Month: May 2024
IUD vs. Birth Control: Understanding the Differences and Choosing the Right Option

When it comes to contraception, there are a plethora of options available to individuals seeking reliable and effective methods to prevent pregnancy. Two popular choices are the intrauterine device (IUD) and traditional birth control methods such as the pill, patch, or vaginal ring. In this article, we will explore the differences between IUDs and traditional birth control methods, helping you make an informed decision about which option is best suited to your needs.
Understanding IUDs
An intrauterine device (IUD) is a small, T-shaped device that is inserted into the uterus by a healthcare provider. There are two types of IUDs: hormonal and non-hormonal.
1. Hormonal IUD: This type of IUD releases a progestin hormone called levonorgestrel into the uterus. The hormone thickens the cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to reach the egg. It also thins the uterine lining, reducing the chances of implantation. Hormonal IUDs can provide contraception for 3 to 7 years, depending on the brand.
2. Non-hormonal IUD: Also known as the copper IUD, this type of IUD is hormone-free. It is made of copper, which creates an environment in the uterus that is toxic to sperm, preventing fertilization. Non-hormonal IUDs can provide contraception for up to 10 years.
Benefits of IUDs:
– Long-acting: IUDs offer long-term contraception, eliminating the need for daily or monthly maintenance.
– High effectiveness: IUDs are one of the most effective forms of contraception, with a failure rate of less than 1%.
– Convenience: Once inserted, IUDs require no further action until removal, making them a convenient option for individuals who prefer a “set it and forget it” approach.
– Reversible: IUDs are easily reversible, and fertility typically returns quickly after removal.
Understanding Traditional Birth Control Methods
Traditional birth control methods encompass a range of options that involve the use of hormonal medications to prevent pregnancy. These methods include:
1. Combination Birth Control Pills: These pills contain a combination of estrogen and progestin hormones. They work by preventing ovulation, thickening cervical mucus, and thinning the uterine lining. Combination pills must be taken daily for maximum effectiveness.
2. Progestin-Only Pills: Also known as the mini-pill, progestin-only pills contain only progestin hormone. They work primarily by thickening cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to reach the egg. Progestin-only pills must be taken at the same time every day for optimal effectiveness.
3. Patch: The birth control patch is a small adhesive patch that is applied to the skin. It releases hormones (estrogen and progestin) into the bloodstream to prevent pregnancy. The patch is typically worn for one week at a time, and a new patch is applied each week for three weeks, followed by a patch-free week.
4. Vaginal Ring: The vaginal ring is a small, flexible ring that is inserted into the vagina. It releases hormones (estrogen and progestin) to prevent pregnancy. The ring is left in place for three weeks, followed by a one-week ring-free period.
Benefits of Traditional Birth Control Methods:
– Convenience: Birth control pills, patches, and vaginal rings are easily self-administered and can be used discreetly.
– Regular menstrual cycles: Some individuals appreciate the regularity of menstrual cycles that hormonal birth control methods provide.
– Reversible: Traditional birth control methods can be discontinued to allow for pregnancy when desired.
Choosing the Right Option for You
When deciding between an IUD and traditional birth control methods, it’s important to consider your individual needs, preferences, and health considerations. Here are some factors to consider:
– Duration: If you prefer long-term contraception with minimal maintenance, an IUD may be a suitable choice. IUDs can provide effective contraception for several years.
– Hormonal vs. Non-hormonal: If you prefer a hormone-free option, a non-hormonal IUD may be preferable. However, if you have specific medical conditions or hormonal considerations, a hormonal IUD or traditional birth control method may be more suitable.
– Convenience: If you prefer a method that requires minimal daily or weekly maintenance, an IUD may be more convenient. However, if you are comfortable with daily or weekly administration, traditional birth control methods may be more suitable.
– Menstrual cycle preferences: Some individuals appreciate the regularity of menstrual cycles that hormonal birth control methods provide. If this is important to you, traditional birth control methods may be preferable.
Consulting with a Healthcare Provider
Choosing the right contraception option is a personal decision that should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider. They can provide guidance based on your medical history, lifestyle, and individual needs. A healthcare provider can discuss the benefits, risks, and effectiveness of each option, helping you make an informed decision.
Choosing between an IUD and traditional birth control methods requires careful consideration of your individual needs, preferences, and health considerations. IUDs offer long-acting, highly effective contraception with minimal maintenance. Traditional birth control methods, such as pills, patches, and vaginal rings, provide convenience and regular menstrual cycles. Consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial to discuss your options and make an informed decision. Remember, selecting the right contraception method is an important step in taking control of your reproductive health and preventing unintended pregnancies.
Does Alcohol Affect Birth Control? Understanding the Potential Interactions

Birth control is a reliable and effective method for preventing pregnancy when used correctly. However, it’s important to consider potential factors that can impact its efficacy. One common concern is whether alcohol consumption can affect the effectiveness of birth control methods. In this article, we will explore the relationship between alcohol and birth control, providing insights into the potential interactions and offering guidance for those using contraception.
