Month: September 2024
How Plastics Impact Male Fertility: What You Need to Know

In today’s world, we are constantly surrounded by plastic—from the containers we store our food in, to the packaging of our everyday items, and even the water bottles we sip from. While plastics have made life more convenient, emerging research is sounding the alarm about the potential risks they pose, especially to male fertility. If you’re concerned about your reproductive health or are curious about how the products you use daily might be affecting it, keep reading. This article breaks down the science, the risks, and how to protect yourself in a world full of plastic.
The Hidden Threat: Chemicals in Plastics
The main concern with plastics and male fertility comes down to one thing: chemicals. Specifically, two types of chemicals found in plastics—phthalates and Bisphenol A (BPA)—are of major concern. These chemicals are known as endocrine disruptors. In other words, they can interfere with the way your hormones function. And when it comes to fertility, hormones play a crucial role.
Hormones, like testosterone, are responsible for sperm production and maintaining reproductive health. Endocrine disruptors like BPA and phthalates can interfere with these hormones, leading to a range of problems such as reduced sperm count, poor sperm quality, and in some cases, infertility.
How Does Plastic Affect Male Fertility?
Let’s get into the specifics of how these chemicals in plastics affect male fertility.
1. Reduced Sperm Count: Research shows that men exposed to high levels of BPA and phthalates often have lower sperm counts. A study published in the *Journal of Reproductive Toxicology* found that men with higher BPA levels had a 23% lower sperm concentration. While that may not sound like a lot, when you’re trying to conceive, every sperm counts.
2. Lower Sperm Motility: Even if your sperm count is normal, the quality of the sperm can be affected by plastic chemicals. Sperm motility refers to the ability of sperm to move effectively, which is essential for fertilizing an egg. Exposure to endocrine disruptors can reduce sperm motility, making it harder for men to conceive naturally.
3. DNA Damage: One of the more concerning effects of plastic chemicals on fertility is their ability to damage sperm DNA. Damaged DNA in sperm can lead to unsuccessful fertilization or even increase the risk of miscarriages. This is because the integrity of sperm DNA is crucial for healthy embryo development.
4. Hormonal Imbalances: As mentioned earlier, BPA and phthalates disrupt hormone production. By mimicking or blocking natural hormones, these chemicals can trick the body into overproducing or underproducing essential hormones like testosterone. Over time, this can lead to not only fertility issues but also other health problems such as erectile dysfunction, reduced libido, and even testicular cancer.
Where Are These Chemicals Found?
You might be wondering, “Where am I being exposed to these harmful chemicals?” The unfortunate answer is: almost everywhere. Plastics are so widespread that it’s hard to avoid them completely. However, here are some of the most common sources:
– Plastic food containers: Especially those that are heated or microwaved.
– Water bottles: Single-use plastic bottles are a major source of BPA.
– Canned food: The lining of cans often contains BPA.
– Personal care products:: Shampoos, lotions, and deodorants often contain phthalates.
– Plastic wrap: Used for food storage, this can leach chemicals into your food.
– Receipts: Thermal paper used for receipts is coated with BPA.
Who’s at Risk?
While everyone is exposed to plastics, certain groups are at a higher risk for fertility issues due to increased exposure to harmful chemicals. These include:
– Men in plastic-heavy industries: If you work in manufacturing, especially in plastic-related industries, your exposure to endocrine disruptors is likely higher.
– Frequent users of plastic products: If you regularly consume food or beverages from plastic containers, you may be at risk.
– Individuals with poor detoxification: Some people are less able to detoxify chemicals from their bodies, which can result in higher levels of endocrine disruptors in their systems.
The Impact on Future Generations
The concerns around plastic and male fertility don’t stop with this generation. There’s growing evidence that exposure to endocrine disruptors like BPA and phthalates may affect the fertility of future generations. Animal studies have shown that exposure to these chemicals can affect the reproductive health of offspring, meaning that the plastics we’re exposed to today could impact the fertility of our children and grandchildren.
How to Minimize Your Risk
While it’s impossible to avoid plastic completely, there are steps you can take to reduce your exposure and protect your fertility. Here’s what you can do:
1. Switch to glass or stainless steel: When it comes to food and drink containers, opt for glass or stainless steel instead of plastic. Not only are these materials BPA- and phthalate-free, but they’re also more durable and eco-friendly.
2. Avoid microwaving food in plastic: Heat can cause chemicals to leach from plastic into your food. If you need to reheat leftovers, transfer them to a glass container before microwaving.
3. Reduce canned food consumption: Opt for fresh or frozen foods instead of canned. Many cans are lined with BPA, which can leach into the food.
4. Read labels: Be mindful of the personal care products you use. Many contain phthalates, which are often listed as “fragrance” on labels. Look for products that specifically say they’re phthalate-free.
5. Filter your water: Invest in a high-quality water filter to reduce your exposure to contaminants, including plastic chemicals, that may be present in tap water.
6. Handle receipts with care: Since receipts are coated with BPA, avoid touching them as much as possible. If you must handle receipts frequently, wash your hands afterward.
7. Be cautious with plastic wrap: Use alternatives like beeswax wraps or silicone lids instead of plastic wrap to cover your food.
Is There Hope for Recovery?
The good news is that the body can recover from exposure to plastics if you take steps to minimize your contact with these harmful chemicals. By making lifestyle changes, such as avoiding plastic products and choosing safer alternatives, you can help protect your fertility and overall health.
Moreover, some studies have shown that reducing exposure to endocrine disruptors can lead to improvements in sperm count and quality. This means that if you’re planning to start a family, it’s never too late to start taking precautions.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
The impact of plastics on male fertility is a growing concern, but the silver lining is that it’s something we can actively address. By understanding the risks, identifying where we’re most exposed, and taking steps to minimize that exposure, we can protect not only our fertility but also the health of future generations.
In a world where plastics are everywhere, it’s more important than ever to be mindful of what we’re exposing ourselves to. By making small changes in our daily lives, we can make a big difference in our reproductive health. So, next time you reach for that plastic water bottle or microwave leftovers in a plastic container, think twice—your fertility might thank you.
Fetal Breathing Movements: What They Mean and Why They’re Important for Baby’s Development
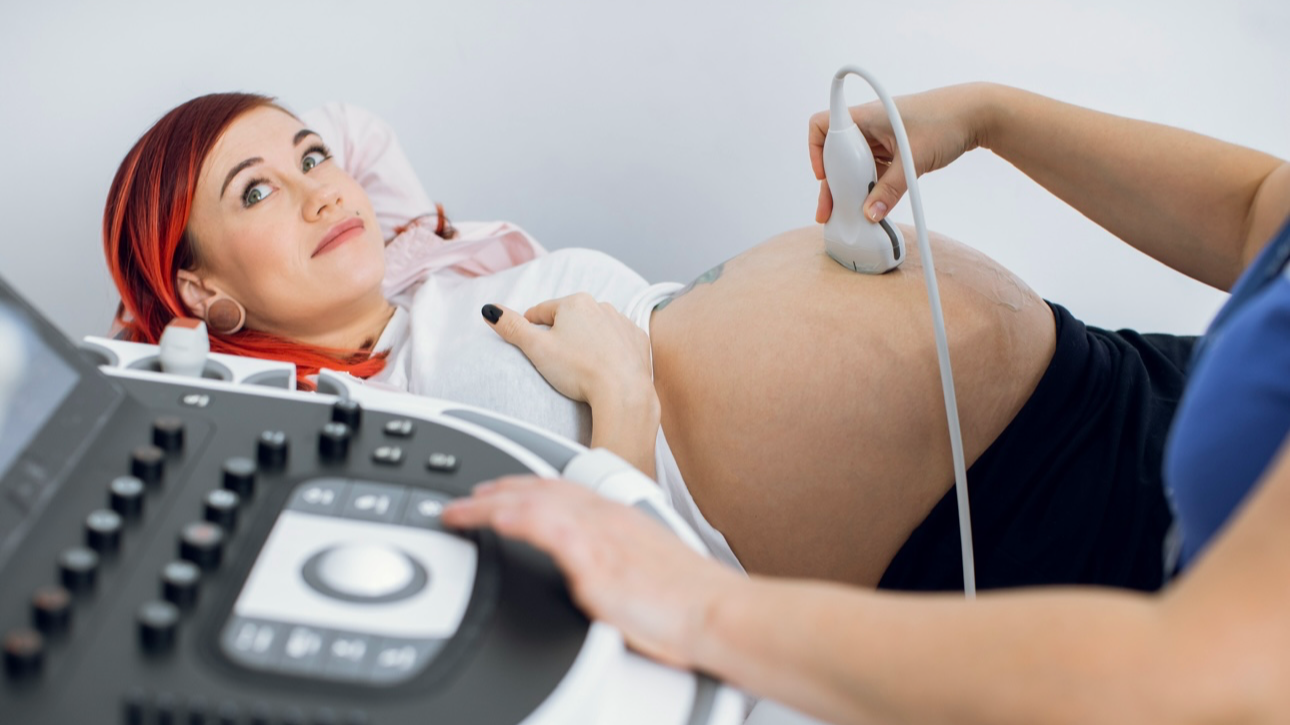
Pregnancy is a magical journey filled with excitement and curiosity, especially when it comes to the development of your growing baby. Among the many fascinating milestones, one that often intrigues expectant parents is the phenomenon of fetal breathing movements. While your baby isn’t actually breathing air in the womb, these movements are an essential part of fetal development. They help prepare your baby for life outside the womb, where real breathing with lungs will become the most crucial survival skill.
