 45 and 55. However, symptoms can start years earlier during perimenopause, the transition phase leading up to menopause. For some women, menopause arrives early due to surgery or medical conditions.
While menopause is completely normal, it comes with a cocktail of hormonal changes that can affect your body and mind. The good news? With the right mindset and strategies, you can tackle it head-on.
Common Symptoms of Menopause
Hormonal shifts during menopause may lead to a range of symptoms, including:
• Hot Flashes: Sudden bursts of heat that can leave you drenched in sweat.
• Mood Swings: Feeling like you’re riding an emotional rollercoaster.
• Sleep Disturbances: Insomnia or waking up in the middle of the night.
• Weight Gain: Hormonal changes may affect your metabolism.
• Decreased Libido: Lower estrogen levels can reduce sex drive.
• Brain Fog: Difficulty concentrating or remembering things.
• Dry Skin and Hair: Collagen production may decrease, leading to dryness.
These symptoms can vary in intensity and duration, but they don’t have to define your life.
Why Women Have No Time for Menopause
The modern woman is juggling multiple roles—entrepreneur, employee, mother, partner, friend, and more. Menopause doesn’t come with a “pause” button for life’s responsibilities, and honestly, who has time to sit around waiting for hot flashes to pass or brain fog to lift?
Women today aren’t letting menopause sideline their ambitions. Instead, they’re looking for practical, effective ways to navigate this phase without missing a beat. It’s all about embracing solutions that fit into your busy lifestyle and help you stay unstoppable.
How to Stay in Control During Menopause
1. Prioritize Your Health
Menopause is the perfect time to double down on self-care. Here’s how:
• Eat Smart: Focus on nutrient-rich foods like leafy greens, lean proteins, and whole grains. Incorporate calcium and vitamin D to support bone health, as osteoporosis risk increases after menopause.
• Stay Active: Regular exercise isn’t just good for your body—it’s great for your mind. Strength training, yoga, and cardio can help reduce symptoms like mood swings, weight gain, and sleep issues.
• Stay Hydrated: Hormonal changes can lead to dry skin, so drink plenty of water to keep your body hydrated.
2. Manage Stress
Stress can exacerbate menopause symptoms, so finding ways to relax is crucial. Try:
• Mindfulness Practices: Meditation and deep breathing can reduce anxiety and improve focus.
• Creative Outlets: Whether it’s painting, writing, or gardening, doing something you love can be a great stress reliever.
• Delegate: Don’t hesitate to ask for help or delegate tasks to lighten your load.
3. Embrace Hormone Therapy
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can be a game-changer for some women, helping to alleviate symptoms like hot flashes and mood swings. Consult your doctor to determine if it’s the right option for you.
4. Stay Social
Isolation can make menopause feel more overwhelming. Surround yourself with supportive friends or join menopause-focused communities online. Sharing your experiences can be incredibly validating.
5. Talk to a Specialist
Menopause doesn’t come with a one-size-fits-all solution. Consulting a menopause specialist can help you create a tailored plan to manage symptoms and maintain your quality of life.
Menopause Myths to Bust
Let’s clear up some common misconceptions:
• Myth: Menopause means the end of your sex life.
Truth: With the right support (like lubricants or hormone therapy), your sex life can be just as satisfying as ever.
• Myth: Menopause equals weight gain.
Truth: While hormonal changes can affect your metabolism, maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine can keep weight in check.
• Myth: Menopause is the end of productivity.
Truth: Many women report feeling more confident and empowered after menopause. It’s a time to focus on your goals without the monthly hormonal fluctuations of earlier years.
Products and Tools to Help You Conquer Menopause
Thanks to innovation, there’s an array of products designed to help women navigate menopause. Consider incorporating these into your routine:
• Cooling Products: Items like cooling pillows or portable fans can help manage hot flashes.
• Sleep Aids: Weighted blankets or herbal teas can promote restful sleep.
• Skincare: Look for collagen-boosting serums to combat dryness and maintain your glow.
• Supplements: Calcium, magnesium, and omega-3 supplements can support overall health.
The Upside of Menopause
While menopause marks the end of one phase of life, it’s also the beginning of a new chapter filled with opportunities. With no periods to worry about, you have more freedom to focus on yourself and your goals. Many women find this phase empowering, as it often comes with greater self-awareness and a renewed sense of purpose.
Consider menopause a chance to reinvent yourself. Take up new hobbies, set ambitious career goals, or travel to places you’ve always dreamed of. This is your time to thrive.
Breaking the Stigma Around Menopause
Despite being a universal experience, menopause is often treated as a taboo topic. It’s time to change the conversation. Women should feel comfortable discussing their symptoms, seeking support, and exploring solutions without shame. By breaking the stigma, we can ensure that menopause is seen as a natural and manageable life stage—not a life sentence.
Final Thoughts
Menopause doesn’t mean slowing down—it’s a time to recalibrate, focus on self-care, and embrace the possibilities ahead. Women today are proving that you can thrive during menopause and beyond, shattering stereotypes and redefining what it means to age gracefully.
With the right strategies, support, and mindset, you can navigate menopause with confidence and strength. So, to all the busy, unstoppable women out there: there’s no time for menopause to hold you back. Keep moving forward, chasing your dreams, and showing the world that this phase of life is just the beginning of something amazing.
#NoTimeForMenopause #ThriveThroughMenopause #MenopauseEmpowerment #HealthyAging #StrongWomen #MenopauseSupport #BreakingTheStigma #SelfCareMatters #WomenInCharge #HormonalHealth
Pregnancy Test in the Morning vs. Night: Does Timing Really Matter?

Taking a pregnancy test can be one of the most nerve-wracking experiences. Whether you’re anxiously hoping for a positive or dreading the possibility, you probably want the most accurate result possible. And then comes the big question: Is it better to take a pregnancy test in the morning or at night?
If you’ve found yourself staring at a box of tests wondering whether to wait for morning or just take it now, this guide is for you. Let’s break down the science, the myths, and the practical tips to help you get the most accurate result—day or night.
How Do Pregnancy Tests Work?
First, let’s cover the basics. Pregnancy tests detect a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in your urine. Your body starts producing hCG after a fertilized egg implants in the uterus, which usually happens about 6–12 days after ovulation.
• The role of hCG: This hormone signals your body to maintain the pregnancy.
When Timing Doesn’t Matter
In some situations, it’s okay to test at any time of the day:
1. Testing After a Missed Period
If it’s been several days since your missed period, your hCG levels are likely high enough to be detected regardless of when you test. At this stage, even diluted urine should give an accurate result.
2. Using High-Sensitivity Tests on
Some pregnancy tests can detect hCG levels as low as 6.5 mIU/mL (microunits per milliliter). These tests, often marketed as “early detection,” are designed to work well at any time of the day.
3. Testing Twice
If you test at night and get a negative result but suspect you’re pregnant, try again the next morning. False negatives can happen, especially with diluted urine or if you’re testing too early.
Tips for Accurate Pregnancy Testing
No matter when you test, follow these tips for the most reliable results:
1. Follow the Instructions
This may seem obvious, but each test is slightly different. Make sure you read the instructions for how long to wait before reading the result and how to interpret faint lines.
2. Wait Until Your Missed Period
While early testing is tempting, waiting until the day of your missed period (or later) will give you the most accurate result.
3. Don’t Drink Excessive Fluids Before Testing
Whether you’re testing in the morning or at night, avoid drinking a lot of water right before taking the test. Diluted urine can lead to false negatives.
4. Use a High-Sensitivity Test
If you’re testing early or at night, choose a test designed for early detection. Brands like First Response and Clearblue often perform better in these situations.
5. Confirm with a Blood Test
If you’re getting mixed results or faint lines, a blood test at your doctor’s office can confirm whether you’re pregnant.