Understanding Birth Control Methods
There are various birth control methods available, including hormonal methods (such as the pill, patch, or vaginal ring), intrauterine devices (IUDs), barrier methods (such as condoms), and permanent methods (such as sterilization). Each method works differently to prevent pregnancy, but the common goal is to either prevent sperm from reaching the egg or inhibit the release of an egg altogether.
Alcohol and Hormonal Birth Control
Hormonal birth control methods, such as the pill, patch, or vaginal ring, contain synthetic hormones (estrogen and/or progestin) that regulate the menstrual cycle and prevent pregnancy. When taken correctly, these methods are highly effective. However, there are factors that can potentially impact their efficacy, and alcohol consumption is one such factor.
Alcohol and Liver Enzymes
Alcohol can affect the metabolism of hormones in the liver. When you consume alcohol, your liver prioritizes the metabolism of alcohol over other substances, including hormones. This can potentially interfere with the breakdown and clearance of hormones from the body, leading to fluctuations in hormone levels.
Inconsistent Pill Use
Alcohol consumption can also impact the consistency of pill use. Excessive alcohol consumption can impair judgment and memory, leading to missed or inconsistent pill intake. Consistency is crucial for the effectiveness of hormonal birth control methods. Missing pills or taking them at irregular times can increase the risk of pregnancy.
Alcohol and Non-Hormonal Birth Control Methods
Non-hormonal birth control methods, such as barrier methods like condoms or spermicides, are not directly affected by alcohol consumption. These methods work by physically preventing sperm from reaching the egg, rather than relying on hormonal regulation. However, it’s important to note that alcohol can impair judgment and decision-making, potentially leading to decreased condom usage or other lapses in contraception.
Tips for Using Birth Control Effectively
To ensure the effectiveness of birth control methods, it’s important to follow these tips:
1. Consistency: Consistency is key for hormonal birth control methods. Take your pill, change your patch, or insert a new vaginal ring as directed by your healthcare provider. Set reminders or use smartphone apps to help you remember.
2. Use Backup Methods: If you’re using hormonal birth control and anticipate heavy alcohol consumption, consider using backup methods, such as condoms, to provide an extra layer of protection.
3. Open Communication: Discuss your birth control use with your partner. Ensure that both partners are aware of and committed to using contraception correctly. Open communication can help prevent misunderstandings or lapses in contraception.
4. Be Mindful of Medication Interactions: Some medications, including certain antibiotics and antifungal drugs, can interact with hormonal birth control and reduce its effectiveness. If you’re prescribed medication, consult with your healthcare provider about potential interactions.
5. Educate Yourself: Stay informed about your chosen birth control method. Understand its proper use, potential side effects, and any factors that can impact its effectiveness. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions and use contraception effectively.
6. Limit Alcohol Consumption: While moderate alcohol consumption is generally considered safe, excessive alcohol intake can impair judgment and memory, potentially leading to lapses in contraception. It’s important to be mindful of your alcohol consumption and make responsible choices.
Consult with a Healthcare Provider
If you have concerns about the potential interactions between alcohol and your chosen birth control method, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific situation and help address any questions or concerns you may have. Additionally, they can discuss alternative contraception options if needed.
While alcohol consumption does not directly impact the effectiveness of non-hormonal birth control methods, it can potentially affect the consistency and metabolism of hormonal birth control. Consistency is crucial for hormonal methods, and alcohol can impair judgment and memory, leading to missed or inconsistent pill intake. It’s important to use birth control methods correctly, follow the prescribed guidelines, and communicate openly with your partner. If you have concerns or questions, consult with a healthcare provider who can provide personalized guidance. Remember, responsible alcohol consumption and informed use of birth control methods are key to preventing unintended pregnancy.
How Long After Implantation Does hCG Rise? Understanding the Early Pregnancy Hormone

Implantation is a crucial step in the early stages of pregnancy. After fertilization, the embryo travels through the fallopian tube and implants itself into the lining of the uterus. Once implantation occurs, the body begins to produce a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). This hormone is responsible for supporting the pregnancy and can be detected through pregnancy tests. In this article, we will explore the timeline of hCG rise after implantation and provide insights into what to expect during early pregnancy.
Understanding Implantation
Implantation typically occurs around 6-12 days after fertilization, although it can vary slightly from woman to woman. During this process, the embryo burrows into the uterine lining and establishes a connection with the mother’s blood supply. Implantation is essential for the successful development of the pregnancy and the production of hCG.
Timeline of hCG Rise After Implantation
After implantation, hCG levels begin to increase. The timeline of hCG rise can vary depending on several factors, including the sensitivity of the pregnancy test used and the individual woman’s hCG production. However, there is a general pattern to the rise of hCG levels in early pregnancy:
1. Early Rise: In the first few days after implantation, hCG levels may be relatively low and may not be detectable by most pregnancy tests. During this time, the embryo is still establishing its connection with the uterine lining, and hCG production is just beginning.
2. Detectable Levels: Around 10-14 days after implantation, hCG levels typically reach a point where they can be detected by a home pregnancy test. However, it’s important to note that the sensitivity of the test can affect when a positive result is obtained. Some tests can detect hCG at lower levels, while others require higher levels for a positive result.