In this article, we’ll explore what fetal breathing movements are, why they’re so important, when they typically begin, and how doctors use them as a marker of your baby’s health.
What Are Fetal Breathing Movements?
Fetal breathing movements are rhythmic contractions of the diaphragm and chest that mimic the process of breathing, even though the baby isn’t inhaling air. Instead, the fetus is practicing the motions of breathing by drawing in amniotic fluid. This exercise helps the baby develop the muscles and neural pathways that will be essential for real breathing after birth.
Fetal breathing movements are a normal and expected part of fetal development. They play a critical role in preparing the lungs and respiratory muscles for life outside the womb. This process allows the baby’s lungs to develop the strength they’ll need to take their first breath of air once they’re born.
When Do Fetal Breathing Movements Begin?
Fetal breathing movements usually begin between 9 and 10 weeks of gestation, although they’re not detectable by the mother at this stage. As the baby grows, these movements become more regular and pronounced, especially in the third trimester.
By the time you reach around 24 to 28 weeks, fetal breathing movements become more frequent, and doctors may start to monitor them during ultrasounds. It’s common for babies to practice these movements intermittently throughout the day, often influenced by your activity level and even your diet. Interestingly, some studies suggest that fetal breathing movements increase after the mother eats or consumes something sugary, likely because of the rise in blood sugar.
By 32 to 34 weeks, fetal breathing movements tend to follow a more predictable pattern. Just like an adult’s breathing slows during sleep and increases during periods of activity, the fetus’s breathing movements can fluctuate depending on their rest or active cycles.
Why Are Fetal Breathing Movements Important?
Fetal breathing movements are more than just adorable practice breaths—they are crucial for several reasons that contribute to your baby’s overall health and development.
1. Lung Development
Perhaps the most obvious reason fetal breathing movements are important is their role in developing the lungs. As the baby practices breathing amniotic fluid in and out, their lungs undergo significant development. The movements help the lungs grow and mature, preparing them to expand and contract properly once the baby is born and needs to breathe air.
Without sufficient practice breathing movements, the lungs may not develop fully, which can lead to respiratory problems after birth.
2. Diaphragm and Muscle Strength
The diaphragm is the primary muscle involved in breathing. During fetal breathing movements, the diaphragm contracts and relaxes, just as it will once the baby starts breathing air. These practice sessions strengthen the diaphragm and other respiratory muscles, ensuring that they’re strong enough to support breathing after birth.
3. Prepares for Birth Transition
At birth, the baby will transition from receiving oxygen through the umbilical cord to breathing on their own. Fetal breathing movements help prepare the respiratory system for this critical change, ensuring that the baby’s lungs and breathing muscles are ready to function as soon as they’re needed.
4. Neurological Development
Breathing movements are controlled by the brain, so they’re an important part of the neurological development process as well. When the fetus practices breathing, the brain and nervous system are working together to coordinate the necessary signals, helping to build and strengthen the brain circuits responsible for controlling the respiratory system.
How Do Doctors Monitor Fetal Breathing Movements?
Doctors can monitor fetal breathing movements as part of routine ultrasounds, particularly during the third trimester. These observations often occur during a biophysical profile (BPP), a test that helps assess the baby’s overall health. The BPP combines an ultrasound evaluation with a non-stress test (which monitors the baby’s heart rate) to provide a comprehensive picture of fetal well-being.
During the ultrasound, the doctor will look for signs of fetal breathing movements and evaluate how frequently they occur. Typically, the doctor will want to see breathing movements lasting for at least 30 seconds during the ultrasound. This ensures that the baby’s lungs and respiratory muscles are practicing adequately.
Fetal breathing movements are often seen as a positive indicator of fetal health and development. If they are absent, it doesn’t necessarily mean something is wrong. However, it could prompt the doctor to conduct additional tests to ensure the baby is receiving enough oxygen and that other development markers are being met.
What If Fetal Breathing Movements Aren’t Detected?
It’s natural to feel concerned if fetal breathing movements aren’t detected during an ultrasound. However, it’s important to remember that babies have rest and activity cycles, just like adults. It’s possible that your baby is simply in a resting phase during the ultrasound and isn’t practicing their breathing movements at that moment.
If your doctor doesn’t observe fetal breathing movements, they may recommend a follow-up ultrasound or additional tests, such as a non-stress test, to evaluate the baby’s overall well-being. It’s rare for the absence of breathing movements to be a cause for immediate concern, especially if other aspects of the biophysical profile are normal.
Fetal Breathing Movements and Delivery
As your due date approaches, fetal breathing movements may slow down. This is a natural part of preparing for labor and delivery. Once your baby is born, they’ll transition from practicing breathing in amniotic fluid to breathing air for the first time.
Immediately after birth, the medical team will ensure that your baby’s lungs inflate properly and that they’re breathing independently. If your baby has trouble breathing after delivery, the healthcare team may provide assistance, such as suctioning fluid from the lungs or offering oxygen support.
Fetal breathing movements are an essential part of your baby’s development in the womb. These practice breaths not only prepare your baby for life outside the womb but also play a critical role in lung development, muscle strength, and neurological function.
As a parent-to-be, it’s comforting to know that these movements are a sign that your baby is preparing for their grand debut. Regular monitoring through ultrasounds and biophysical profiles ensures that your baby is on track for a healthy delivery. While it’s normal for these movements to fluctuate, they’re an important indicator of fetal health and can offer valuable insight into your baby’s readiness for the world.
If you have concerns about fetal breathing movements or any aspect of your baby’s development, it’s always best to consult with your healthcare provider to ensure peace of mind.
ICSI Procedure Explained: Step-by-Step Guide to Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection

If you’ve been exploring fertility treatments, you’ve likely come across the term ICSI, short for Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection. This advanced form of IVF (in vitro fertilization) has been a game-changer for many couples struggling with infertility, especially those dealing with male factor infertility. But how does it work, and what can you expect if you’re undergoing this procedure?
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the ICSI procedure step by step, breaking down each phase so you know exactly what to anticipate. Whether you’re just starting to learn about fertility treatments or preparing for your first round of ICSI, this article will give you an in-depth look at the entire process.
What Is ICSI?
ICSI, or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection, is a specialized form of IVF in which a single sperm is injected directly into an egg. This method is particularly useful for couples facing male infertility issues, such as low sperm count, poor sperm motility, or abnormal sperm shape.
The ICSI technique bypasses many of the common barriers to conception, as it does not require the sperm to swim through the female reproductive system to reach and fertilize the egg. Instead, it is manually inserted, ensuring fertilization occurs.
Step-by-Step Guide to the ICSI Procedure
The ICSI process can be broken down into several key steps. Let’s explore each one in detail:
1. Ovarian Stimulation
The first step in ICSI is ovarian stimulation, which is very similar to the initial phase of traditional IVF. The goal of ovarian stimulation is to encourage the ovaries to produce multiple mature eggs, rather than the single egg typically released during a normal menstrual cycle.
You’ll begin by taking hormonal medications (usually gonadotropins) for about 8-14 days to stimulate the ovaries. Your doctor will monitor your progress with blood tests and ultrasounds to ensure the follicles (which contain the eggs) are growing appropriately.
Once the follicles have reached the desired size, you’ll receive a trigger shot of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which helps the eggs complete their maturation. Timing is essential at this stage, as the egg retrieval must be done just before ovulation.
2. Egg Retrieval
Egg retrieval is a minimally invasive procedure performed under light sedation. It typically takes about 20-30 minutes.
During the retrieval, your fertility specialist will use an ultrasound-guided needle to aspirate the eggs from your ovaries. The eggs are then collected and immediately sent to the lab for fertilization.
This procedure is generally pain-free due to sedation, but you may experience mild cramping or discomfort afterward. You’ll likely be advised to rest for the remainder of the day.
3. Sperm Collection and Preparation
On the same day as the egg retrieval, a sperm sample will be collected from your partner or sperm donor. This can be done via ejaculation or, in cases of severe male infertility, through surgical extraction (like testicular sperm extraction, or TESE).
