Month: June 2024
How to Prevent Fibroids: A Comprehensive Guide

Fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyomas, are noncancerous growths that develop in the uterus. They are relatively common, affecting many women during their reproductive years. While the exact cause of fibroids is unknown, certain risk factors have been identified. Fortunately, there are steps you can take to help prevent the development and growth of fibroids. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide on how to prevent fibroids and promote uterine health.
Understanding Fibroids
Fibroids are benign tumors that develop within the muscular walls of the uterus. They can vary in size, from small, undetectable growths to large masses that distort the shape of the uterus. Fibroids are typically hormonally responsive, meaning they grow in response to estrogen and progesterone. Common symptoms of fibroids include heavy or prolonged menstrual periods, pelvic pain or pressure, frequent urination, and fertility issues.
Prevention Tips for Fibroids
While it is not possible to completely prevent the development of fibroids, certain lifestyle modifications and strategies may help reduce your risk or slow their growth. Consider the following tips for fibroid prevention:
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity has been linked to an increased risk of developing fibroids. Therefore, maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet can help reduce your risk.
2. Eat a Nutritious Diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can promote overall health and potentially lower the risk of fibroids. Incorporate foods with high levels of antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and nuts, which may have protective effects against fibroids.
3. Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption has been associated with an increased risk of fibroids. Limit your alcohol intake to moderate levels or avoid it altogether to promote uterine health.
4. Quit Smoking: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of fibroids and can also worsen fibroid symptoms. Quitting smoking is not only beneficial for fibroid prevention but also for overall health.
5. Manage Stress Levels: Chronic stress can negatively impact hormonal balance and contribute to various health issues, including fibroids. Incorporate stress management techniques into your daily routine, such as exercise, meditation, or engaging in hobbies.
6. Use Hormonal Birth Control: Some studies suggest that using hormonal birth control methods, such as oral contraceptives, may lower the risk of developing fibroids. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the most suitable birth control option for you.
7. Monitor Your Iron Levels: Heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids can lead to iron deficiency anemia. Regularly monitor your iron levels and consider iron-rich foods or supplements to prevent anemia.
8. Regular Gynecological Check-ups: Routine gynecological check-ups are important for early detection and monitoring of fibroids. Regular screenings can help identify any changes in the uterus and allow for prompt intervention if needed.
9. Consider Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Pregnancy and breastfeeding have been associated with a reduced risk of developing fibroids. Although the exact mechanisms are unclear, the hormonal changes that occur during these periods may have a protective effect.
10. Discuss Family History: If you have a family history of fibroids, inform your healthcare provider. Although you cannot change your genetics, knowing your risk factors can help guide preventive measures and early detection.
While it is not possible to completely prevent the development of fibroids, adopting a healthy lifestyle and following these prevention tips can help reduce your risk or slow their growth. Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a nutritious diet, limiting alcohol consumption, and managing stress levels are all important factors in promoting uterine health. Regular gynecological check-ups and discussions with your healthcare provider are crucial for early detection and intervention if necessary. By taking proactive steps, you can contribute to your overall well-being and potentially minimize the impact of fibroids on your life.
Female Obesity and Infertility: Understanding the Connection and Finding Solutions
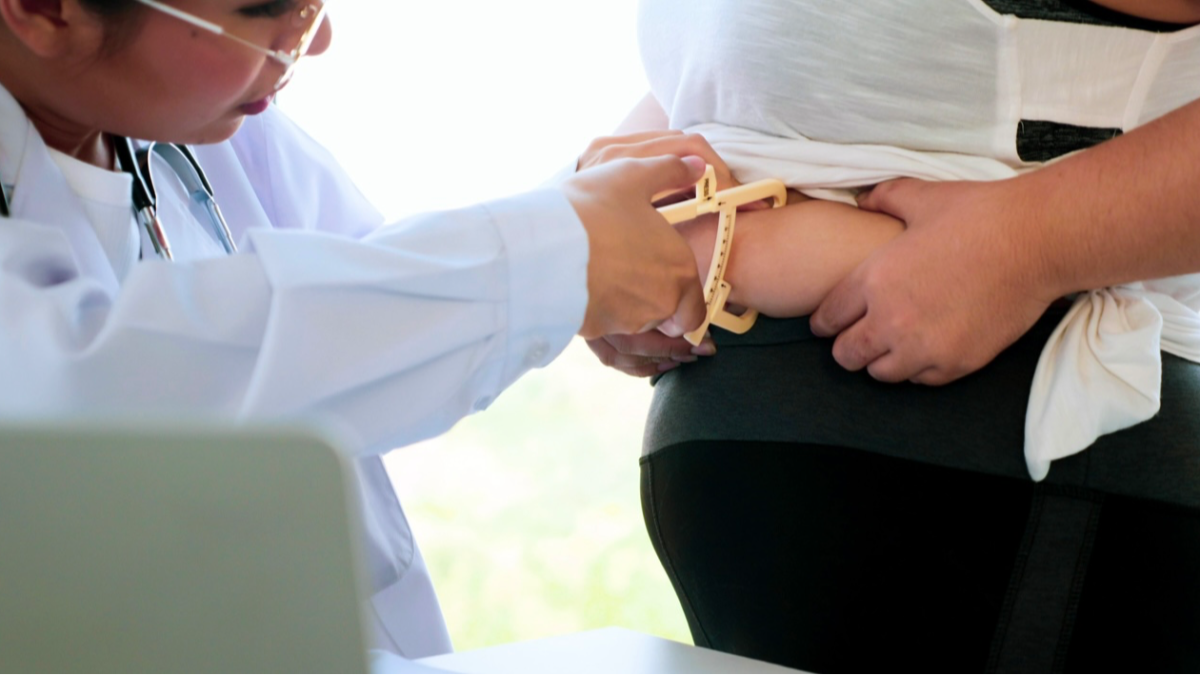
Obesity has become a global health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide. It is well-established that obesity is associated with various health complications, including an increased risk of infertility in women. The complex relationship between female obesity and infertility is multifaceted and can have a significant impact on a woman’s reproductive health. In this article, we will explore the connection between female obesity and infertility, as well as discuss potential solutions and treatment options.