3. Doubling Every 48-72 Hours: After the initial detection of hCG, levels should double every 48-72 hours in a healthy pregnancy. This rapid increase is a positive sign and indicates that the pregnancy is progressing as expected. However, it’s important to note that individual hCG levels can vary, and a slower rate of increase does not necessarily indicate a problem.
4. Peak Levels: hCG levels continue to rise throughout the first trimester of pregnancy. By around 10 weeks gestation, hCG levels reach their peak and begin to decline gradually. This decline is normal and does not indicate a problem.
Factors Affecting hCG Levels
Several factors can influence hCG levels and the rate of rise after implantation. These factors include:
1. Number of Embryos Implanted: In pregnancies resulting from assisted reproductive technologies, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), hCG levels may be higher due to the potential presence of multiple embryos.
2. Timing of Implantation: The timing of implantation can vary from woman to woman. If implantation occurs later than average, it may delay the rise of hCG levels and the detection of pregnancy.
3. Individual Variation: Each woman’s body produces hCG at a slightly different rate. Some women may have higher hCG levels, while others may have lower levels, but both can still have healthy pregnancies.
4. Viability of the Pregnancy: In some cases, slow-rising or declining hCG levels may indicate a potential problem with the pregnancy, such as an ectopic pregnancy or a miscarriage. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and interpretation of hCG levels.
Seeking Medical Advice
If you suspect you are pregnant and have taken a home pregnancy test with a positive result, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider for confirmation and further guidance. They may perform a blood test to measure hCG levels and monitor their progression. This can provide valuable information about the viability and progression of the pregnancy.
It’s important to remember that hCG levels alone cannot determine the viability of a pregnancy. Other factors, such as ultrasound imaging and the presence of pregnancy symptoms, should also be taken into consideration.
hCG levels rise after implantation, signaling the beginning of a pregnancy. The timeline of hCG rise can vary, but in general, hCG levels become detectable by home pregnancy tests around 10-14 days after implantation. hCG levels should double every 48-72 hours in a healthy pregnancy. Factors such as the number of embryos implanted, timing of implantation, and individual variation can affect hCG levels and the rate of rise. If you suspect you are pregnant, it is best to consult with a healthcare provider for confirmation and further evaluation. They can provide guidance and support throughout the early stages of pregnancy.
Altruistic Surrogacy: A Selfless Act of Love

In recent years, surrogacy has gained significant attention as a method for individuals and couples to fulfill their dreams of parenthood. While the concept of surrogacy may seem straightforward, there are different types of surrogacy arrangements that vary in terms of compensation and motivation. One such type is altruistic surrogacy, which involves a selfless act of love and compassion. In this article, we will explore the concept of altruistic surrogacy, its benefits, and the ethical considerations surrounding this noble practice.
Altruistic surrogacy, also known as non-commercial surrogacy, is a form of surrogacy where the surrogate mother does not receive any financial compensation for carrying and delivering a child for another person or couple. Instead, the surrogate mother volunteers her time, energy, and body to help someone else achieve their dream of becoming a parent. The motivation behind altruistic surrogacy is rooted in empathy, compassion, and a genuine desire to help others.
One of the key benefits of altruistic surrogacy is the deep emotional connection that can develop between the surrogate mother and the intended parents. Unlike commercial surrogacy, where financial transactions may create a more business-like relationship, altruistic surrogacy allows for a more personal and intimate bond to form. The surrogate mother often becomes a cherished part of the intended parents’ lives, sharing in the joy and happiness of bringing a child into the world.
Another advantage of altruistic surrogacy is the lower financial burden it places on the intended parents. In commercial surrogacy arrangements, the intended parents are required to cover the costs associated with the surrogacy process, including the surrogate mother’s compensation, medical expenses, legal fees, and more. Altruistic surrogacy eliminates the financial aspect, making it a more accessible option for individuals and couples who may not have the means to pursue commercial surrogacy.
Ethical considerations play a crucial role in the practice of altruistic surrogacy. It is essential to ensure that the surrogate mother fully understands the implications and emotional challenges that may arise throughout the surrogacy journey. Open and honest communication between the surrogate mother and the intended parents is vital to establish boundaries, expectations, and ensure the well-being of all parties involved.
Furthermore, legal frameworks surrounding surrogacy vary from country to country, and it is crucial to abide by the laws and regulations in place. Altruistic surrogacy should always be conducted within a legal and ethical framework that protects the rights and interests of all parties involved, including the child.
Altruistic surrogacy is a selfless act that can bring immense joy and fulfillment to both the surrogate mother and the intended parents. It allows individuals and couples who are unable to conceive or carry a child the opportunity to experience the joys of parenthood. The bond that forms between the surrogate mother and the intended parents can create lifelong connections and extended support networks.
In addition to the emotional benefits, altruistic surrogacy also has a positive impact on society as a whole. It promotes empathy, compassion, and the selfless act of helping others in need. By choosing altruistic surrogacy, individuals and couples demonstrate their commitment to building families based on love and understanding.