The sperm sample is then prepared in the lab, where embryologists will select the healthiest and most viable sperm for the ICSI procedure. The goal is to find sperm with optimal motility and morphology (shape), even if overall sperm count or quality is low.
4. Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
Now comes the pivotal moment of the ICSI process: the actual injection. Under a powerful microscope, the embryologist carefully selects a single sperm and injects it directly into the cytoplasm of a mature egg using a fine, hollow needle.
The use of such precise technology ensures that fertilization takes place, even when sperm are unable to penetrate the egg naturally.
Once the sperm is injected into the egg, the egg is placed in a controlled incubator to allow fertilization to occur. Within 16-20 hours, the embryologists will be able to determine whether fertilization was successful.
5. Fertilization Monitoring and Embryo Development
After fertilization, the embryos are carefully monitored in the lab for several days (typically 3-5 days) as they begin to develop. The embryos will grow from a single cell into a multi-cell organism called a blastocyst, which is ideal for implantation.
During this period, the lab will assess the quality and development of the embryos, identifying the healthiest and most viable ones for transfer or freezing.
6. Embryo Transfer
The next crucial step is embryo transfer, which occurs 3-5 days after the egg retrieval. The best-quality embryo(s) are selected for transfer into the woman’s uterus.
The embryo transfer procedure is quick and painless, similar to a Pap smear. A thin catheter is used to insert the embryo(s) into the uterine cavity, where it is hoped they will implant and develop into a successful pregnancy.
If you have multiple high-quality embryos, some may be frozen for future use, a process known as cryopreservation.
7. The Two-Week Wait
After the embryo transfer, the dreaded two-week wait begins. During this period, you’ll wait to see if the embryo implants and results in a pregnancy.
Your doctor will typically schedule a blood pregnancy test around 10-14 days after the embryo transfer to determine if you’re pregnant. While this waiting period can be emotionally intense, it’s important to stay calm and take care of your body.
Who Is ICSI Recommended For?
ICSI is particularly beneficial for couples facing the following fertility issues:
– Male factor infertility: Low sperm count, poor motility, or abnormal morphology.
– Previous failed IVF cycles: Couples who have had unsuccessful IVF attempts due to fertilization failure.
– Sperm extraction: Men who require sperm to be surgically extracted from the testicles.
– Frozen sperm use: Sperm that has been previously frozen (for example, before cancer treatments) may benefit from ICSI to ensure higher chances of fertilization.
Success Rates of ICSI
The success rate of ICSI varies depending on several factors, including the age of the woman, the quality of the eggs and sperm, and the overall health of the couple. On average, the fertilization success rate with ICSI is around 70-80, though this does not guarantee pregnancy. The overall success of the procedure also depends on factors like embryo quality and uterine receptivity.
Women under 35 tend to have the highest success rates, with a live birth rate of about 40% per cycle. As maternal age increases, success rates generally decline, but ICSI remains one of the most effective fertility treatments for overcoming male infertility.
Risks and Considerations
While ICSI is a safe and effective procedure, it’s important to be aware of potential risks:
– Egg damage: There’s a small risk that the egg could be damaged during injection, which would prevent fertilization.
– Multiple pregnancies: If multiple embryos are transferred, there’s a higher likelihood of twins or triplets, which can carry additional health risks.
– Genetic concerns: In some cases, male infertility is linked to genetic issues, and these may be passed on to the child. Genetic screening is recommended if there’s a known genetic condition in the family.
The ICSI procedure has revolutionized the way we approach infertility, particularly for couples dealing with male factor infertility. By injecting a single sperm directly into the egg, ICSI maximizes the chances of fertilization, offering hope to many couples who might otherwise struggle to conceive.
With proper medical care and an understanding of the process, ICSI can be a highly effective treatment option. If you’re considering ICSI, working closely with your fertility specialist will help you navigate each step of the journey toward building your family.
Remember, while ICSI doesn’t guarantee pregnancy, it offers an incredible opportunity for couples facing significant fertility challenges.
Experiencing Dizziness 3 Weeks Postpartum? Causes, Symptoms, and When to Seek Help

After giving birth, your body undergoes a remarkable transformation, shifting from pregnancy back to its pre-pregnancy state. However, this postpartum period is not without its challenges. One common yet disorienting symptom that some new mothers experience is dizziness. If you’ve been feeling lightheaded or dizzy three weeks after giving birth, you may wonder whether this is normal or a sign of something more serious.
In this article, we’ll explore the potential causes of dizziness during the postpartum period, common symptoms to watch for, and when to seek medical help. Understanding the reasons behind this issue can help new moms feel more informed and empowered to take care of their health.
Why Am I Feeling Dizzy 3 Weeks Postpartum?
Dizziness in the weeks following childbirth can be unsettling, especially when you’re adjusting to life with a newborn. Several factors could contribute to dizziness at three weeks postpartum. These causes can range from physical recovery to underlying health conditions. Let’s take a closer look at the most common reasons.
1. Blood Loss and Anemia
One of the leading causes of postpartum dizziness is anemia. which is a condition that occurs when your body doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells to carry adequate oxygen to your tissues. Many women experience significant blood loss during childbirth, whether they deliver vaginally or via C-section. If the body loses too much blood, it can lead to anemia, which commonly causes dizziness, fatigue, and shortness of breath.
Other signs of postpartum anemia may include:
– Pale skin
– Rapid heartbeat
– Extreme tiredness or weakness
Your doctor may recommend a complete blood count (CBC) test to determine whether anemia is the cause of your dizziness. If you’re diagnosed with anemia, iron supplements, and iron-rich foods such as spinach, beans, and lean red meats can help restore your iron levels.
2. Hormonal Changes
Pregnancy and childbirth cause a whirlwind of hormonal fluctuations. After giving birth, levels of hormones such as estrogen and progesterone drop dramatically. These hormones regulate various bodily functions, including blood pressure and fluid balance. As your body adjusts to these changes, it’s common to experience symptoms like dizziness, fatigue, and even mood swings.
Estrogen plays a key role in maintaining normal blood circulation and vascular health, so when estrogen levels plummet after delivery, you may feel lightheaded, especially when standing up or moving quickly.
3. Dehydration
Dehydration is another potential culprit for postpartum dizziness. As a new mom, you’re likely juggling numerous tasks, from feeding your baby to managing household duties, and it’s easy to forget to drink enough water throughout the day. Dehydration can cause a drop in blood pressure, resulting in dizziness.
If you’re breastfeeding, staying hydrated is even more crucial because the body uses extra fluids to produce breast milk. Common signs of dehydration include:
– Thirst
– Dark-colored urine
– Dry mouth
– Fatigue
Make it a habit to drink plenty of water, especially if you’re nursing, to avoid dehydration-related dizziness. Keep a water bottle nearby throughout the day to remind yourself to stay hydrated.
4. Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension)
Postpartum low blood pressure, or hypotension, can lead to dizziness or even fainting. Blood pressure fluctuations are normal during pregnancy and after delivery, but in some cases, they can become problematic.
If you notice symptoms such as blurred vision, nausea, or fainting along with dizziness, it may be due to low blood pressure. A sudden drop in blood pressure is often caused by dehydration, excessive blood loss, or the body adjusting to hormonal changes.
5. Fatigue and Sleep Deprivation
Sleep deprivation is par for the course when you’re a new mom. Those middle-of-the-night feedings and frequent baby wake-ups can take a toll on your energy levels, and sleep deprivation is a known cause of dizziness. When your body isn’t getting the rest it needs, it’s harder for your brain and other systems to function properly, leading to lightheadedness and cognitive fog.
It’s important to get as much rest as possible, even if it means asking for help with the baby or household chores. Napping when your baby naps and allowing your partner or family members to help can give you some much-needed rest.
6. Postpartum Thyroiditis
Postpartum thyroiditis is an inflammation of the thyroid gland that can develop within the first year after childbirth. This condition can lead to an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) followed by an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism), both of which can cause dizziness.
Symptoms of postpartum thyroiditis include:
– Unexplained weight changes
– Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
– Fatigue
– Irritability
– Cold sensitivity
If you suspect your thyroid may be affecting your health, it’s essential to see your doctor for a thyroid function test. Early detection and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent long-term complications.
7. Vestibular Issues or Ear Infections
In some cases, dizziness may not be directly related to postpartum changes but rather due to issues with your inner ear. The inner ear controls balance, and conditions such as vestibular disorders or ear infections can disrupt your equilibrium, leading to dizziness or vertigo.
If you’ve recently had a cold or sinus infection, your dizziness could be the result of an inner ear infection. Other signs include ear pain, pressure, and difficulty hearing.