Understanding Female Obesity and Infertility
Obesity is defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher. It is a condition characterized by excess body fat accumulation, often resulting from a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Obesity can lead to hormonal imbalances and metabolic disturbances that negatively affect reproductive health.
Impact of Female Obesity on Fertility
Female obesity can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance necessary for regular ovulation and menstrual cycles. It can lead to:
1. Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Obesity can cause hormonal imbalances, such as elevated levels of estrogen and insulin, which can disrupt the normal menstrual cycle. Irregular or absent menstrual periods make it more challenging to conceive.
2. Anovulation: Obesity is associated with an increased risk of anovulation, which is the absence of ovulation. Without ovulation, the release of a mature egg for fertilization does not occur, making it difficult to achieve pregnancy.
3. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is a common hormonal disorder characterized by enlarged ovaries with multiple small cysts. Obesity increases the risk of developing PCOS, which further contributes to infertility due to anovulation and hormonal imbalances.
4. Insulin Resistance: Obesity often leads to insulin resistance, a condition in which the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin. Insulin resistance can disrupt ovarian function and increase the risk of infertility.
5. Decreased Fertility Treatment Success: Obesity is associated with lower success rates in fertility treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF). It can affect the response to fertility medications, embryo implantation, and pregnancy outcomes.
Solutions for Female Obesity and Infertility
The good news is that addressing obesity can positively impact fertility outcomes for women. Here are some strategies and solutions to consider:
1. Weight Loss: Losing weight through a combination of a balanced diet and regular exercise can help improve fertility in obese women. Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% of body weight can have significant benefits. Consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to develop a personalized weight loss plan.
2. Healthy Diet: Adopting a healthy, balanced diet is essential for weight management and fertility. Focus on consuming whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and high-calorie snacks.
3. Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity helps promote weight loss, improve insulin sensitivity, and regulate hormonal levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise each week, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling.
4. Fertility-Friendly Supplements: Some supplements, such as folic acid, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamin D, may support fertility and reproductive health. However, always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplements.
5. Medical Intervention: In some cases, medical intervention may be necessary to address obesity-related infertility. Medications can be prescribed to regulate ovulation and hormonal imbalances. Bariatric surgery, in certain situations, may also be considered to promote weight loss and improve fertility outcomes.
6. Fertility Treatments: In cases where lifestyle changes alone are not sufficient, fertility treatments such as assisted reproductive technologies (ART) may be recommended. These treatments can help bypass certain obstacles caused by obesity and increase the chances of successful conception.
7. Emotional Support: Dealing with obesity-related infertility can be emotionally challenging. Seek support from healthcare professionals, support groups, or therapists specializing in reproductive health to address any emotional or psychological concerns.
Female obesity can have a significant impact on fertility and reproductive health. It disrupts hormonal balance, leads to irregular menstrual cycles, anovulation, and increases the risk of conditions like PCOS. However, by addressing obesity through weight loss, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and seeking appropriate medical intervention, it is possible to improve fertility outcomes. Consult with healthcare professionals specialized in reproductive health to develop a personalized plan that addresses both weight management and fertility goals. By taking proactive steps and seeking appropriate support, women can increase their chances of achieving a healthy pregnancy and fulfilling their dreams of starting a family.
Understanding Teenage Behavior: A Comprehensive Guide for Parents

The teenage years are a period of significant growth and development, both physically and emotionally. As parents, it can be challenging to navigate the complexities of teenage behavior and understand the underlying reasons behind their actions. However, gaining insight into teenage behavior is crucial for maintaining open communication, fostering healthy relationships, and supporting your teenager’s overall well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various aspects of teenage behavior, common challenges, and strategies for parents to navigate this transformative stage.