In conclusion, altruistic surrogacy is a remarkable practice that exemplifies the power of selflessness and compassion. It offers a path to parenthood for those facing challenges in conceiving or carrying a child. The emotional connection and support that develop between the surrogate mother and the intended parents can create lasting bonds and transform lives. As society continues to evolve, it is crucial to recognize and appreciate the invaluable contribution of altruistic surrogacy in helping individuals and couples fulfill their dreams of becoming parents.
What is a Partial Hysterectomy: A Comprehensive Guide
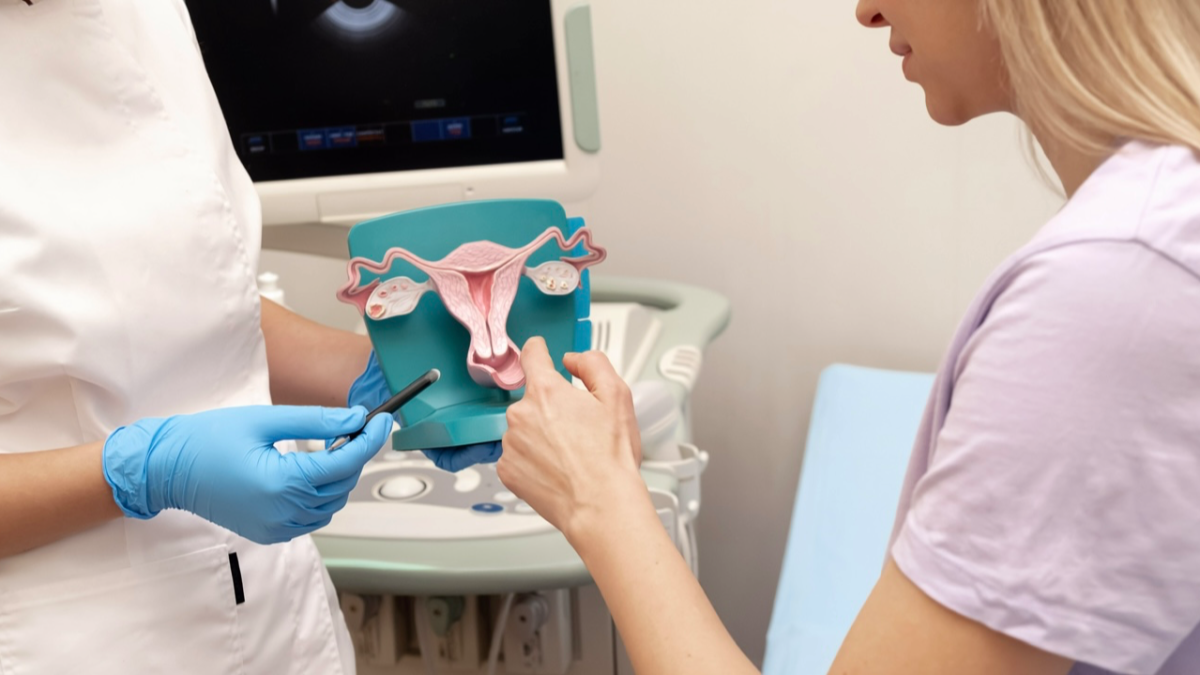
When it comes to women’s health, there are various medical procedures that can address specific conditions and improve overall well-being. One such procedure is a partial hysterectomy. In this article, we will delve into the details of what a partial hysterectomy entails, its benefits, potential risks, and recovery process. Whether you are considering this procedure or simply seeking to expand your knowledge, this comprehensive guide will provide you with the information you need.
A partial hysterectomy, also known as a subtotal hysterectomy, is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the uterus while leaving the cervix intact. This means that the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina, is not removed during the procedure. The purpose of a partial hysterectomy is to address certain medical conditions or alleviate symptoms that are affecting a woman’s quality of life.
There are several reasons why a partial hysterectomy may be recommended by a healthcare professional. One of the most common indications for this procedure is the presence of benign (non-cancerous) conditions, such as uterine fibroids or adenomyosis. Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths that can cause heavy or painful periods, pelvic pain, and pressure on nearby organs. Adenomyosis is a condition where the lining of the uterus grows into the muscular wall, leading to heavy bleeding and severe menstrual cramps.
Another reason for a partial hysterectomy is the treatment of abnormal uterine bleeding that does not respond to other medical interventions. This can include excessive or prolonged menstrual bleeding, irregular periods, or bleeding between periods. In some cases, a partial hysterectomy may be recommended as a preventive measure for women at high risk of developing uterine cancer or ovarian cancer.
Before undergoing a partial hysterectomy, it is essential to have a thorough consultation with a healthcare professional to determine if this procedure is the most suitable option for your specific condition. They will consider factors such as your medical history, the severity of your symptoms, and your future reproductive goals.
During the procedure, which is typically performed under general anesthesia, the surgeon will make an incision in the lower abdomen to access the uterus. The uterus is then carefully removed, while the cervix is left in place. In some cases, the fallopian tubes and ovaries may also be removed, depending on the individual circumstances and the patient’s preferences.