Common Questions About Pregnancy Testing
1. Can I trust a faint line?
A faint line usually means you’re pregnant, but it might be early, and hCG levels are still low. Retest in a day or two for confirmation.
2. How soon can I test after ovulation?
Most tests recommend waiting until at least 10–14 days after ovulation for accurate results. Testing too early can lead to false negatives.
3. Can medications affect the results?
Fertility medications containing hCG (like trigger shots) can cause false positives. Always consult your doctor if you’re undergoing fertility treatments.
The Verdict: Morning or Night?
So, when’s the best time to take a pregnancy test? Morning wins for early testing, thanks to higher urine concentration and increased accuracy. However, if you’re a few days past your missed period or using a high-sensitivity test, nighttime testing can still give reliable results.
The key is to manage your expectations and follow up with a second test (or a blood test) if you’re unsure. Remember, whether you’re testing at dawn or dusk, you’re taking an important step toward clarity—and hopefully, good news!
PCOS vs. Endometriosis: Understanding the Differences and Similarities

When it comes to reproductive health, two conditions often come up in conversation: polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and endometriosis. Both are common, both can wreak havoc on your body, and both can make you want to throw your hands up in frustration. But while they share some overlapping symptoms, they’re very different conditions that require distinct approaches to treatment.
In this guide, we’ll dive into everything you need to know about PCOS vs. endometriosis—what they are, how they differ, and what to do if you suspect you have one (or both!).
What Is PCOS?
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS, is a hormonal disorder that affects how your ovaries function. Despite the name, not everyone with PCOS has ovarian cysts, but it’s characterized by a trio of key symptoms:
1. Irregular or Missed Periods: Hormonal imbalances can prevent regular ovulation.
2. Excess Androgens: These “male” hormones can lead to acne, hair thinning, and unwanted body or facial hair.
3. Polycystic Ovaries: The ovaries may become enlarged and contain many small follicles, but these aren’t true cysts.
PCOS is primarily driven by insulin resistance and hormonal imbalance, which can also lead to weight gain, difficulty losing weight, and increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
What Is Endometriosis?
Endometriosis is a completely different beast. It’s a chronic condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (the endometrium) grows outside the uterus. These rogue tissues can attach to organs like the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or even the intestines, causing inflammation, scarring, and pain.
Key Symptoms of Endometriosis
• Severe Period Pain: Cramping that goes beyond “normal” discomfort.
• Chronic Pelvic Pain: Pain that lingers even outside of your period.
• Painful Sex: Discomfort during or after intercourse.
• Infertility: Endometriosis can affect the fallopian tubes and egg quality.
Unlike PCOS, endometriosis isn’t directly linked to insulin resistance or hormonal imbalances—it’s more about inflammation and tissue growth where it doesn’t belong.
How Are PCOS and Endometriosis Similar?
At first glance, PCOS and endometriosis might seem interchangeable because of some shared symptoms. Let’s take a look at the overlap:
1. Irregular Periods
• PCOS: Irregular periods are common due to a lack of ovulation.
• Endometriosis: Irregular periods can happen, but they’re usually secondary to pain or heavy bleeding.
2. Infertility
Both conditions can make it harder to conceive, but for different reasons:
• PCOS: Hormonal imbalances can disrupt ovulation.
• Endometriosis: Scar tissue and inflammation can block or damage reproductive organs.
3. Pain (Sometimes)
• PCOS: Pain is not a hallmark symptom, though some may experience ovarian discomfort.
• Endometriosis: Pain is one of the most defining and debilitating symptoms.
How Are PCOS and Endometriosis Different?
While the overlap can be confusing, these conditions have distinct causes and mechanisms.
1. Root Cause
• PCOS: Driven by hormonal imbalances, particularly excess androgens and insulin resistance.
• Endometriosis: Caused by abnormal tissue growth and inflammation, though its exact trigger remains unclear.
2. Main Symptoms
• PCOS: Focuses on hormonal issues like acne, weight gain, and missed periods.
• Endometriosis: Centers on pain, heavy periods, and inflammation.
3. Diagnosis
• PCOS: Diagnosed based on symptoms, blood tests, and sometimes ultrasound imaging.
• Endometriosis: Often requires laparoscopic surgery for a definitive diagnosis.
Can You Have Both PCOS and Endometriosis?
Unfortunately, yes. Some women face the double challenge of managing both conditions. Having PCOS and endometriosis simultaneously can complicate diagnosis and treatment, as symptoms may overlap or mask one another.
For example, someone with PCOS and endometriosis might experience:
• Irregular periods from PCOS combined with severe pain from endometriosis.
• Infertility issues caused by both conditions.
• Difficulty determining whether weight gain is due to PCOS or the hormonal effects of endometriosis treatments.
How Are PCOS and Endometriosis Treated?
Treatment varies widely for each condition, depending on your symptoms, goals (e.g., fertility or symptom relief), and overall health.
PCOS Treatments
1. Lifestyle Changes: Diet, exercise, and weight management are crucial for managing insulin resistance.
2. Medications:
• Birth Control Pills: Regulate periods and reduce androgen-related symptoms.
• Metformin: Improves insulin sensitivity.
• Spironolactone: Reduces androgen-related symptoms like acne and hair growth.
3. Fertility Treatments: Ovulation-stimulating medications like clomiphene or letrozole.
Endometriosis Treatments
1. Pain Management: NSAIDs like ibuprofen can help with inflammation and pain.
2. Hormonal Therapies:
• Birth Control Pills: Reduce or stop periods, limiting endometrial tissue growth.
• GnRH Agonists: Suppress estrogen to shrink tissue growth.
3. Surgery: Laparoscopic surgery can remove endometrial tissue and scar tissue, improving fertility and reducing pain.
How to Tell If You Have PCOS, Endometriosis, or Both
If you suspect one or both of these conditions, here’s what you can do:
1. Track Your Symptoms: Keep a journal of your menstrual cycle, pain levels, and any other symptoms like acne or weight changes.
2. Visit Your Doctor: Share your symptoms and ask for specific tests, such as hormone panels or imaging.
3. Push for a Referral: If your symptoms are severe or your doctor isn’t giving you answers, don’t hesitate to ask for a referral to a specialist like a gynecologist or endocrinologist.
4. Consider Surgery: If endometriosis is suspected and other tests are inconclusive, laparoscopic surgery may be necessary.
Living with PCOS or Endometriosis
Managing either condition (or both) can feel overwhelming, but there are plenty of resources and treatments to help you take control.
For PCOS:
• Focus on lifestyle changes like a low-glycemic diet and regular exercise.
• Consider support groups or online communities for shared tips and motivation.
For Endometriosis:
• Advocate for pain management—your pain is valid and deserves attention.
• Explore holistic options like acupuncture or anti-inflammatory diets alongside medical treatments.
The Bottom Line
While PCOS and endometriosis are very different conditions, they’re both manageable with the right approach. Understanding the key differences—and how they can overlap—is the first step to taking control of your reproductive health.
If you suspect you have PCOS, endometriosis, or both, don’t wait to seek help. You deserve to live pain-free, with the power to make informed decisions about your body and your future. And remember: you’re not alone in this journey!
Cabergoline and Pregnancy: What You Need to Know

If you’re navigating the world of fertility treatments or hormonal imbalances, you’ve likely heard about cabergoline. This medication is commonly prescribed to treat conditions related to high prolactin levels, like prolactinomas or hyperprolactinemia. But how does cabergoline impact pregnancy? Is it safe to take while trying to conceive, or during pregnancy itself? Let’s break it all down in a trendy, easy-to-digest guide.
What Is Cabergoline, and Why Is It Prescribed?