When Should You Seek Medical Help?
While dizziness is often a normal part of postpartum recovery, it’s important to know when it’s time to call your doctor. Persistent or severe dizziness, especially if it’s accompanied by other symptoms, may signal a more serious issue. Here’s when you should seek medical attention:
– Prolonged dizziness: If dizziness lasts for more than a few minutes or occurs frequently.
– Chest pain: If you experience dizziness along with chest pain or shortness of breath.
– Severe headaches: Dizziness accompanied by intense headaches could indicate preeclampsia or other complications.
– Fainting or loss of consciousness: If dizziness leads to fainting, seek immediate medical attention.
– Blurred vision: If your vision is affected along with dizziness, it could be a sign of a more serious problem.
– Heart palpitations: Rapid or irregular heartbeats along with dizziness may indicate a cardiovascular issue.
How to Manage Postpartum Dizziness
If you’re experiencing mild dizziness three weeks postpartum, there are several steps you can take to manage it:
1. Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids throughout the day, especially if you’re breastfeeding.
2. Eat Small, Frequent Meals: Eating balanced, nutritious meals can help stabilize your blood sugar and prevent dizziness.
3. Rest and Recharge: Make sleep a priority, and ask for help when needed to ensure you’re getting enough rest.
4. Move Slowly: Get up slowly from sitting or lying positions to avoid sudden drops in blood pressure.
5. Take Iron Supplements: If your doctor has diagnosed you with anemia, taking prescribed iron supplements can improve your condition.
Dizziness three weeks postpartum can be unsettling, but it’s often a common and manageable symptom during the recovery phase. Whether it’s caused by hormonal changes, fatigue, dehydration, or more serious health issues, knowing the possible causes can help you manage the discomfort and get back on your feet.
If you find that dizziness persists or worsens, don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider. They can evaluate your symptoms, offer treatment options, and ensure that you’re on the path to a healthy postpartum recovery. In the meantime, take care of your body, rest when you can, and seek support from those around you.
Painful Sex After Menopause: Causes, Treatments, and Tips for Relief

Menopause marks a significant transition in a woman’s life. With the end of menstruation comes a series of changes in the body, many of which can be unexpected and sometimes challenging. One such issue that affects a large number of postmenopausal women is dyspareunia,or painful sex. While it’s common, it can be a distressing and sensitive subject to discuss. However, understanding the causes and exploring available treatments can help women reclaim comfort and intimacy after menopause.
In this article, we’ll break down the causes of painful sex after menopause, offer treatment options, and provide actionable tips for relief to improve both physical and emotional well-being.
Why Does Painful Sex Happen After Menopause?
As women approach menopause, their bodies undergo a significant drop in estrogen levels. Estrogen plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of vaginal tissues, keeping them lubricated, elastic, and well-supplied with blood. With menopause, the loss of estrogen can lead to a condition known as vaginal atrophy or genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM), which is often the primary cause of pain during sex.
Here are the key reasons behind postmenopausal pain during intercourse:
1. Vaginal Dryness
The drop in estrogen levels leads to a decrease in natural lubrication in the vagina, causing vaginal dryness. Without proper lubrication, sex can become uncomfortable and even painful, leading to irritation and soreness during and after intercourse.
2. Thinning of Vaginal Tissue
Estrogen also maintains the thickness and elasticity of vaginal tissue. Postmenopause, vaginal walls can become thinner, more fragile, and less elastic, making penetration more difficult and uncomfortable.
3. Decreased Blood Flow
Lower estrogen levels also reduce blood flow to the vaginal area, leading to reduced arousal and sensitivity. This can make it harder to get physically ready for intercourse, resulting in pain and discomfort.
4. Pelvic Floor Muscle Changes
Aging and hormonal changes can affect the muscles of the pelvic floor. Pelvic floor dysfunction can cause tightness or spasms in the muscles, contributing to pain during penetration. In some cases, conditions like vaginismus, where the muscles involuntarily contract, can make intercourse painful or impossible.
5. Emotional Factors
While physical changes play a primary role, emotional and psychological factors can also contribute to painful sex. Postmenopausal women may experience anxiety, stress, or a decrease in self-esteem related to aging, which can influence sexual desire and contribute to discomfort during intimacy.
Treatments for Painful Sex After Menopause
The good news is that there are several treatment options available to help alleviate the discomfort and pain associated with postmenopausal sex. Depending on the underlying cause, various medical and lifestyle solutions can restore comfort and pleasure.
1. Lubricants and Moisturizers
One of the easiest and most immediate solutions for vaginal dryness is the use of over-the-counter lubricants. Opt for water-based or silicone-based lubricants that provide sufficient moisture without irritation. It’s important to avoid lubricants that contain glycerin, parabens, or fragrances, as these can cause irritation or allergic reactions.
Vaginal moisturizers, such as Replens, can also be used regularly to maintain vaginal moisture and reduce dryness over time. While lubricants are used before intercourse, moisturizers can be applied a few times a week to maintain hydration.
2. Vaginal Estrogen Therapy
For women experiencing severe vaginal dryness and atrophy, vaginal estrogen therapy is an effective option. Available in the form of creams, tablets, or rings, low-dose vaginal estrogen helps restore the health of vaginal tissues by replenishing local estrogen levels. This treatment can improve lubrication, elasticity, and blood flow to the vaginal area.
Because the dose is localized, vaginal estrogen therapy tends to have fewer risks than systemic hormone replacement therapy (HRT). However, it’s important to discuss this treatment option with your doctor to ensure it’s right for you.
3. Systemic Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
For women experiencing multiple menopausal symptoms, including hot flashes, mood swings, and painful sex, systemic hormone replacement therapy may be considered. HRT involves taking estrogen (and sometimes progesterone) in the form of pills, patches, or gels to treat overall menopausal symptoms. While effective, HRT does carry certain risks, including an increased risk of blood clots and breast cancer, so it’s essential to weigh the pros and cons with your healthcare provider.
4. DHEA Vaginal Inserts
DHEA (dehydroepiandrosterone) vaginal inserts, such as the product Intrarosa, are a newer option for postmenopausal women. DHEA is a hormone that the body converts into estrogen and testosterone. When applied locally in the vagina, it helps improve lubrication, vaginal health, and sexual function without the risks associated with systemic estrogen therapies.
5. Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy
If pelvic floor dysfunction is contributing to painful sex, working with a pelvic floor physical therapist can be incredibly helpful. These specialists teach exercises to relax and strengthen the pelvic muscles, which can reduce pain and improve sexual comfort. Techniques such as biofeedback and myofascial release are often used to ease pelvic floor tension and restore muscle control.
6. Non-Hormonal Medications
For women who cannot or prefer not to use hormonal treatments, there are non-hormonal medications available to address postmenopausal symptoms. One option is ospemifene (brand name Osphena), which is an oral medication that acts like estrogen in vaginal tissues to reduce dryness and improve tissue elasticity without the need for direct hormone therapy.
Tips for Improving Comfort During Sex
In addition to medical treatments, there are several lifestyle changes and strategies that can make sex more comfortable and enjoyable after menopause:
1. Foreplay and Communication
Taking the time to engage in more extended foreplay can help with natural lubrication and arousal, making intercourse smoother and less painful. Open communication with your partner about what feels good and what doesn’t can also alleviate anxiety and improve the overall experience.
2. Stay Active
Regular exercise, including Kegel exercises, helps strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and improve blood flow to the vaginal area. Staying physically active also boosts mood and overall well-being, which can positively impact sexual desire.
3. Maintain a Healthy Diet
Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats can support hormonal balance and improve the health of your skin and tissues, including vaginal tissues. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon and flaxseeds, as well as antioxidant-rich foods like berries and leafy greens, can benefit overall health and reduce inflammation.
4. Consider Counseling
For women experiencing emotional or psychological barriers to sexual activity post-menopause, talking with a counseloror sex therapist can be beneficial. Addressing issues like anxiety, depression, or body image concerns can help rebuild confidence and improve intimacy with your partner.
When to Seek Professional Help
While occasional discomfort during sex is common after menopause, persistent pain or severe symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. Untreated vaginal atrophy can worsen over time, making sex increasingly painful and negatively impacting quality of life. If pain is affecting your relationships, emotional well-being, or self-esteem, don’t hesitate to reach out to a gynecologist or pelvic health specialist.
Painful sex after menopause is a common issue, but it doesn’t have to be a permanent one. With the right treatments, lifestyle changes, and open communication with your healthcare provider, it’s possible to restore comfort and intimacy in your relationships. Whether it’s through hormonal therapies, vaginal moisturizers, or pelvic floor exercises, there are plenty of options available to help you feel your best and reclaim your sexual health after menopause.