One of the advantages of a partial hysterectomy is the preservation of the cervix. By leaving the cervix intact, some women may experience a lower risk of certain complications, such as pelvic organ prolapse, urinary incontinence, or changes in sexual function. Additionally, the preservation of the cervix can eliminate the need for routine Pap smears, which are typically performed to screen for cervical cancer.
Like any surgical procedure, a partial hysterectomy carries certain risks and potential complications. These can include infection, bleeding, damage to nearby organs, adverse reactions to anesthesia, and blood clots. It is crucial to discuss these risks with your healthcare provider and address any concerns you may have before making a decision.
The recovery process following a partial hysterectomy varies from person to person but generally involves a period of rest and healing. Most women can expect to stay in the hospital for a day or two after the procedure to ensure proper monitoring and pain management. During the recovery period, it is essential to follow all post-operative instructions provided by your healthcare team, including restrictions on physical activity, lifting heavy objects, and sexual intercourse.
It is normal to experience some discomfort, vaginal bleeding, and fatigue in the weeks following the surgery. However, if you experience severe pain, heavy bleeding, fever, or any other concerning symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.
In terms of long-term effects, a partial hysterectomy does not lead to menopause. Since the ovaries are not typically removed during this procedure, hormone production continues, and menopause occurs naturally when the ovaries naturally cease to function. However, it is essential to discuss the potential hormonal changes and their impact on your overall health with your healthcare provider.
In conclusion, a partial hysterectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the uterus while leaving the cervix intact. It is often performed to address benign conditions, abnormal uterine bleeding, or as a preventive measure for certain types of cancer. While there are risks and potential complications associated with this procedure, it can provide significant relief from symptoms and improve a woman’s quality of life. If you are considering a partial hysterectomy, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional who can guide you through the decision-making process and provide the necessary support throughout your journey to better health.
PCOD vs PCOS: Understanding the Differences and Similarities

Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and polycystic ovary disease (PCOD) are two terms often used interchangeably to describe a common hormonal disorder affecting many women. While they share similarities in symptoms and causes, it is important to understand that PCOD and PCOS are not the same condition. In this article, we will delve into the differences and similarities between PCOD and PCOS, shedding light on their causes, symptoms, and management.
What is PCOD?
Polycystic ovary disease (PCOD), also known as polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), is a condition characterized by the presence of multiple small cysts on the ovaries. These cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form due to hormonal imbalances, specifically an excess of androgens (male hormones) in the body. PCOD affects the reproductive system and can cause irregular periods, fertility issues, and hormonal imbalances.
What is PCOS?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a broader term that encompasses not only the presence of ovarian cysts but also other hormonal and metabolic imbalances. PCOS is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age and is characterized by irregular periods, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), acne, and insulin resistance. Women with PCOS may also experience weight gain, mood swings, and difficulties with fertility.
Differences between PCOD and PCOS
1. Terminology: PCOD and PCOS are often used interchangeably, but PCOD is technically a more accurate term. PCOD refers specifically to the presence of multiple cysts on the ovaries, whereas PCOS includes additional hormonal and metabolic imbalances.
2. Diagnostic Criteria: The diagnostic criteria for PCOD and PCOS differ slightly. PCOD is primarily diagnosed through ultrasound imaging that reveals the presence of multiple cysts on the ovaries. On the other hand, PCOS is diagnosed based on a combination of symptoms, including irregular periods, excessive hair growth, and hormonal imbalances.
3. Hormonal Imbalances: Both PCOD and PCOS involve hormonal imbalances, but the specific hormone levels may vary. PCOD is characterized by elevated levels of androgens, while PCOS may involve imbalances in multiple hormones, including androgens, estrogen, and insulin.
4. Metabolic Factors: PCOS is associated with metabolic factors such as insulin resistance and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. These metabolic abnormalities are not commonly associated with PCOD.
Similarities between PCOD and PCOS
1. Irregular Periods: Both PCOD and PCOS can cause irregular menstrual cycles. Women with these conditions may experience infrequent periods, heavy or prolonged bleeding, or a complete absence of menstruation.
2. Hormonal Imbalances: Both conditions involve hormonal imbalances that can disrupt the normal functioning of the reproductive system. Elevated levels of androgens in both PCOD and PCOS can lead to symptoms such as acne, excessive hair growth, and mood swings.
3. Fertility Issues: PCOD and PCOS can both affect a woman’s fertility. The hormonal imbalances and irregular ovulation associated with these conditions can make it more challenging to conceive. However, with proper management, many women with PCOD or PCOS are able to conceive and have successful pregnancies.
Managing PCOD and PCOS
While there is no cure for PCOD or PCOS, there are various management strategies that can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall health:
1. Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can have a significant impact on managing PCOD and PCOS. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and maintaining a healthy weight can help regulate hormone levels and improve symptoms.
2. Medications: Hormonal birth control pills may be prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles and reduce androgen levels. Other medications, such as anti-androgens and insulin-sensitizing drugs, may also be used to manage specific symptoms.
3. Fertility Treatments: Women with PCOD or PCOS who are trying to conceive may require fertility treatments such as ovulation induction, in vitro fertilization (IVF), or other assisted reproductive technologies.