Cabergoline is a dopamine agonist, which means it works by activating dopamine receptors in your brain. This reduces the production of prolactin, a hormone that plays a role in milk production and menstrual cycles. High prolactin levels, or hyperprolactinemia, can lead to irregular periods, infertility, or even spontaneous lactation (yep, milk production when you’re not breastfeeding).
Cabergoline is often prescribed for:
• Prolactinomas: Benign tumors of the pituitary gland that cause excess prolactin.
• Hyperprolactinemia: Elevated prolactin levels that disrupt ovulation.
• Restoring Fertility: By lowering prolactin, cabergoline can help restore ovulation, increasing your chances of conceiving.
Cabergoline and Fertility: A Match Made in Hormonal Heaven
For many women struggling with infertility due to high prolactin levels, cabergoline is a game-changer. High prolactin suppresses the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), which are essential for ovulation. By lowering prolactin, cabergoline restores the hormonal balance needed for regular cycles and ovulation.
Why Prolactin Matters for Pregnancy
Prolactin isn’t just about milk production; it plays a role in regulating your menstrual cycle. When prolactin levels are too high:
• Ovulation may stop altogether (anovulation).
• Periods can become irregular or disappear (amenorrhea).
• Hormonal imbalances can make it tough to conceive.
Cabergoline steps in as the ultimate hormonal hero, clearing the way for ovulation and increasing your chances of getting pregnant.
Taking Cabergoline While Trying to Conceive
If you’re using cabergoline to lower prolactin and regulate ovulation, the big question is: what happens when you do conceive?
Should You Stop Cabergoline Once Pregnant?
The answer depends on your specific situation. Studies show that cabergoline is relatively safe for use in early pregnancy, especially if prescribed to treat a prolactinoma. However, most doctors recommend discontinuing the medication once pregnancy is confirmed, unless you have a large prolactinoma that could cause complications during pregnancy.
Why? The pituitary gland naturally enlarges during pregnancy, which can exacerbate symptoms in women with untreated prolactinomas. In such cases, your healthcare provider may continue cabergoline to prevent complications.
Is Cabergoline Safe During Pregnancy?
What the Research Says
Research on cabergoline’s safety during pregnancy is reassuring. Studies involving women who took cabergoline before and during early pregnancy show no significant increase in the risk of:
• Birth defects
• Miscarriage
• Preterm birth
However, because cabergoline hasn’t been studied extensively in pregnant women, it’s usually stopped once pregnancy is confirmed unless absolutely necessary.
FDA Pregnancy Category
Cabergoline is classified as Category B by the FDA, which means animal studies haven’t shown harm to the fetus, but there aren’t enough human studies to confirm its safety.
How Does Cabergoline Affect Breastfeeding?
If you’re planning to breastfeed after giving birth, cabergoline might throw a wrench in those plans. Since cabergoline suppresses prolactin, the hormone responsible for milk production, it can make breastfeeding difficult.
In fact, cabergoline is sometimes prescribed postpartum to stop milk production for women who choose not to breastfeed or who need to wean quickly.
If breastfeeding is important to you, discuss this with your doctor. They’ll help weigh the benefits of continuing cabergoline against the potential impact on milk supply.
Managing Prolactinomas During Pregnancy
For women with prolactinomas, pregnancy can be a bit more complex. Prolactinomas are benign, but pregnancy hormones can cause them to grow, potentially leading to symptoms like:
• Headaches
• Vision changes
• Pituitary gland dysfunction
If you have a prolactinoma, your healthcare provider will monitor you closely throughout pregnancy. In some cases, cabergoline or another dopamine agonist, like bromocriptine, may be used to manage symptoms.
Side Effects of Cabergoline
Let’s be real: no medication is without side effects. While cabergoline is generally well-tolerated, some people experience:
• Nausea
• Dizziness
• Fatigue
• Low blood pressure
These side effects are usually mild and tend to improve as your body adjusts to the medication. Taking cabergoline with food can help minimize nausea.
Alternatives to Cabergoline
If cabergoline isn’t the right fit for you, there are alternatives. Bromocriptine, another dopamine agonist, is often used for the same conditions. While it’s an older medication, bromocriptine has been studied more extensively in pregnancy and may be preferred for women planning to conceive.
Other treatments for hyperprolactinemia or prolactinomas include:
• Surgery: For large or medication-resistant prolactinomas.
• Radiation Therapy: Rarely used, but an option for aggressive tumors.
Tips for Taking Cabergoline While TTC
1. Stick to the Schedule: Take cabergoline exactly as prescribed to keep your prolactin levels in check.
2. Track Your Ovulation: Cabergoline can help restore ovulation, so tracking your cycles with ovulation tests or basal body temperature can improve your chances of conceiving.
3. Communicate With Your Doctor: Let your doctor know as soon as you suspect or confirm pregnancy so they can adjust your treatment plan.
4. Monitor Symptoms: If you have a prolactinoma, report any symptoms like headaches or vision changes immediately.
Real Talk: Cabergoline Success Stories
Many women credit cabergoline with helping them achieve their dream of pregnancy. Success stories often involve women who struggled with infertility for years due to high prolactin levels, only to conceive within months of starting the medication.
While everyone’s journey is unique, cabergoline can be a powerful ally in overcoming hormonal hurdles and taking control of your fertility.
The Takeaway
Cabergoline is a popular and effective treatment for high prolactin levels, making it a key player in fertility treatments. While it’s generally safe to use while trying to conceive, it’s typically discontinued during pregnancy unless necessary to manage a prolactinoma.
If you’re on cabergoline and planning for pregnancy, the most important thing is to work closely with your healthcare provider. Together, you can develop a plan that prioritizes both your health and your baby’s well-being.
Remember, every fertility journey is unique, and there’s no one-size-fits-all answer. With the right guidance and care, cabergoline could be the first step toward achieving your dream of parenthood.
Alcohol and Its Impact on Male Fertility: Understanding the Risks

Male fertility plays a crucial role in conception, yet it is often overlooked when discussing reproductive health. Among the many lifestyle factors that can influence fertility, alcohol consumption stands out as a significant contributor. While moderate drinking is socially acceptable and may seem harmless, excessive or long-term alcohol use can negatively affect male fertility in profound ways. In this article, we’ll explore how alcohol impacts male reproductive health, the science behind it, and practical steps to mitigate its effects.
Understanding Male Fertility
Male fertility primarily hinges on two key factors: the quality and quantity of sperm. Healthy sperm must be produced in adequate numbers and have the ability to move efficiently to fertilize an egg. Testicular function, hormonal balance, and lifestyle choices all contribute to a man’s reproductive health. When any of these factors are disrupted, fertility issues may arise.
Alcohol and Fertility: The Connection
Alcohol is a known disruptor of bodily systems, including those involved in reproduction. Here’s a breakdown of how alcohol affects male fertility:
1. Hormonal Imbalances
Alcohol consumption can interfere with the hormonal balance necessary for sperm production. Testosterone, the primary male hormone, plays a vital role in sperm development. Excessive alcohol intake reduces testosterone levels and increases the production of estrogen, the female sex hormone, in men. This hormonal shift can suppress sperm production and lead to a decrease in sperm count and quality.
2. Reduced Sperm Quality
Alcohol has a toxic effect on the testes, where sperm are produced. Research shows that excessive drinking can damage Sertoli cells, which are essential for nurturing developing sperm. This damage can result in:
• Lower sperm count
• Abnormal sperm shape (morphology)
• Poor sperm motility (movement)
All of these factors significantly reduce the chances of successful fertilization.
3. Oxidative Stress
Alcohol consumption increases oxidative stress in the body by producing free radicals and reducing antioxidant defenses. The testes, being highly sensitive to oxidative damage, can suffer impaired function. Oxidative stress can damage the DNA in sperm, which may not only reduce fertility but also increase the risk of miscarriage or developmental issues in offspring.