Pros and Cons of Abortion: Weighing the Medical, Ethical, and Emotional Aspects

Abortion is one of the most controversial topics in society today. The conversation surrounding abortion is multifaceted, touching on areas like medical safety, ethics, legality, personal freedom, and emotional consequences. Deciding whether to have an abortion or not is deeply personal and can be influenced by various factors, including physical health, emotional well-being, financial stability, and personal beliefs. Understanding the pros and cons of abortion can help provide clarity in making an informed decision.
We explore the benefits and drawbacks of abortion, considering the different perspectives that come into play when discussing this sensitive topic.
The Medical Pros and Cons of Abortion
From a medical perspective, abortion is a procedure that comes with both potential health benefits and risks, like any other medical intervention.
Pros:
1. Control Over Reproductive Health
One of the major benefits of access to abortion is that it allows women to have control over their reproductive health. If a woman experiences an unintended pregnancy or if a pregnancy poses serious health risks, abortion provides a medical option to terminate the pregnancy safely. This can be crucial in cases where carrying a pregnancy to term would pose life-threatening risks, such as with ectopic pregnancies or severe pre-existing health conditions.
2. Safety in Legal Contexts
In countries and regions where abortion is legal and properly regulated, the procedure is generally very safe. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), when performed by a trained medical professional in sanitary conditions, legal abortions are extremely safe and have a lower risk of complications than childbirth. Access to safe and legal abortions has contributed to a significant decrease in maternal mortality rates globally.
3. Health Protection
In some cases, abortion is necessary to protect the physical or mental health of the pregnant individual. If a pregnancy is the result of sexual assault or poses serious mental or emotional stress, abortion can provide relief from the trauma and prevent long-term psychological harm. Moreover, when the fetus has severe abnormalities that would prevent survival outside the womb, terminating the pregnancy can prevent further physical complications for the mother.
Cons:
1. Medical Risks
Although abortion is generally safe, it is still a medical procedure, and as with any surgery, there are potential risks. Complications such as infection, heavy bleeding, and injury to reproductive organs can occur, though these risks are minimal when the procedure is performed by a qualified healthcare professional. In some cases, repeated abortions could potentially affect future fertility, though this is rare.
2. Emotional and Psychological Impact
For some individuals, the decision to have an abortion can have a lasting emotional and psychological impact. Feelings of guilt, sadness, or depression may arise after the procedure, especially if the decision was made under duress or in difficult circumstances. Post-abortion emotional challenges, while not experienced by everyone, are something to consider and should be addressed through counseling or mental health support when needed.
3. Potential Complications in Later Pregnancy
While most people who have abortions go on to have healthy pregnancies later, some research suggests that there may be a small risk of complications, such as preterm birth, in future pregnancies after multiple abortions. However, these risks are generally associated with complications from the procedure itself, such as infection, rather than the act of abortion.
The Ethical Pros and Cons of Abortion
Ethical considerations surrounding abortion are often the most debated. These discussions usually focus on the moral status of the fetus, individual autonomy, and societal values.
Pros:
1. Right to Personal Autonomy
Many people argue that the decision to have an abortion falls under the right to personal autonomy and bodily integrity. Women, as autonomous individuals, should have the freedom to make decisions about their bodies, including whether to carry a pregnancy to term. In this view, denying access to abortion infringes on a person’s right to control their reproductive health.
2. Relief from Financial or Social Hardship
In some cases, abortion is seen as an ethical choice when bringing a child into the world would result in severe financial or social hardship. For individuals or families who cannot afford to care for a child or who are not in a stable environment to raise one, abortion provides a way to avoid putting both the parent(s) and the child in an unfavorable situation. This can be particularly important in cases where the person may already have children or where the pregnancy resulted from rape or abuse.
3. Reduction of Unsafe, Illegal Abortions
Legal and accessible abortions reduce the incidence of unsafe and illegal abortions. Before abortion was legalized in many countries, unsafe abortion procedures were a major cause of maternal mortality. From an ethical standpoint, providing safe, legal abortion services is essential to protecting the health and well-being of women who would otherwise resort to dangerous methods.
Cons:
1. Moral Debate Over Fetal Life
A key ethical concern for many is the question of when life begins and the moral status of the fetus. Those who are pro-life often believe that life begins at conception and that abortion is morally equivalent to ending a life. From this perspective, abortion is seen as ethically wrong because it involves the intentional termination of a potential human life.
2. Religious and Cultural Beliefs
In many cultures and religions, abortion is viewed as morally unacceptable. Some belief systems hold that every life is sacred from the moment of conception, and terminating a pregnancy is seen as a violation of these principles. In communities where these beliefs are widespread, abortion may be seen as ethically problematic, leading to societal pressure and judgment on individuals who choose this option.
3. Impact on Future Generations
Some argue that abortion not only affects the current generation but has broader implications for society. By terminating pregnancies, some believe that future generations are deprived of potential individuals who could contribute positively to the world. This viewpoint is often rooted in the belief that every potential life has intrinsic value.
The Emotional and Social Aspects of Abortion
Beyond medical and ethical considerations, abortion carries significant emotional and social weight for individuals and society as a whole.
Pros:
1. Empowerment and Relief
For many, the ability to choose abortion can be empowering. It allows individuals to decide when, and under what circumstances, they want to become parents. For those experiencing an unplanned or unwanted pregnancy, abortion can provide a sense of relief and a chance to pursue personal, educational, or career goals without the responsibility of raising a child.
2. Social Equality
Access to abortion is often viewed as a critical component of women’s rights and gender equality. The ability to control one’s reproductive choices can influence economic and social opportunities, allowing women to achieve parity with men in the workforce and beyond.
Cons:
1. Emotional Complexity
While some individuals feel relief after an abortion, others experience complex emotions such as guilt, sadness, or regret. Societal stigma surrounding abortion can exacerbate these feelings, making it more difficult for individuals to process their emotions and find support.
2. Family and Relationship Strain
The decision to have an abortion can sometimes cause strain in relationships, especially if partners, family members, or friends have differing views on the subject. This can lead to feelings of isolation or tension within close relationships, further complicating an already difficult situation.
The Complexities of Abortion
Abortion is a deeply personal decision that involves weighing the pros and cons of medical, ethical, and emotional factors. Each individual’s circumstances are unique, and what might be right for one person may not be right for another. Ultimately, it’s crucial for individuals facing this decision to have access to accurate information, supportive healthcare, and counseling services to make an informed choice that’s best for their physical, emotional, and ethical well-being.
Essential Do’s and Don’ts During IVF Stimulation: Maximize Success with Expert Tips

In-vitro fertilization (IVF) is a complex and emotionally charged journey for many couples trying to conceive. One of the most crucial phases of this process is IVF stimulation, during which medications are used to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs for retrieval. While the medical professionals will guide the technical side of things, there are important lifestyle factors and habits that can enhance your chances of success. Understanding the do’s and don’ts during IVF stimulation can help you optimize your results and maintain your emotional well-being throughout the process.
In this article, we’ll explore key guidelines on what you should and shouldn’t do during IVF stimulation to support your health and fertility outcomes.
The Do’s During IVF Stimulation
1. Follow Your Medication Schedule Religiously
One of the most important aspects of IVF stimulation is the consistent use of fertility medications that stimulate the ovaries. These medications include hormone injections like gonadotropins, which encourage the development of multiple eggs. Since timing is critical in IVF, following your medication schedule exactly as prescribed is essential. Missing doses or injecting at the wrong times can disrupt the cycle and impact the development of the eggs.
Tip: Set reminders on your phone or use a fertility app to track your injections and medication schedule to ensure you stay on top of it.
2. Maintain a Healthy Diet
During IVF stimulation, what you eat can have an impact on your body’s response to the treatment. A balanced, nutrient-rich diet can help optimize your reproductive health and support egg quality. Focus on including:
– Fruits and vegetables: Rich in antioxidants that help reduce inflammation and support overall health.
– Lean proteins: Sources such as chicken, turkey, and plant-based proteins can support your body’s energy needs during treatment.
– Healthy fats: Omega-3 fatty acids, found in foods like salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds, support hormone production and overall reproductive health.
– Whole grains: Complex carbohydrates like quinoa, brown rice, and oats provide sustained energy without causing spikes in blood sugar levels.
3. Stay Hydrated
Staying hydrated is key during IVF stimulation. Water helps transport hormones and nutrients throughout the body, and adequate hydration ensures your body is functioning optimally. Dehydration can lead to fatigue, headaches, and bloating, which are the last things you need during your IVF cycle.
Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water per day, and more if you’re engaging in light exercise or living in a warm climate.