4. Emotional Support: Living with PCOD or PCOS can be emotionally challenging due to the physical symptoms and potential fertility concerns. Seeking emotional support from loved ones, support groups, or therapists can be beneficial in coping with the condition.
While PCOD and PCOS share similarities in symptoms and hormonal imbalances, it is important to recognize that they are not the same condition. PCOD refers specifically to the presence of multiple cysts on the ovaries, while PCOS encompasses a broader range of hormonal and metabolic imbalances. Understanding the differences and similarities between PCOD and PCOS is crucial for proper diagnosis, management, and treatment. If you suspect you may have either condition, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Signs of Pregnancy After Abortion: What to Look Out For

Experiencing an abortion can be an emotionally and physically challenging experience for any woman. After an abortion, it’s important to take care of your physical and emotional well-being. One concern that may arise is the possibility of becoming pregnant again after the procedure. In this article, we will discuss the signs of pregnancy to look out for after an abortion, as well as provide guidance on what to do if you suspect you may be pregnant.
Understanding the Menstrual Cycle After an Abortion
Before delving into the signs of pregnancy after an abortion, it’s crucial to understand how the menstrual cycle may be affected. After an abortion, your menstrual cycle will likely take some time to regulate. It’s normal for your periods to be irregular for a few months following the procedure. Your body needs time to recover and adjust hormonally. It’s also worth noting that the timing of your first period after an abortion can vary depending on the type of abortion you had and how far along you were in the pregnancy.
Signs of Pregnancy After an Abortion
While the menstrual cycle may be irregular after an abortion, it’s still possible to become pregnant. Here are some signs to look out for that may indicate a pregnancy after an abortion:
1. Missed Period: If you have been having regular periods after your abortion and suddenly miss a period, it could be a sign of pregnancy. However, it’s important to note that irregular periods are common after an abortion, so a missed period may not necessarily indicate pregnancy.
2. Breast Tenderness: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause breast tenderness or sensitivity. If you notice that your breasts feel more tender than usual, it could be a sign of pregnancy.
3. Nausea and Fatigue: Morning sickness, which includes feelings of nausea and fatigue, is a common early sign of pregnancy. If you experience these symptoms after an abortion, it’s worth considering the possibility of pregnancy.
4. Changes in Appetite: Pregnancy hormones can also cause changes in appetite. Some women may experience cravings or aversions to certain foods. Pay attention to any sudden changes in your eating habits.
5. Frequent Urination: The hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy can increase blood flow to the pelvic area, resulting in more frequent urination. If you find yourself needing to urinate more frequently than usual, it could be a sign of pregnancy.
6. Mood Swings: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy can cause mood swings. If you notice sudden changes in your mood, such as feeling more emotional or irritable, it could be a sign of pregnancy.
Taking a Pregnancy Test
If you experience any of the above signs of pregnancy after an abortion, it’s important to take a pregnancy test to confirm whether or not you are pregnant. Home pregnancy tests are widely available and can provide accurate results when used correctly. It’s best to wait until at least a week after your missed period to take a pregnancy test for the most accurate results.
If the test result is positive, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to confirm the pregnancy and discuss your options moving forward. They can provide guidance on prenatal care and support you in making informed decisions about your pregnancy.
Seeking Emotional Support
Experiencing a pregnancy after an abortion can bring up a range of emotions. It’s important to prioritize your emotional well-being during this time. Reach out to your support system, whether it’s friends, family, or a therapist, to talk about your feelings and seek support. They can provide a listening ear and help you navigate your emotions in a healthy way.
Experiencing signs of pregnancy after an abortion can be a complex and emotional situation. While the menstrual cycle may be irregular after an abortion, it’s still possible to become pregnant. Pay attention to signs such as a missed period, breast tenderness, nausea, fatigue, changes in appetite, frequent urination, and mood swings. If you suspect you may be pregnant, take a home pregnancy test and consult with a healthcare professional for confirmation and guidance. Remember to prioritize your emotional well-being during this time and seek the support you need.
Brain Health in Menopause: Strategies for Maintaining Cognitive Well-being

Menopause is a natural transition in a woman’s life that marks the end of her reproductive years. While menopause is commonly associated with physical changes, such as hot flashes and night sweats, it also has an impact on brain health and cognitive function. Many women experience cognitive changes during menopause, including memory lapses, difficulty concentrating, and mental fog. However, it is important to note that these changes are usually temporary and can be managed with proper care. In this article, we will explore the impact of menopause on brain health, strategies for maintaining cognitive well-being, and lifestyle factors that can support brain health during this stage of life.
Understanding the Impact of Menopause on Brain Health
During menopause, there is a decline in the production of estrogen and progesterone, two hormones that play a significant role in brain health. Estrogen, in particular, has neuroprotective properties and supports cognitive functions, including memory and attention. As estrogen levels decrease, women may experience cognitive changes and an increased risk of certain conditions, such as:
1. Memory Lapses: Many women report experiencing memory lapses or “brain fog” during menopause. These lapses are often characterized by forgetfulness, difficulty recalling information, and feeling mentally sluggish.