4. Sexual Dysfunction
Chronic alcohol use can lead to sexual health issues such as erectile dysfunction or loss of libido. Without the ability to engage in regular intercourse, conception becomes challenging. Alcohol also impairs the central nervous system, which can further contribute to sexual performance problems.
5. Impact on Testicular Health
Long-term alcohol abuse can lead to testicular atrophy, where the testes shrink and lose their ability to produce sperm efficiently. This is often irreversible and represents a significant threat to male fertility.
How Much Alcohol is Too Much?
Not all alcohol consumption will necessarily harm fertility. Moderate drinking, defined as up to two drinks per day for men, may not have a significant impact on reproductive health for most individuals. However, heavy or binge drinking poses a serious risk.
Binge drinking is typically defined as consuming five or more drinks in a single session. This pattern of drinking can lead to acute hormonal disruptions, oxidative stress, and long-term damage to the reproductive system.
Scientific Evidence on Alcohol and Male Fertility
Several studies underscore the connection between alcohol and reduced male fertility:
• A study published in Andrology found that men who consumed more than 14 alcoholic drinks per week had significantly lower sperm counts and reduced sperm motility compared to moderate drinkers.
• Research in Alcohol and Alcoholism highlighted that men with alcohol dependency often exhibit hormonal imbalances, including lower testosterone levels and higher levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which are markers of testicular dysfunction.
• Another study in Human Reproduction revealed that even moderate alcohol consumption could negatively impact sperm morphology, making it harder for sperm to fertilize an egg.
Secondary Effects of Alcohol on Fertility
Alcohol’s impact on fertility isn’t limited to direct effects on sperm. It also has indirect consequences, including:
1. Weight Gain and Obesity
Alcohol is high in empty calories, contributing to weight gain. Excess weight can lead to hormonal imbalances, including lower testosterone levels, which negatively impact fertility.
2. Liver Damage
Chronic alcohol consumption can damage the liver, which plays a role in hormone regulation. A damaged liver can lead to increased levels of estrogen in men, further impairing sperm production.
3. Lifestyle Changes
Heavy drinking often leads to unhealthy lifestyle habits such as poor nutrition, lack of exercise, and inadequate sleep—all of which can exacerbate fertility problems.
Reversing the Effects of Alcohol on Fertility
The good news is that the negative effects of alcohol on male fertility can often be reversed, especially if the damage is not severe. Here are some steps to take:
1. Reduce or Eliminate Alcohol Intake
Cutting back on alcohol or abstaining altogether is the most effective way to protect and improve fertility. Even a few weeks of sobriety can lead to measurable improvements in sperm quality and hormonal balance.
2. Maintain a Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in antioxidants (found in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains) can help combat oxidative stress and improve overall reproductive health. Zinc, selenium, and vitamins C and E are particularly beneficial for sperm health.
3. Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity can help regulate hormones, improve blood circulation to the testes, and maintain a healthy weight—all of which support fertility.
4. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can exacerbate the effects of alcohol on fertility by further disrupting hormonal balance. Incorporate stress-relief techniques such as meditation, yoga, or counseling into your routine.
5. Seek Medical Advice
If you suspect that alcohol use has affected your fertility, consult a healthcare professional. A fertility specialist can assess your sperm health and provide tailored advice for improving reproductive outcomes.
Key Takeaways
While moderate alcohol consumption may not significantly harm fertility, heavy or chronic drinking poses serious risks to male reproductive health. The effects range from hormonal imbalances and reduced sperm quality to testicular damage and sexual dysfunction. However, by making proactive lifestyle changes and reducing alcohol intake, many men can restore their fertility and improve their chances of conception.
If you’re planning to start a family or want to safeguard your reproductive health, consider your alcohol consumption habits. Small changes today can have a lasting impact on your future fertility and overall well-being.
Birth Control for Endometriosis: Managing Symptoms and Taking Control

Endometriosis is one of those conditions that’s both common and deeply misunderstood. If you’re dealing with it, you know how much it can affect your daily life, from the intense cramps and pelvic pain to heavy periods and the emotional toll it brings. But here’s the good news: there’s help available, and birth control is often one of the go-to solutions for managing the symptoms of endometriosis.
In this guide, we’ll break down how birth control works to manage endometriosis, the different types to consider, and what you should know to make an informed choice. Whether you’re newly diagnosed or exploring new treatment options, we’ve got you covered in a tone that feels more like advice from a friend than a lecture from a doctor.
What Is Endometriosis, and Why Does It Hurt So Much?
First things first: endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (the endometrium) grows outside of it. These rogue tissues can attach to the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or other pelvic organs, leading to inflammation, scarring, and a whole lot of pain.
Why is it so painful? Unlike the tissue inside your uterus that sheds during your period, these misplaced tissues have nowhere to go. They react to hormonal changes, bleeding during your cycle and causing all kinds of discomfort—from sharp cramps to chronic pelvic pain.
How Does Birth Control Help With Endometriosis?
Here’s the deal: while birth control doesn’t cure endometriosis, it can be a game-changer for symptom management. Most birth control methods work by regulating or halting your menstrual cycle, which means less stimulation for those pesky endometrial-like tissues.
Key Ways Birth Control Helps:
• Reduces or Eliminates Periods: By suppressing ovulation, birth control can minimize or even stop your periods, cutting down on the pain and inflammation caused by endometriosis.
• Balances Hormones: Many hormonal birth control options reduce estrogen levels, which slows the growth of endometrial-like tissue.
• Eases Pain and Cramps: With less endometrial tissue reacting to your cycle, you may experience fewer and less intense cramps.
The Best Types of Birth Control for Endometriosis
Not all birth control is created equal, and what works for one person might not work for another. Here’s a breakdown of the most popular options and how they can help with endometriosis:
1. The Pill (Combined Oral Contraceptives)
The classic birth control pill combines estrogen and progestin to regulate your hormones. Taking it continuously (skipping the placebo pills) can stop your period altogether, which is a big win for many people with endometriosis.
• Pros: Effective, affordable, and easy to stop if you want to try getting pregnant.
• Cons: You have to remember to take it every day, and some people experience side effects like nausea or mood swings.
2. Progestin-Only Pills
These are another pill option but without estrogen. They’re ideal for people who can’t tolerate estrogen or have other health conditions that make estrogen-based birth control risky.
• Pros: Safe for a wider range of users.
• Cons: Slightly less effective than combination pills if not taken perfectly.
3. Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
Hormonal IUDs like Mirena or Liletta release progestin directly into the uterus, reducing pain and heavy bleeding associated with endometriosis. Bonus: they last for years!
• Pros: Long-term, low-maintenance, and highly effective.
• Cons: Insertion can be uncomfortable, and there’s a small risk of side effects like spotting or cramping.
4. Birth Control Shots (Depo-Provera)
This progestin-only option involves getting a shot every three months. It suppresses ovulation and often stops periods altogether after a few cycles.
• Pros: No daily pills to remember, and many users experience no periods at all.
• Cons: You’ll need to visit your doctor regularly, and it can take a while for your cycle to return to normal after stopping.
5. Birth Control Implants (Nexplanon)
This tiny rod is inserted under your skin and releases progestin to prevent ovulation. It can last up to three years and is highly effective for managing endometriosis symptoms.
• Pros: Long-lasting and hassle-free.
• Cons: Some users report irregular bleeding or spotting.
6. Vaginal Rings (NuvaRing)
This flexible ring delivers a steady dose of estrogen and progestin when inserted into the vagina. You wear it for three weeks, then remove it for one week.
• Pros: Fewer hormonal spikes compared to pills.
• Cons: Some people find it uncomfortable or difficult to insert.
Natural Cycles vs. Hormonal Control
If you’re someone who prefers a more “natural” approach, you might be hesitant about hormonal birth control. While it’s true that lifestyle changes like diet, exercise, and stress management can help with overall health, they usually aren’t enough to tackle the full-blown symptoms of endometriosis.