4. Engage in Gentle Exercise
Exercise is important for maintaining physical and mental well-being, but during IVF stimulation, it’s best to opt for gentle forms of physical activity. Overexertion or high-intensity workouts can increase the risk of ovarian torsion—a rare but serious complication where the ovary twists due to increased size from stimulation.
Stick to light exercises such as:
– Walking
– Prenatal yoga
– Swimming
These activities can help improve blood flow, reduce stress, and support overall health without putting undue strain on your body.
5. Prioritize Rest and Stress Management
The IVF process can be physically and emotionally exhausting, and stress can negatively affect your body’s response to fertility treatments. Prioritize sleep and stress management techniques to help your body recover and remain resilient.
Consider incorporating practices such as:
– Meditation or mindfulness exercises: These can help calm your mind and ease anxiety.
– Acupuncture: Some studies suggest acupuncture may improve blood flow to the ovaries and help manage stress during IVF.
– Deep breathing exercises: Breathing techniques can reduce cortisol levels and promote relaxation.
6. Communicate Openly with Your Doctor
It’s crucial to maintain open lines of communication with your fertility specialist during IVF stimulation. Report any unusual symptoms, such as extreme bloating, shortness of breath, or dizziness, as these may be signs of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), a potentially serious condition caused by an exaggerated response to fertility medications.
Your doctor can adjust your treatment plan based on how your body responds, so don’t hesitate to ask questions and voice concerns.
The Don’ts During IVF Stimulation
1. Don’t Engage in High-Impact or Strenuous Exercise
While staying active is beneficial, engaging in high-impact activities like running, heavy weightlifting, or high-intensity interval training (HIIT) during IVF stimulation can increase the risk of ovarian torsion. As your ovaries become enlarged due to the stimulation medications, they are more vulnerable to twisting, which can cause severe pain and may require surgical intervention.
Stick to low-impact exercises and consult your doctor before resuming your normal workout routine post-treatment.
2. Avoid Alcohol and Caffeine
Both alcohol and caffeine can negatively impact fertility outcomes. Studies have shown that excessive alcohol consumption can affect hormone levels, disrupt the menstrual cycle, and reduce the likelihood of conception. While small amounts of caffeine may be acceptable, many fertility experts recommend limiting your intake to less than 200 milligrams per day—the equivalent of one small cup of coffee.
It’s best to avoid alcohol entirely during IVF stimulation, and if you’re a regular coffee drinker, consider switching to decaf or reducing your caffeine intake to optimize your chances of success.
3. Don’t Smoke
Smoking has been linked to reduced fertility and can negatively affect egg quality, sperm quality, and the success rate of IVF treatments. If you’re a smoker, quitting before starting IVF can significantly improve your chances of a successful pregnancy. Smoking increases oxidative stress in the body, which can damage the eggs and decrease ovarian reserve.
Additionally, smoking can reduce the effectiveness of fertility medications, making it harder for your body to produce quality eggs during stimulation.
4. Avoid Exposure to Environmental Toxins
Environmental toxins and chemicals found in everyday products can interfere with hormone function and fertility. During IVF stimulation, it’s especially important to limit your exposure to these toxins. Some key things to avoid include:
– Harsh cleaning products: Opt for natural, non-toxic alternatives.
– Pesticides: Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly, or buy organic when possible.
– BPA and phthalates: These chemicals, commonly found in plastics, have been linked to hormone disruption. Avoid heating food in plastic containers and opt for BPA-free products.
5. Don’t Overthink the Process
IVF is already a stressful and emotional experience, and it’s easy to get caught up in analyzing every symptom or side effect during the stimulation phase. Overthinking and obsessing about the outcome can increase stress and negatively impact your mental health. Trust the process, follow your doctor’s guidance, and remember that each IVF cycle is unique. Comparing your experience to others can add unnecessary pressure.
6. Avoid Drastic Diet Changes or Supplements Without Doctor Approval
While maintaining a healthy diet is essential, making sudden or drastic changes to your diet, or adding new supplements without your doctor’s approval, can affect your IVF cycle. Some supplements or dietary changes may interfere with fertility medications or hormone levels. Always consult your fertility specialist before adding any new vitamins, herbs, or supplements to your routine.
A Balanced Approach to IVF Stimulation
The IVF journey is both physically and emotionally challenging, but by following these do’s and don’ts during the stimulation phase, you can optimize your chances of success while keeping your body healthy. Focus on staying hydrated, nourishing your body with nutrient-rich foods, and managing stress to create a supportive environment for egg development. Always communicate with your fertility specialist about your concerns and follow their instructions closely.
While IVF stimulation can be an intense process, remember that every step brings you closer to your ultimate goal. With patience, self-care, and medical support, you’re giving yourself the best chance for a successful outcome.
40 Weeks Pregnant and No Signs of Labor: What to Expect and When to Call Your Doctor

At 40 weeks pregnant, you’ve likely been eagerly awaiting the arrival of your baby for months. You’ve prepped the nursery, packed your hospital bag, and even nested your way through the house a dozen times. But now you’re officially at your due date with no signs of labor in sight. If you’re feeling anxious or even frustrated, you’re not alone! Many women go beyond 40 weeks before labor begins. So, what should you expect if you’re still pregnant at 40 weeks? And when should you call your doctor? Let’s dive into everything you need to know.
Understanding the 40-Week Mark: Is It Really “Late”?
First, it’s important to remember that your due date is just an estimate. Only about 5% of babies are born on their actual due date, and it’s perfectly normal for labor to start anytime between 37 and 42 weeks. Pregnancy is considered full-term at 37 weeks, but going past your due date doesn’t necessarily mean anything is wrong.
Why Labor May Be Delayed
There are several reasons why your baby might be staying cozy inside the womb a little longer than expected. Here are some common factors that could contribute to labor taking its time:
1. First-Time Pregnancy
If this is your first pregnancy, it’s not unusual to go past 40 weeks. First-time moms tend to have longer pregnancies as their bodies take more time to prepare for labor. Your cervix may need a bit more time to soften, thin out, and dilate.
2. Baby’s Position
Your baby’s position in the womb can also affect when labor begins. If your baby isn’t in an ideal position—such as if they are sunny-side up (facing your abdomen), or if their head isn’t fully engaged in the pelvis—it might take a little longer for labor to start.
3. Miscalculated Due Date
Despite the precision of modern medicine, your due date is still just an estimate, and the exact timing of conception can sometimes be miscalculated. If your menstrual cycle is irregular or you weren’t tracking ovulation, it’s possible that your due date was set too early.
4. Genetic Factors
For some women, going past their due date might be part of their genetics. If your mom or sister had longer pregnancies, you might, too. It’s not uncommon for families to have a history of “late” babies.
Common Signs of Labor to Watch For
Even if you haven’t noticed any clear signs of labor yet, it’s good to be aware of what to look for as your body continues to prepare. Here are some common signs that labor might be on the horizon:
1. Contractions
One of the most obvious signs of labor is regular contractions. These may start as mild cramping or backache and eventually become more intense and frequent. True labor contractions will gradually get closer together and last longer over time. If your contractions are irregular or stop when you change positions, it could be false labor (Braxton Hicks contractions).
2. Loss of Mucus Plug
The ‘mucus plug’ is a thick collection of mucus that seals your cervix during pregnancy to prevent bacteria from entering. As your cervix begins to dilate, you may notice the loss of your mucus plug. It may come out all at once or in smaller bits over a few days. While this is a sign that labor is approaching, it doesn’t mean it’s imminent—labor could still be days away.
3. Water Breaking
When your water breaks, it’s a sign that labor could start soon. However, it’s worth noting that only about 10-15% of women experience their water breaking before labor starts. For many women, the water breaks later in labor, so don’t be alarmed if this doesn’t happen right away.
4. Cervical Changes
Your doctor or midwife may check your cervix during prenatal appointments as you get closer to your due date. Effacement (thinning) and dilation (opening) of the cervix are good indicators that labor is approaching. However, even if you’re not dilated or effaced yet at 40 weeks, labor can still begin suddenly.
When Should You Call Your Doctor?
While waiting for labor to start can be frustrating, there are certain signs that indicate it’s time to reach out to your healthcare provider, whether or not you’re showing classic signs of labor. Call your doctor if:
1. Your Water Breaks
Even if you aren’t having contractions yet, if your water breaks (whether it’s a gush or a slow leak), it’s time to call your healthcare provider. This usually means labor will start soon, but your provider may want to monitor you and the baby to reduce the risk of infection.
2. Decreased Fetal Movement
If you notice a significant decrease in your baby’s movements, call your doctor right away. It’s normal for movements to change as your baby grows and runs out of room, but a noticeable drop in activity could be a sign that something is wrong and should be checked.