2. Reduced Cognitive Flexibility: Menopause can affect cognitive flexibility, which refers to the brain’s ability to switch between different tasks or adapt to new situations. Some women may find it challenging to multitask or adjust to changes in routine.
3. Increased Risk of Cognitive Disorders: Estrogen decline during menopause has been associated with an increased risk of cognitive disorders, such as mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer’s disease. However, it’s important to note that the majority of women do not develop these conditions.
Strategies for Maintaining Cognitive Well-being during Menopause
While cognitive changes during menopause are common, there are strategies women can implement to support brain health and maintain cognitive well-being:
1. Stay Mentally Active: Engaging in mentally stimulating activities can help maintain cognitive function. Read books, solve puzzles, play brain games, or learn a new skill to keep your mind sharp.
2. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can support brain health during menopause. Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Stay hydrated and limit the consumption of processed foods, sugary snacks, and excessive alcohol.
3. Regular Physical Exercise: Exercise has numerous benefits for brain health. Engage in regular aerobic exercise, such as walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling, to improve blood flow to the brain and enhance cognitive function.
4. Manage Stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact cognitive function. Practice stress management techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga, to reduce stress levels and promote mental well-being.
5. Prioritize Sleep: Quality sleep is essential for brain health. Establish a regular sleep schedule and create a sleep-friendly environment. Avoid excessive caffeine and electronic devices before bedtime.
6. Socialize and Stay Connected: Maintain social connections and engage in activities that involve social interaction. Socializing can stimulate cognitive function and provide emotional support during menopause.
7. Hormone Therapy: For some women, hormone therapy (HT) may be an option to alleviate menopause symptoms and potentially support cognitive health. HT involves the use of estrogen alone or combined with progesterone (in women with a uterus). However, the decision to pursue HT should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider, considering individual risks and benefits.
8. Seek Professional Help: If cognitive changes significantly affect daily life or cause distress, it is important to seek professional help. A healthcare provider can evaluate symptoms, provide guidance, and recommend appropriate interventions if needed.
Menopause is a natural stage of life that can bring about cognitive changes for many women. While memory lapses and cognitive challenges may occur during this transition, it is essential to remember that they are typically temporary and manageable. By implementing strategies to support brain health, such as staying mentally active, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and seeking professional help when necessary, women can maintain cognitive well-being during menopause. Embracing a positive mindset and adopting a holistic approach to brain health can contribute to overall well-being and enhance the journey through this transformative stage of life.
7 Steps to Getting Pregnant with Blocked Fallopian Tubes

Blocked fallopian tubes can be a significant obstacle for couples trying to conceive. When the fallopian tubes are blocked, it becomes difficult for the sperm to reach the egg, resulting in infertility. However, there are steps you can take to increase your chances of getting pregnant, even with blocked fallopian tubes. In this article, we will discuss seven steps you can follow to improve your fertility and increase the likelihood of conception.
1. Consult with a Fertility Specialist
If you suspect that you have blocked fallopian tubes, it’s important to consult with a fertility specialist. They will be able to diagnose the blockage and determine the best course of action. The specialist may recommend additional tests, such as an HSG (hysterosalpingogram), to get a clearer picture of the condition of your fallopian tubes.
2. Explore Treatment Options
There are various treatment options available for couples with blocked fallopian tubes. Depending on the severity of the blockage, your fertility specialist may recommend:
– Laparoscopic Surgery: In cases where the blockage is due to scar tissue or adhesions, laparoscopic surgery may be performed to remove the blockage and restore the normal function of the fallopian tubes.
– In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): IVF is a highly effective fertility treatment that bypasses the need for the fallopian tubes. During IVF, eggs are retrieved and fertilized with sperm in a laboratory setting. The resulting embryos are then transferred to the uterus.
– Tubal Reversal Surgery: If the blockage is due to a previous tubal ligation procedure, tubal reversal surgery may be an option. This surgery reconnects the fallopian tubes to allow for natural conception.
3. Focus on Optimizing Overall Health
Improving your overall health can positively impact your fertility. Maintain a healthy weight, eat a balanced diet rich in nutrients, exercise regularly, and manage stress levels. These lifestyle factors can enhance your reproductive health and increase your chances of getting pregnant.
4. Consider Natural Remedies
Some natural remedies may help improve the condition of your fallopian tubes and increase fertility. Herbs such as red clover and dong quai are believed to have properties that can help clear blockages. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any natural remedies to ensure they are safe and suitable for your specific situation.
5. Optimize Sexual Timing
Understanding your menstrual cycle and timing intercourse correctly can significantly increase your chances of conception. Track your ovulation using methods such as basal body temperature charting, ovulation predictor kits, or fertility apps. Have intercourse regularly in the days leading up to and during ovulation to maximize the chances of sperm meeting the egg.
6. Consider Alternative Fertilization Methods
If the fallopian tubes are completely blocked, alternative fertilization methods such as intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) may be considered. ICSI involves directly injecting a single sperm into the egg to facilitate fertilization. This method can be used in conjunction with IVF to increase the chances of successful conception.