Hormonal birth control isn’t about masking the problem; it’s about giving your body a break from the hormonal rollercoaster that worsens the condition. That said, it’s always worth discussing your preferences with a healthcare provider to find the right balance.
Are There Risks or Side Effects?
Like any medication, hormonal birth control comes with potential side effects. These can include:
• Nausea
• Headaches
• Mood changes
• Weight fluctuations
• Spotting between periods
It’s important to weigh these side effects against the benefits of pain relief and improved quality of life. If one method doesn’t work for you, don’t give up—there are plenty of options to try.
What If You’re Trying to Get Pregnant?
For those with endometriosis who want to conceive, birth control obviously isn’t the long-term solution. However, it can be part of a strategic plan. Doctors sometimes recommend taking hormonal birth control for a while to suppress endometrial tissue growth, then stopping it to try for pregnancy.
If you’re struggling to conceive, fertility treatments like in-vitro fertilization (IVF) or laparoscopic surgery to remove excess tissue may be options worth exploring.
Talking to Your Doctor: What to Ask
Choosing the right birth control method for endometriosis starts with an honest conversation with your doctor. Here are some questions to ask:
• Which birth control method do you recommend for my symptoms?
• How long will it take to see results?
• What are the potential side effects of this method?
• Can I use this method if I want to get pregnant in the future?
• Are there non-hormonal options for managing my symptoms?
The Takeaway
Endometriosis is tough, but you’re tougher. Birth control can be a powerful tool to manage the pain, heavy periods, and other symptoms that come with this condition. From pills and IUDs to implants and shots, there’s a method out there to fit your lifestyle and needs.
The key is to work with your healthcare provider to find what works best for you. Don’t settle for suffering—take control of your symptoms and get back to living your life on your terms. Endometriosis might be part of your story, but it doesn’t have to define it.
Breast Pain in Menopause: Why It Happens and How to Manage It

Menopause comes with a long list of symptoms—hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, you name it. But one symptom that doesn’t get enough attention? Breast pain. Yes, even though menopause signals the end of your monthly cycle, it doesn’t mean your breasts get a free pass.
For many women, breast pain during menopause can be confusing, frustrating, and downright uncomfortable. So let’s break it down: why does it happen, when should you be concerned, and what can you do to ease the discomfort?
What Causes Breast Pain During Menopause?
Breast pain, also called mastalgia, can occur for several reasons during menopause. While it’s more common during perimenopause (the transition phase leading up to menopause), some women continue to experience it post-menopause.
Here are the main culprits:
1. Hormonal Fluctuations
During perimenopause, your estrogen and progesterone levels are all over the place—one day high, the next day low. These hormonal shifts can cause tenderness, swelling, or aching in your breasts.
Even in post-menopause, when hormone levels stabilize, the lower levels of estrogen can cause changes in breast tissue that lead to discomfort.
2. Changes in Breast Tissue
As estrogen levels drop, your breast tissue becomes less dense and more fatty. This natural change can cause a different kind of breast pain, often described as soreness or a dull ache.
3. Lifestyle Factors
Your habits can also play a role in breast pain. For instance:
• Caffeine: Too much coffee or tea can increase breast tenderness.
• Diet: High-fat diets and processed foods can contribute to inflammation.
• Stress: Stress increases cortisol levels, which can indirectly affect breast tissue.
4. Medications
Certain medications, including hormone replacement therapy (HRT), can cause breast pain as a side effect. If you’re taking HRT to manage menopause symptoms, your doctor may adjust your dose to reduce discomfort.
Types of Breast Pain in Menopause
Not all breast pain is the same, and understanding the type you’re experiencing can help pinpoint the cause and the best course of action.
1. Cyclical Breast Pain
This is the kind of pain many women experience during their menstrual cycles—tender, swollen breasts that come and go with hormonal changes. During perimenopause, you might notice this type of pain as your cycles become irregular.
2. Non-Cyclical Breast Pain
Non-cyclical pain is not tied to your menstrual cycle and is more common in post-menopausal women. It may feel like a sharp, burning sensation or a constant ache.
3. Chest Wall Pain
Sometimes, what feels like breast pain is actually pain in the chest wall, muscles, or ribs underneath the breast. This type of pain can be caused by injury, inflammation, or even posture.
When Should You Be Concerned About Breast Pain?
Breast pain during menopause is usually not a cause for alarm. However, it’s essential to stay vigilant and know when to seek medical advice.
Red Flags to Watch For:
• Lumps or Thickened Tissue: While most breast pain isn’t related to cancer, any new lump should be checked by a doctor.
• Nipple Discharge: Especially if it’s bloody or occurs without squeezing.
• Localized Pain: Persistent pain in one area of the breast that doesn’t go away.
• Changes in Appearance: Skin dimpling, redness, or changes in breast size or shape.
If you notice any of these symptoms, schedule a visit with your healthcare provider for further evaluation.
How to Relieve Breast Pain During Menopause
The good news? There are plenty of ways to manage and reduce breast pain, whether it’s mild or more severe.
1. Wear a Supportive Bra
The right bra can make a world of difference. Look for bras with:
• Proper support (no underwires digging into your skin).
• Wide straps for even weight distribution.
• A good fit (get measured if you’re unsure!).
Sports bras can also provide extra comfort, especially during exercise.
2. Adjust Your Diet
What you eat can have a significant impact on breast pain:
• Cut back on caffeine: Studies suggest reducing coffee, tea, and chocolate can help decrease tenderness.
• Reduce salt intake: Less sodium means less water retention, which can reduce swelling.
• Focus on anti-inflammatory foods: Incorporate more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids (found in salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds).
3. Apply Hot or Cold Packs
A warm compress can help relax breast tissue and reduce soreness, while a cold pack can numb pain and reduce swelling. Experiment with both to see which works best for you.
4. Stay Active
Regular exercise improves circulation, reduces inflammation, and helps maintain a healthy weight—all of which can ease breast pain. Try low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or yoga.
5. Manage Stress
High stress levels can make breast pain worse. Try stress-reducing techniques like:
• Meditation or deep breathing.
• Gentle yoga or stretching.
• Spending time outdoors.
6. Try Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
If the pain is particularly bothersome, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help.
7. Consider Natural Remedies
Some women find relief with natural remedies, including:
• Evening Primrose Oil: Contains gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), which may help reduce breast pain.
• Vitamin E: May alleviate tenderness in some women.
• Flaxseed: Contains phytoestrogens that may help balance hormones.
Always talk to your doctor before starting supplements, especially if you’re taking other medications.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) and Breast Pain
If you’re using HRT to manage menopause symptoms, you might notice breast pain as a side effect. This is usually due to the estrogen component of HRT, which can cause breast tissue to swell.
What to Do:
• Talk to Your Doctor: They might adjust your dose or switch you to a different type of HRT.
• Give It Time: Breast pain caused by HRT often improves after a few months as your body adjusts.
FAQs About Breast Pain in Menopause
1. Is breast pain normal during menopause?
Yes, breast pain is a common symptom during perimenopause and sometimes post-menopause. It’s usually linked to hormonal changes and is rarely a sign of something serious.
2. Can menopause cause breast lumps?
Hormonal changes can lead to the formation of benign lumps, like cysts or fibroadenomas. However, any new lump should be evaluated by a doctor.
3. Will breast pain go away after menopause?
For most women, breast pain decreases after menopause as hormone levels stabilize. However, some women may continue to experience non-cyclical breast pain.
The Bottom Line
Breast pain during menopause can be annoying, but it’s usually nothing to worry about. Hormonal fluctuations, changes in breast tissue, and lifestyle factors all play a role in this common symptom.