3. Signs of Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a serious condition that can develop late in pregnancy, and it requires immediate medical attention. If you experience symptoms such as severe headaches, sudden swelling (especially in the face or hands), visual disturbances, or upper abdominal pain, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
4. If You Reach 41-42 Weeks
If you’ve reached 41 weeks with no signs of labor, your healthcare provider will likely recommend additional monitoring. You may be scheduled for a ‘non-stress test’ or biophysical profile to check on your baby’s well-being. At 42 weeks, most doctors will recommend inducing labor to minimize the risks associated with post-term pregnancy.
Inducing Labor: What to Expect
If you’re approaching or past 42 weeks and still haven’t gone into labor naturally, your healthcare provider may discuss induction options. Here are some common methods of inducing labor:
1. Membrane Sweeping
This is a technique where your healthcare provider manually separates the amniotic sac from the cervix during a vaginal exam. This can help trigger labor by stimulating the release of prostaglandins, which soften the cervix.
2. Cervical Ripening Agents
Your doctor may use medication, such as misoprostol or a Foley catheter, to help soften and open your cervix in preparation for labor.
3. Pitocin
Pitocin is a synthetic form of oxytocin, the hormone that causes contractions. If your body isn’t contracting on its own, Pitocin can help stimulate labor.
Self-Care While Waiting for Labor
While you wait for labor to begin, there are a few things you can do to stay comfortable and help your body prepare:
– Stay Active: Gentle exercise, like walking or prenatal yoga, can encourage your baby to move into the right position and help stimulate contractions.
– Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water keeps you hydrated and may help prevent Braxton Hicks contractions.
– Get Rest: Once labor starts, you’ll need all your energy, so take this time to rest as much as possible.
– Stay Positive: It’s easy to get frustrated when you’re past your due date, but remember that every pregnancy is different, and your baby will come when the time is right.
Patience is Key
Being 40 weeks pregnant with no signs of labor can be stressful, but try to stay calm and patient. Your body knows what it’s doing, and your baby will arrive when they’re ready. In the meantime, keep communicating with your healthcare provider, stay active, and take care of yourself. If necessary, medical induction is a safe and effective way to ensure both you and your baby have a healthy delivery.
Patience is tough at this stage, but rest assured, your baby will soon make their grand entrance!
Iatrogenic Pregnancy: Causes, Risks, and Prevention in Medical Procedures

When we think about pregnancy, we often focus on natural or assisted conception. However, there’s a lesser-known and unintended form of pregnancy that can occur due to medical interventions—this is known as an iatrogenic pregnancy. The term “iatrogenic” comes from the Greek words ‘iatros’ (physician) and ‘genic’ (caused by), referring to any condition or issue unintentionally caused by medical treatment or procedures. In the case of pregnancy, it refers to conception that occurs as an unintended result of medical actions.
While rare, iatrogenic pregnancies highlight an important topic in modern medicine, particularly within the field of reproductive health. Understanding what iatrogenic pregnancies are, their causes, the risks they pose, and the steps medical professionals can take to prevent them is crucial for both patients and practitioners. This article explores these aspects in detail.
What Is an Iatrogenic Pregnancy?
An iatrogenic pregnancy is one that occurs as an unintended consequence of medical intervention. The medical procedures that can lead to such pregnancies are typically associated with reproductive health and gynecological treatments. For example, certain surgical procedures, hormonal treatments, or even fertility treatments intended to assist with conception may, in rare instances, result in a pregnancy that was not the intended outcome of the intervention.
These pregnancies are most frequently associated with cases where fertility treatments lead to more than the desired number of pregnancies (such as with multiple embryos), or where patients undergoing contraception or sterilization procedures end up conceiving due to technical errors or complications.
Common Causes of Iatrogenic Pregnancies
There are several medical circumstances and interventions that may unintentionally result in an iatrogenic pregnancy. Some of the most common causes include:
1. Fertility Treatments
Iatrogenic pregnancies are most commonly associated with fertility treatments like in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intrauterine insemination (IUI). Sometimes, fertility clinics will transfer more embryos than necessary, leading to an unexpected multiple pregnancy. In other cases, patients may experience complications when more embryos implant than expected, creating a scenario where the patient is pregnant with twins, triplets, or more.
High-dose fertility drugs can also stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, increasing the chances of multiple pregnancies.
2. Failed Contraceptive Procedures
Iatrogenic pregnancies can also occur after sterilization procedures, such as tubal ligation or vasectomy, when the procedure fails to prevent conception. While modern contraceptive methods and sterilizations are highly effective, no method is 100% guaranteed. Occasionally, fallopian tubes may heal or reconnect after a tubal ligation, allowing for pregnancy to occur. Similarly, vasectomies can sometimes fail, leading to sperm release and, subsequently, an unexpected pregnancy.
3. Mismanaged Hormonal Therapies
Hormonal therapies, such as those used to treat conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or endometriosis, can inadvertently lead to pregnancy if ovulation occurs unexpectedly. These treatments often regulate or suppress ovulation, but in rare cases, they can stimulate an unintended ovulatory cycle.
4. Post-Surgical Fertility Restoration
In some cases, patients may undergo surgery to correct a reproductive issue, like removing uterine fibroids, endometriosis, or other conditions affecting the reproductive organs. These procedures can sometimes restore fertility in patients who were previously infertile, and pregnancy can occur if the patient isn’t aware of their regained fertility potential and doesn’t use contraception post-surgery.
5. Inaccurate Fertility Diagnoses
Misdiagnosis of infertility can sometimes lead to an iatrogenic pregnancy. If a patient is incorrectly diagnosed as infertile, they may not take the necessary precautions to prevent pregnancy, leading to an unintended conception after a medical intervention.
Risks and Complications of Iatrogenic Pregnancies
Iatrogenic pregnancies can pose a number of risks, both for the mother and the fetus, depending on the circumstances. Some of the risks include:
1. Multiple Pregnancies
One of the primary risks associated with fertility treatments is the possibility of multiple pregnancies (twins, triplets, or more). Multiple pregnancies can lead to complications such as preterm birth, low birth weight, gestational diabetes, and high blood pressure (preeclampsia). These conditions can put both the mother and babies at risk, making the pregnancy more difficult to manage.
2. Ectopic Pregnancy
In some cases, medical interventions can increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy, where the embryo implants outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tubes. Ectopic pregnancies are dangerous and require immediate medical intervention, as they can cause severe complications if not treated.
3. Emotional and Psychological Stress
The unexpected nature of an iatrogenic pregnancy can place emotional strain on the intended parents. Whether it’s the shock of conceiving after a sterilization procedure or the challenge of managing a high-risk multiple pregnancy, patients may experience significant anxiety, stress, and confusion as they navigate this unplanned situation.
4. Health Complications for the Mother
For women who were undergoing medical treatments unrelated to pregnancy, the sudden change in health status caused by an unexpected pregnancy can be a significant burden. Some medical treatments can be harmful during pregnancy, requiring immediate adjustment of medication or procedures to ensure the safety of both mother and child.
Preventing Iatrogenic Pregnancies
While iatrogenic pregnancies are often unintended, there are several preventive measures that can be taken by healthcare providers to minimize the risk.
1. Careful Monitoring During Fertility Treatments
When undergoing fertility treatments, healthcare providers should carefully monitor patients to ensure that they are not overstimulating the ovaries or transferring more embryos than necessary. Responsible fertility practices can significantly reduce the likelihood of multiple pregnancies and other complications.