7. Seek Emotional Support
Dealing with blocked fallopian tubes and infertility can be emotionally challenging. It’s important to seek emotional support from your partner, friends, family, or a support group. Consider talking to a therapist who specializes in fertility issues to help you navigate the emotional aspects of your fertility journey.
While blocked fallopian tubes can present a significant hurdle to conception, there are steps you can take to improve your chances of getting pregnant. Consult with a fertility specialist to explore treatment options, optimize your overall health, consider natural remedies (with professional guidance), focus on timing intercourse correctly, and explore alternative fertilization methods if necessary. Remember to seek emotional support throughout your journey, as the emotional impact of infertility can be challenging. With the right support and treatment, many couples with blocked fallopian tubes are able to achieve their dream of becoming parents.
Vaginal Odor and Menopause: Causes, Management, and Tips for Freshness

Menopause is a natural stage in a woman’s life that marks the end of her reproductive years. Along with hormonal changes, menopause can bring about various physical and emotional changes. One common concern that women may experience during menopause is vaginal odor. In this article, we will explore the causes of vaginal odor during menopause, discuss management strategies, and provide tips for maintaining freshness and comfort.
Causes of Vaginal Odor During Menopause
Vaginal odor can be attributed to a variety of factors during menopause. Some of the common causes include:
1. Hormonal Changes: Menopause is characterized by a decline in estrogen levels. This decrease in estrogen can lead to changes in the vaginal pH balance, resulting in an overgrowth of certain bacteria and a subsequent increase in vaginal odor.
2. Vaginal Dryness: Estrogen helps maintain the moisture and elasticity of the vaginal tissues. As estrogen levels decline during menopause, vaginal dryness can occur. This dryness can cause irritation and inflammation, leading to an imbalance in the vaginal flora and an associated odor.
3. Infections: Menopausal women may be more prone to vaginal infections, such as bacterial vaginosis or yeast infections. These infections can cause an unpleasant odor as a result of the imbalance of vaginal bacteria.
4. Poor Hygiene Practices: Inadequate hygiene practices, such as not washing the vaginal area properly or using harsh soaps or douches, can disrupt the natural balance of the vagina and contribute to an unpleasant odor.
Managing Vaginal Odor During Menopause
If you are experiencing vaginal odor during menopause, there are several steps you can take to manage it effectively:
1. Practice Good Hygiene: Proper hygiene is crucial for maintaining vaginal health. Clean the external genital area gently with warm water and a mild, unscented soap. Avoid using harsh soaps, douches, or perfumed products, as they can disrupt the natural pH balance of the vagina.
2. Stay Hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water helps keep the body hydrated, including the vaginal tissues. Staying hydrated can help prevent vaginal dryness and maintain the natural moisture of the vagina.
3. Wear Breathable Underwear: Opt for cotton underwear and avoid tight-fitting clothing. Cotton allows for better airflow and absorbs moisture, reducing the risk of bacterial overgrowth and odor.
4. Use Lubricants: If you are experiencing vaginal dryness, using water-based lubricants during sexual activity can help alleviate discomfort and reduce friction. Avoid using petroleum-based or scented lubricants, as they can cause irritation.
5. Maintain a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help support overall vaginal health. Avoid excessive consumption of sugary foods and drinks, as they can contribute to the growth of yeast and potentially worsen odor.
6. Consider Vaginal Moisturizers or Estrogen Therapy: If vaginal dryness is a persistent issue, you may consider using over-the-counter vaginal moisturizers or lubricants. In more severe cases, your healthcare provider may recommend low-dose estrogen therapy to help restore vaginal health.
7. Seek Medical Advice: If you are experiencing persistent or severe vaginal odor, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider. They can assess your symptoms, perform necessary tests, and provide appropriate treatment options tailored to your specific needs.
Tips for Freshness and Comfort
In addition to managing vaginal odor, here are some tips for maintaining freshness and comfort during menopause:
1. Change Tampons or Pads Regularly: If you use tampons or pads during menstruation, be sure to change them regularly to prevent bacterial overgrowth and odor.
2. Avoid Scented Products: Avoid using scented sanitary pads, tampons, or panty liners, as they can cause irritation and disrupt the natural balance of the vagina.
3. Practice Safe Sex: Engage in safe sexual practices to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), which can contribute to vaginal odor.
4. Consider Probiotics: Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help restore and maintain a healthy vaginal flora. Consider incorporating probiotic-rich foods or supplements into your diet with the guidance of your healthcare provider.
5. Stay Active: Regular physical activity can help improve blood circulation and promote overall vaginal health. Engage in activities such as walking, swimming, or yoga to maintain good blood flow to the pelvic area.
Experiencing vaginal odor during menopause can be bothersome and may affect a woman’s self-confidence and overall well-being. Understanding the causes of vaginal odor during menopause and implementing proper management strategies can help alleviate symptoms and promote vaginal health. Practice good hygiene, stay hydrated, wear breathable underwear, and consider using lubricants or vaginal moisturizers. If symptoms persist or worsen, consult with your healthcare provider for further evaluation and appropriate treatment options. Remember, vaginal odor is a common concern during menopause, and with proper care, you can maintain freshness and comfort throughout this transitional phase of life.