If the pain is mild, simple lifestyle tweaks like wearing a supportive bra, adjusting your diet, and managing stress can make a big difference. For more severe or persistent pain, consult your doctor to rule out any underlying issues and explore treatment options.
Menopause might be a wild ride, but with the right tools and knowledge, you can navigate it like a pro!
Feeling Cold in Early Pregnancy: What It Means and How to Manage It

When you think about early pregnancy symptoms, your mind probably goes straight to the classics: morning sickness, fatigue, and the endless bathroom trips. But what about feeling cold? If you’ve noticed that you’re suddenly reaching for an extra blanket or shivering in rooms where everyone else seems fine, you’re not alone.
Feeling cold in early pregnancy is less talked about but can be a real experience for many expectant moms. Let’s unpack why it happens, whether it’s normal, and what you can do to stay comfortable (and warm!).
Why Do You Feel Cold in Early Pregnancy?
Feeling cold during early pregnancy can leave you scratching your head. After all, many women experience the opposite: feeling warm or even overheated thanks to the extra blood flow and hormonal shifts. So what gives?
Here are some possible reasons for the chills:
1. Hormonal Changes
Early pregnancy is like a hormonal rollercoaster, and your body is still figuring things out. One of the key hormones, progesterone, rises significantly during the first trimester. While progesterone has many roles (like supporting your pregnancy), it can sometimes affect your body temperature regulation, leaving you feeling colder than usual.
2. Increased Blood Flow
Your body is working overtime to pump more blood to your uterus to support your growing baby. While this process can make some women feel warm, others may feel colder as blood flow redirects to your core and away from your extremities like hands and feet.
3. Fatigue and Energy Drain
Pregnancy is exhausting, especially in the early stages. Your body is burning more calories to support your baby’s development, which can leave you feeling drained and more sensitive to temperature changes.
4. Anemia
Low iron levels are common in pregnancy, especially if you’re not getting enough iron-rich foods or supplements. Anemia can cause a drop in your red blood cells, reducing oxygen circulation and making you feel cold.
5. Thyroid Changes
Pregnancy hormones can temporarily impact your thyroid function, which regulates your metabolism and body temperature. If your thyroid is underactive (a condition called hypothyroidism), it could lead to feeling cold.
When Is Feeling Cold in Pregnancy a Concern?
While feeling cold during early pregnancy is often harmless, it’s important to know when to check in with your healthcare provider.
Signs to Watch For:
• Persistent or Severe Chills: If you can’t seem to warm up and are experiencing chills or shaking, it could signal an underlying issue like an infection.
• Fever: Feeling cold followed by a fever could mean you have an illness or infection that needs medical attention.
• Fatigue with Other Symptoms: If you’re unusually tired and experiencing other signs like dizziness, rapid heartbeat, or shortness of breath, it could indicate anemia or thyroid problems.
When in doubt, always consult your doctor to rule out any serious concerns.
How to Stay Warm and Comfortable
If you’re feeling cold, there’s no need to suffer in silence (or in layers of sweaters). Here are some simple tips to stay cozy during early pregnancy:
1. Dress in Layers
Layering is key, especially if you’re dealing with unpredictable body temperature swings. Start with a warm base layer and add a sweater or scarf you can easily remove if you start to feel too warm.
2. Sip on Warm Drinks
A cozy cup of herbal tea (like chamomile or ginger) or warm water with lemon can do wonders for warming you up. Plus, staying hydrated is essential during pregnancy.
3. Use a Blanket or Heating Pad
Keep a soft blanket or heating pad handy for when the chills strike. Just be cautious with heating pads—use them on a low setting and avoid prolonged use on your abdomen.
4. Eat Iron-Rich Foods
Boost your iron intake with foods like spinach, red meat, beans, and fortified cereals. Pair iron-rich foods with vitamin C (like oranges or strawberries) to improve absorption.
5. Stay Active
Light exercise, like walking or prenatal yoga, can get your blood flowing and help you warm up naturally. Plus, it’s a great way to boost your energy levels.
6. Check Your Thyroid Levels
If feeling cold persists, ask your doctor to check your thyroid function. If hypothyroidism is the culprit, your doctor can recommend treatments to restore balance.
Can Feeling Cold Be a Sign of Pregnancy?
Interestingly, feeling cold is not a classic early pregnancy symptom, but it can happen. More commonly, women notice symptoms like fatigue, nausea, breast tenderness, and frequent urination in the early weeks.
That said, if you’re feeling chilly and suspect you might be pregnant, consider taking a test or consulting your healthcare provider. Remember, every pregnancy is different, and your body might just be reacting in its own unique way!
Feeling Cold vs. Feeling Hot During Pregnancy
While some women experience chills, others feel like they’ve stepped into a sauna. So what’s the deal with these opposite reactions?
• Feeling Hot: Hormonal surges, increased blood flow, and a boosted metabolism can leave some women feeling warm or even overheated during pregnancy.
• Feeling Cold: Less common but still normal, this is often linked to changes in blood circulation, fatigue, or hormonal shifts.
Common Myths About Feeling Cold in Pregnancy
Let’s bust a few myths surrounding the topic:
Myth #1: Feeling Cold Means Something Is Wrong
Not necessarily. In most cases, feeling cold is a harmless response to the changes your body is going through.
Myth #2: You Should Always Be Hot During Pregnancy
While many women report feeling warm, every pregnancy is different. Feeling cold is just another variation of how your body reacts.
Myth #3: Cold Hands and Feet Mean Poor Circulation
Cold extremities can be caused by redirected blood flow during pregnancy, not necessarily poor circulation or a health problem.
FAQs About Feeling Cold in Early Pregnancy
1. Is it normal to feel cold in early pregnancy?
Yes, it can be. Hormonal shifts, changes in blood flow, and increased fatigue can all contribute to feeling chilly.
2. Should I be worried if I feel cold during pregnancy?
Not usually. However, if you have additional symptoms like fever, extreme fatigue, or chills, it’s best to consult your doctor.
3. Can feeling cold be a pregnancy symptom before a missed period?
It’s possible but not common. Feeling cold could be related to hormonal changes that occur early in pregnancy.
The Bottom Line
Feeling cold in early pregnancy can be an unexpected (and under-discussed) symptom. While it’s usually harmless and related to hormonal changes or increased energy demands, it’s always a good idea to check in with your doctor if you’re concerned.
In the meantime, layer up, sip something warm, and focus on keeping yourself comfortable. Pregnancy is a unique journey, and every little symptom is just a reminder of the incredible changes your body is undergoing to grow your baby. Stay cozy—you’ve got this!
Kinh Nguyệt Màu Nâu: Hiểu Rõ Nguyên Nhân Và Giải Pháp Toàn Diện
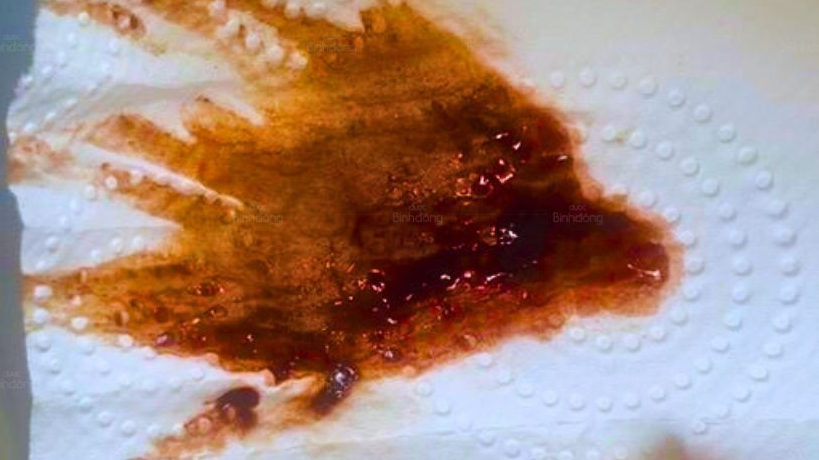
Kinh nguyệt màu nâu là một trong những hiện tượng phổ biến khiến không ít chị em phụ nữ cảm thấy lo lắng. Đây có phải là dấu hiệu bình thường hay là cảnh báo những vấn đề tiềm ẩn về sức khỏe? Trong bài viết dưới đây, lương y Nguyễn Thị Thùy Trang – cố vấn của Dược Bình Đông, chuyên gia y học cổ truyền với hơn 30 năm kinh nghiệm, sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ nguyên nhân, cách nhận biết và phương pháp khắc phục tình trạng kinh nguyệt màu nâu một cách hiệu quả.