2. Rigorous Follow-Up Post-Contraceptive Procedures
For patients who have undergone sterilization procedures, it’s essential to schedule follow-up appointments to confirm that the surgery was successful. Testing to ensure that the fallopian tubes
Dry Skin During Pregnancy: Causes, Remedies, and Skincare Tips for Moms-to-Be
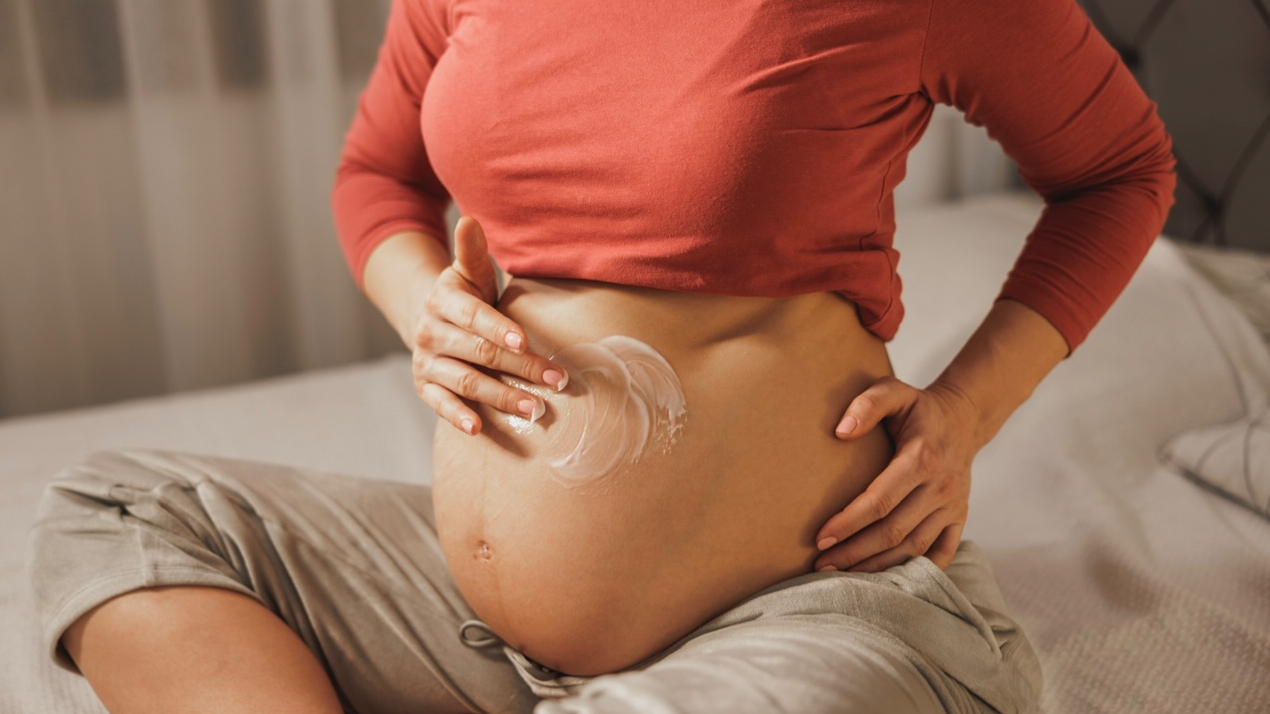

Pregnancy is an exciting time for expectant mothers, but along with the many joys and changes it brings, some less-than-glamorous symptoms can appear. One common issue experienced by many women during pregnancy is dry skin. As your body undergoes hormonal changes, shifts in your skincare routine may be necessary to accommodate new sensitivities and conditions.
If you’re wondering why your skin feels more parched than usual or what you can do to manage it, don’t worry—you’re not alone, and it’s completely normal! This article will dive into the causes of dry skin during pregnancy, offer remedies, and provide helpful skincare tips tailored to moms-to-be.
Why Does Dry Skin Occur During Pregnancy?
Pregnancy leads to a multitude of hormonal and physical changes in your body, which can significantly impact your skin. Here are the primary reasons dry skin is common during pregnancy:
1. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal shifts, especially the increase in progesterone and estrogen, can alter how your skin retains moisture. This may lead to skin feeling drier, itchier, or more sensitive than usual. These hormones can also cause your skin to become thinner, making it more vulnerable to dryness.
2. Increased Blood Flow
Pregnancy increases your blood flow to nourish the baby, and as a result, some areas of your skin may lose hydration. This can create patches of dry skin, especially on the belly, face, and limbs.
3. Stretching Skin
As your baby bump grows, your skin stretches to accommodate your expanding abdomen. This stretching can weaken the skin’s natural barrier, resulting in dryness, tightness, and itchiness. This is often experienced as pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy (PUPPP), a common condition that affects the skin during pregnancy.
4. Loss of Natural Oils
Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause a decrease in the skin’s production of natural oils, leaving it more vulnerable to environmental factors like dry air, wind, and heat. This reduction in natural oils can cause the skin to lose its moisture balance, leading to flakiness and irritation.
5. Dehydration
Pregnant women are more prone to dehydration because their bodies are using more fluids to support the baby. If you’re not drinking enough water, it can exacerbate dry skin symptoms. Staying hydrated is crucial for both you and your baby.
Common Areas Affected by Dry Skin During Pregnancy
While dry skin can appear anywhere on your body during pregnancy, certain areas are more prone to becoming parched or irritated:
– Belly: As your skin stretches to accommodate your growing baby, dryness and itchiness are common.
– Breasts: Your breasts will also grow during pregnancy, leading to potential dry patches or discomfort.
– Face: Pregnancy can alter the skin’s natural oil balance, causing your face to feel tight and dry.
– Hands and Feet: Hormonal changes can affect the moisture levels in your extremities, leading to dry, cracked skin on your hands and feet.
Remedies for Dry Skin During Pregnancy
Fortunately, dry skin during pregnancy is manageable, and with a few adjustments to your routine, you can relieve discomfort and improve your skin’s hydration levels. Here are some remedies to consider:
1. Moisturize Regularly
One of the best ways to combat dry skin is to moisturize frequently. Opt for a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer that’s safe for pregnancy. Products rich in ingredients like shea butter, cocoa butter, glycerin, and hyaluronic acid are excellent choices because they lock in moisture and help restore the skin’s natural barrier.
Apply moisturizer right after showering when your skin is still damp to seal in as much hydration as possible.
2. Use Natural Oils
Incorporating natural oils like coconut oil, almond oil, or jojoba oil into your skincare routine can help restore moisture and prevent further drying. These oils are generally safe during pregnancy and provide a protective layer that locks in hydration.
A thin layer of these oils can be applied to your belly, breasts, and other dry areas. Plus, they have the added benefit of potentially helping with stretch marks.
3. Hydrate from Within
Drinking plenty of water is essential for maintaining hydration, both for your skin and overall health during pregnancy. Aim to drink at least 8-10 glassesof water per day to ensure that your skin remains hydrated from the inside out. You can also incorporate hydrating foods, such as fruits and vegetables with high water content (like cucumbers, watermelon, and oranges).
4. Choose Mild, Hydrating Soaps
Switch to gentle, moisturizing cleansers that won’t strip your skin of its natural oils. Avoid using harsh soaps or body washes with strong fragrances and alcohol-based ingredients, as these can exacerbate dryness. Look for products labeled as hypoallergenicand fragrance-free.
5. Avoid Hot Showers and Baths
While it might be tempting to take a long, hot shower or bath to relax during pregnancy, hot water can actually strip your skin of essential moisture, leading to dryness. Opt for lukewarm water instead, and limit your showers to 10 minutes or less to prevent further drying.
6. Exfoliate Gently
Exfoliating your skin can help remove dead skin cells and promote smoother, healthier skin. However, be gentle when exfoliating during pregnancy. Use mild exfoliants like a sugar scrub or a soft washcloth to avoid irritating your skin further. Over-exfoliating can lead to more dryness and irritation, so aim to exfoliate only once or twice a week.
7. Invest in a Humidifier
Dry indoor air, especially during the colder months, can make your skin feel even drier. Using a humidifier in your bedroom or living space can help add moisture to the air, which can benefit your skin. It’s particularly useful at night, when your body is working to repair and regenerate itself.
8. Consult Your Doctor
If your dry skin becomes severe or if you develop conditions like eczema or PUPPP, it’s a good idea to consult your doctor or dermatologist. They can recommend pregnancy-safe treatments and medicated creams to manage symptoms.
Skincare Tips for Moms-to-Be
Pregnancy is a time when your skin may become more sensitive, so it’s essential to adjust your skincare routine to meet its new needs. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
– Stick to Gentle Products: Pregnancy can cause your skin to react differently to products that may have worked well for you before. Opt for gentle, pregnancy-safe skincare products that are free from harsh chemicals, parabens, and fragrances.
– Don’t Forget Sunscreen: Pregnancy can make your skin more susceptible to sun damage, which can worsen dryness. Use a broad-spectrum SPF 30 or higher daily to protect your skin from harmful UV rays.
– Use Stretch Mark Creams: While it’s impossible to completely prevent stretch marks, using moisturizing creams specifically designed for stretch marks can help keep your skin hydrated and reduce their appearance. Look for creams containing vitamin E, aloe vera, and collagen to support skin elasticity.
– Maintain a Healthy Diet: What you eat can affect the health of your skin. Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (like salmon and flaxseeds) to promote skin hydration. Additionally, make sure you’re getting enough vitamins A, C, and E, which are known to support skin health.
– Don’t Scratch: It’s tempting to scratch dry, itchy skin, but doing so can worsen irritation and even lead to scarring. Instead, apply a cool, damp cloth to the affected area or use an anti-itch cream recommended by your healthcare provider.
Dealing with dry skin during pregnancy is a common and manageable condition. With a few adjustments to your skincare routine and some extra TLC, you can keep your skin hydrated and healthy throughout your pregnancy journey. Remember to stay moisturized, drink plenty of water, and consult your healthcare provider if you experience severe dryness or irritation.
Your skin may change during pregnancy, but with the right care, you can ensure that it stays comfortable, glowing, and healthy.