1. Kinh Nguyệt Màu Nâu Là Gì?
Kinh nguyệt màu nâu là hiện tượng máu kinh ra ngoài với màu sắc khác biệt so với bình thường. Thay vì màu đỏ tươi hoặc đỏ sẫm, máu kinh có thể chuyển sang màu nâu nhạt hoặc nâu đen. Hiện tượng này thường xảy ra vào cuối chu kỳ kinh nguyệt, khi máu cũ còn sót lại trong tử cung và bị oxy hóa trước khi được đào thải ra ngoài.
Tuy nhiên, kinh nguyệt màu nâu không phải lúc nào cũng là hiện tượng bình thường. Nếu nó kéo dài nhiều ngày, xuất hiện ở giữa chu kỳ hoặc kèm theo các triệu chứng bất thường khác, đây có thể là dấu hiệu cảnh báo một vấn đề sức khỏe nghiêm trọng.
2. Nguyên Nhân Kinh Nguyệt Màu Nâu
2.1. Nguyên Nhân Sinh Lý
- Máu cũ còn sót lại trong tử cung: Thường xảy ra vào cuối chu kỳ kinh nguyệt, khi lượng máu kinh ít và chảy chậm, dẫn đến việc máu bị oxy hóa và chuyển sang màu nâu.
- Rối loạn nội tiết tố: Sự mất cân bằng hormone estrogen và progesterone có thể làm ảnh hưởng đến chu kỳ kinh nguyệt, gây ra hiện tượng máu kinh màu nâu.
- Mang thai: Trong một số trường hợp, máu kinh màu nâu có thể xuất hiện ở giai đoạn đầu thai kỳ do phôi thai bám vào thành tử cung. Tuy nhiên, đây cũng có thể là dấu hiệu cảnh báo nguy cơ sảy thai hoặc thai ngoài tử cung.
- Tiền mãn kinh: Phụ nữ bước vào giai đoạn tiền mãn kinh thường gặp tình trạng kinh nguyệt không đều, kinh nguyệt màu nâu do sự suy giảm hormone.
2.2. Nguyên Nhân Bệnh Lý
-
Viêm nhiễm phụ khoa:
- Nhiễm khuẩn âm đạo hoặc tử cung có thể khiến máu kinh có màu nâu, kèm theo mùi hôi khó chịu, khí hư bất thường và ngứa rát vùng kín.
-
Lạc nội mạc tử cung:
- Tình trạng các tế bào nội mạc tử cung phát triển sai vị trí, gây đau bụng kinh dữ dội, máu kinh màu nâu và rối loạn chu kỳ kinh nguyệt.
-
U xơ tử cung:
- U xơ tử cung có thể gây ra tắc nghẽn dòng chảy của máu kinh, khiến máu lưu lại lâu trong tử cung và chuyển sang màu nâu hoặc đen.
-
Hội chứng buồng trứng đa nang (PCOS):
- Đây là một rối loạn nội tiết tố phổ biến, gây kinh nguyệt không đều, máu kinh màu nâu hoặc đen, kèm theo tình trạng tăng cân, mọc lông nhiều và khó thụ thai.
-
Polyp cổ tử cung:
- Các khối polyp lành tính ở cổ tử cung có thể gây chảy máu kinh màu nâu, chảy máu bất thường giữa chu kỳ hoặc sau khi quan hệ tình dục.
-
Ung thư nội mạc tử cung:
- Máu kinh màu nâu kéo dài, kèm theo đau bụng dưới và chảy máu bất thường cần được thăm khám ngay để loại trừ nguy cơ ung thư.
3. Kinh Nguyệt Màu Nâu Có Nguy Hiểm Không?
Trong phần lớn các trường hợp, kinh nguyệt màu nâu là hiện tượng bình thường và không đáng lo ngại. Tuy nhiên, nếu tình trạng này đi kèm các triệu chứng bất thường như đau bụng dữ dội, mệt mỏi, sốt, máu có mùi hôi, hoặc nếu nó xuất hiện liên tục qua nhiều chu kỳ, đây có thể là dấu hiệu của một vấn đề sức khỏe cần được can thiệp.
Hãy nhanh chóng thăm khám bác sĩ nếu bạn gặp phải các tình trạng sau:
- Kinh nguyệt kéo dài hơn 7 ngày.
- Chu kỳ kinh nguyệt quá ngắn (dưới 21 ngày) hoặc quá dài (trên 35 ngày).
- Đau bụng dưới dữ dội, đau rát âm đạo.
- Chảy máu bất thường giữa chu kỳ hoặc sau khi quan hệ.
4. Cách Điều Trị Kinh Nguyệt Màu Nâu
4.1. Tây Y
- Thuốc điều hòa nội tiết: Bác sĩ có thể chỉ định thuốc chứa estrogen và progesterone để điều trị rối loạn nội tiết tố, cân bằng chu kỳ kinh nguyệt.
- Thuốc kháng sinh: Dùng để điều trị các bệnh viêm nhiễm phụ khoa.
- Can thiệp ngoại khoa: Nếu nguyên nhân là u xơ tử cung, polyp cổ tử cung hoặc lạc nội mạc tử cung, bác sĩ có thể chỉ định phẫu thuật.
4.2. Đông Y – Liệu Pháp Tự Nhiên, Lành Tính
Theo Đông y, kinh nguyệt màu nâu thường liên quan đến tình trạng huyết ứ, khí huyết không lưu thông hoặc khí hư hàn. Các bài thuốc Đông y không chỉ giúp điều hòa kinh nguyệt mà còn cân bằng nội tiết tố, hỗ trợ sức khỏe toàn diện cho phụ nữ.
Bài Thuốc Đông Y Tiêu Biểu:
-
Bài thuốc điều hòa khí huyết:
- Thành phần: 12g Ích mẫu, 8g Đương quy, 8g Ngải cứu, 8g Xuyên khung, 6g Bạch thược.
- Công dụng: Giảm huyết ứ, cải thiện lưu thông khí huyết, giảm đau bụng kinh.
-
Bài thuốc bổ khí huyết:
- Thành phần: 12g Đảng sâm, 12g Thục địa, 10g Bạch truật, 8g Hoàng kỳ, 6g Chích thảo.
- Công dụng: Tăng cường khí huyết, cân bằng nội tiết tố.
Song Phụng Điều Kinh – sản phẩm kế thừa từ bài thuốc cổ phương "Tứ vật thang" – là một lựa chọn tối ưu giúp điều hòa kinh nguyệt, giảm tình trạng kinh nguyệt màu nâu, bổ máu và thông huyết.
5. Các Biện Pháp Hỗ Trợ Tại Nhà
- Uống đủ nước: Giúp cơ thể loại bỏ độc tố và cải thiện lưu thông máu.
- Tập thể dục nhẹ nhàng: Yoga và thiền giúp giảm căng thẳng, cân bằng hormone.
- Dinh dưỡng hợp lý: Bổ sung thực phẩm giàu sắt (thịt đỏ, rau xanh) và vitamin C (cam, ổi).
- Uống trà gừng: Gừng có tác dụng làm ấm tử cung, giảm đau bụng kinh và cải thiện lưu thông khí huyết.
6. Phòng Ngừa Kinh Nguyệt Màu Nâu
- Theo dõi chu kỳ kinh nguyệt: Dùng ứng dụng hoặc ghi chép lại để phát hiện sớm các bất thường.
- Ăn uống lành mạnh: Hạn chế đồ ăn nhiều dầu mỡ, tăng cường rau xanh và trái cây.
- Vệ sinh vùng kín đúng cách: Không thụt rửa sâu và sử dụng dung dịch vệ sinh phù hợp.
- Khám phụ khoa định kỳ: Giúp phát hiện sớm các bệnh lý tiềm ẩn và điều trị kịp thời.
7. Kết Luận
Kinh nguyệt màu nâu là một hiện tượng phổ biến, nhưng khi nó đi kèm các triệu chứng bất thường, chị em không nên chủ quan. Hãy lắng nghe cơ thể, duy trì lối sống lành mạnh và tìm đến sự hỗ trợ từ các chuyên gia y tế khi cần thiết. Ngoài ra, các giải pháp từ Đông y như Song Phụng Điều Kinh của Dược Bình Đông là lựa chọn an toàn và hiệu quả, giúp điều hòa kinh nguyệt và cải thiện sức khỏe phụ nữ.
Được viết bởi:
Nguyễn Thị Thùy Trang
Lương y Nguyễn Thị Thùy Trang, cố vấn của Dược Bình Đông, chuyên gia y học cổ truyền với hơn 30 năm kinh nghiệm, luôn đồng hành cùng sức khỏe phụ nữ Việt.
Cetrotide and IVF: Everything You Need to Know

If you’re on an IVF journey, you’ve probably come across a medication called Cetrotide. It’s one of those buzzwords you hear in fertility clinics, forums, and discussions about treatment protocols. But what exactly is Cetrotide, and how does it fit into the intricate puzzle that is IVF?
Whether you’re gearing up for your first IVF cycle or just curious about the process, this guide will break down everything you need to know about Cetrotide in a straightforward, trendy tone—no medical jargon overload here!
What Is Cetrotide?
Let’s start with the basics. Cetrotide (generic name: cetrorelix acetate) is a medication used in IVF to prevent premature ovulation. Think of it as a “gatekeeper” that ensures your body doesn’t release eggs before they’re ready.
In IVF, timing is everything. If your eggs are released too early, they can’t be retrieved for fertilization. Cetrotide keeps your ovaries in check, giving your doctor full control over when ovulation occurs.
How Does Cetrotide Work?
Cetrotide belongs to a class of drugs called GnRH antagonists (gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists). Here’s how it works:
1. Blocks Natural Hormones: Cetrotide temporarily suppresses the release of luteinizing hormone (LH), which triggers ovulation.
2. Prevents Premature Ovulation: By blocking LH, Cetrotide ensures your eggs stay put until they’re mature and ready for retrieval.
Essentially, Cetrotide buys your follicles a little extra time to grow and develop, maximizing the chances of retrieving high-quality eggs during your IVF cycle.
When Is Cetrotide Used During IVF?
Cetrotide is typically introduced midway through an IVF cycle, after your ovaries have been stimulated with fertility medications like gonadotropins (e.g., Gonal-F, Menopur).
Step-by-Step Timeline
1. Ovarian Stimulation: You’ll start with injections of gonadotropins to encourage multiple follicles to grow.
2. Monitoring: Your doctor will monitor your progress with blood tests and ultrasounds to track follicle growth.
3. Cetrotide Starts: Once your follicles reach a certain size (usually around 12–14mm), you’ll begin daily Cetrotide injections to prevent ovulation.
4. Trigger Shot: When your follicles are mature, you’ll stop Cetrotide and take a “trigger shot” (e.g., hCG) to induce ovulation before egg retrieval.
How to Use Cetrotide
Using Cetrotide is straightforward, but if the thought of injecting yourself makes you nervous, don’t worry—you’re not alone! Here’s a simple guide:
1. Prepare the Injection
Cetrotide comes as a powder that needs to be mixed with sterile water. The kit includes everything you need:
• A vial of Cetrotide powder
• A pre-filled syringe of sterile water
• Mixing and injection needles
Follow these steps:
1. Attach the mixing needle to the syringe.
2. Inject the sterile water into the vial of powder.
3. Gently swirl (don’t shake!) the vial to dissolve the powder.
4. Switch to the injection needle.
2. Choose an Injection Site
Cetrotide is injected subcutaneously (under the skin), usually into the lower abdomen. Pinch a small fold of skin, insert the needle, and inject the medication.
3. Stick to the Schedule
Timing is crucial. Cetrotide is usually taken at the same time each day—your doctor will give you specific instructions.
Possible Side Effects of Cetrotide
Like all medications, Cetrotide comes with potential side effects. The good news? Most are mild and short-lived.
Common Side Effects
• Redness or Swelling: At the injection site. This usually goes away within a few hours.
• Nausea: A mild upset stomach is possible.
• Headaches: Some people experience minor headaches.
Rare Side Effects
• Allergic Reactions: Signs include itching, rash, or swelling. Contact your doctor immediately if this happens.
• Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS): While not directly caused by Cetrotide, it can occur during IVF cycles with over-stimulated ovaries. Symptoms include bloating, rapid weight gain, and abdominal pain.
Why Is Cetrotide Important for IVF?
You might be wondering: “Can’t my body just handle this on its own?” The answer is no—not when it comes to IVF.
In a natural cycle, your body would release a single egg. But in IVF, the goal is to retrieve multiple eggs to increase the chances of fertilization and successful implantation. Cetrotide ensures your body doesn’t jump the gun by ovulating before the eggs are ready.
By keeping your hormones in check, Cetrotide:
• Increases the number of mature eggs available for retrieval.
• Improves the chances of a successful IVF cycle.
Cetrotide vs. Other GnRH Antagonists
Cetrotide isn’t the only GnRH antagonist used in IVF—Ganirelix is another common option. So, how do you choose?
Cetrotide
• Requires mixing before injection.
• Slightly lower risk of injection site reactions.
Ganirelix
• Comes pre-mixed for easier use.
• Higher risk of redness or swelling at the injection site.
Both medications are equally effective, so the choice often comes down to personal preference and your doctor’s recommendation.
FAQs About Cetrotide and IVF
1. Does Cetrotide Hurt?
The injection itself is quick and usually not painful. Some people experience mild stinging or redness at the injection site.
2. Can I Miss a Dose?
Missing a dose of Cetrotide can lead to premature ovulation, which may jeopardize your IVF cycle. If you forget a dose, contact your doctor immediately for guidance.
3. Is Cetrotide Covered by Insurance?
Coverage varies depending on your insurance plan and location. Many fertility clinics offer financing or discounts for medications if you’re paying out of pocket.
Tips for Managing Cetrotide Injections
• Set Reminders: Use your phone or a calendar to keep track of injection times.
• Stay Calm: If you’re nervous about injecting yourself, take a few deep breaths and follow the instructions carefully.
• Rotate Injection Sites: To avoid irritation, switch up the spot on your abdomen each day.
• Ask for Help: If self-injections feel overwhelming, ask a partner or friend to assist you.
The Bottom Line
Cetrotide is an essential part of many IVF protocols, helping to prevent premature ovulation and ensuring your eggs are retrieved at their peak. While the thought of daily injections might sound intimidating, the process is manageable—and worth it when you’re working toward your dream of parenthood.
By understanding how Cetrotide works and what to expect, you can approach your IVF cycle with confidence. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey—your fertility team is there to guide you every step of the way.
So take a deep breath, trust the process, and keep your eyes on the prize: a happy, healthy baby. You’ve got this!