1. Hormonal Changes
During adolescence, teenagers experience significant hormonal changes as they enter puberty. These hormonal fluctuations can influence their behavior, emotions, and overall mood. It’s important for parents to recognize that mood swings, irritability, and emotional sensitivity are common during this time. By understanding the impact of hormonal changes, parents can approach their teenagers with empathy and patience.
2. Peer Influence
Peers play a crucial role in shaping teenage behavior. Teenagers seek acceptance, validation, and a sense of belonging among their peers. This desire for social connection can influence their choices, preferences, and behaviors. Parents should be aware of the influence of peer pressure and help their teenagers develop critical thinking skills, assertiveness, and the ability to make independent decisions.
3. Brain Development
The teenage brain is still undergoing significant development, particularly in the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for decision-making, impulse control, and emotional regulation. This ongoing brain development can contribute to impulsive behaviors, risk-taking, and difficulty considering long-term consequences. Parents can support their teenagers by providing guidance, setting clear boundaries, and helping them develop problem-solving and decision-making skills.
4. Emotional Roller Coaster
Teenagers often experience intense emotions, ranging from excitement and enthusiasm to sadness and anger. These emotional ups and downs can be overwhelming for both teenagers and their parents. Encouraging open communication, active listening, and validating their emotions can help teenagers navigate their feelings in a healthy way. Parents should avoid dismissing or minimizing their teenagers’ emotions, as this can hinder trust and communication.
5. Seeking Independence
Teenagers strive for independence and autonomy as they transition from childhood to adulthood. This desire for independence may manifest in behaviors such as questioning authority, asserting opinions, and seeking more freedom. Parents can support this developmental stage by gradually granting age-appropriate responsibilities, encouraging open dialogue, and fostering a sense of trust and mutual respect.
6. Risk-Taking Behaviors
Teenagers are more prone to engaging in risk-taking behaviors due to a combination of factors such as brain development, peer influence, and a desire for novelty and excitement. Risk-taking behaviors can include experimenting with substances, reckless driving, and engaging in unsafe sexual activities. Parents should establish clear expectations, provide education on potential risks, and maintain open lines of communication to help teenagers make informed choices and manage risks.
7. Digital and Social Media Influence
In today’s digital age, social media plays a significant role in teenagers’ lives. It can shape their self-esteem, body image, and social interactions. Parents should actively engage in conversations about responsible social media use, digital citizenship, and online safety. Encouraging a healthy balance between online and offline activities is crucial for maintaining overall well-being.
8. Mental Health Challenges
Teenagers may also face mental health challenges, such as anxiety, depression, and eating disorders. It’s essential for parents to be vigilant for signs of mental distress, including changes in behavior, mood, or academic performance. Creating a safe and non-judgmental environment for open discussions about mental health is vital. If concerns arise, seeking professional help from a mental health provider is recommended.
Understanding teenage behavior is key to fostering healthy relationships and supporting your teenager’s development. By recognizing the impact of hormonal changes, peer influence, brain development, and the need for independence, parents can navigate the challenges of the teenage years more effectively. Open communication, active listening, setting clear boundaries, and providing guidance are essential strategies for parents to guide their teenagers through this transformative stage. By fostering a supportive and nurturing environment, parents can help their teenagers navigate the complexities of adolescence and emerge as confident, resilient, and well-adjusted individuals.
What to Do with a Newborn: A Comprehensive Guide for New Parents

Welcoming a newborn into your life is an exciting and joyous experience. However, it can also be overwhelming, especially for first-time parents who may feel uncertain about how to care for their little one. From feeding and diaper changes to sleep routines and bonding, there’s a lot to consider when it comes to taking care of a newborn. In this comprehensive guide, we will provide essential tips and guidance on what to do with a newborn to ensure their health, happiness, and development.
Feeding Your Newborn
1. Breastfeeding: Breast milk is considered the best source of nutrition for newborns. It provides essential antibodies, enzymes, and nutrients that support healthy growth and development. Aim to breastfeed your baby every 2-3 hours, or whenever they show hunger cues, such as rooting or sucking on their fists. Seek support from a lactation consultant if needed to ensure a successful breastfeeding journey.
2. Formula Feeding: If breastfeeding is not an option or you choose to formula feed, opt for a commercially prepared infant formula. Follow the instructions on the formula packaging for preparation and feeding amounts. Formula-fed babies typically feed every 3-4 hours.
3. Burping: After feeding, make sure to burp your baby to release any trapped air. Gently hold your baby against your shoulder or sit them upright while supporting their head, and pat or rub their back until they burp.
Diaper Changing and Hygiene
1. Diaper Changing: Newborns require frequent diaper changes, as they typically soil their diapers 8-12 times a day. Keep your baby’s diaper area clean and dry to prevent diaper rash. Use gentle wipes or warm water and a soft cloth to clean their bottom, and apply a thin layer of diaper rash cream if needed.
2. Bathing: Until your baby’s umbilical cord stump falls off, give them sponge baths using warm water and a mild baby cleanser. Once the stump has healed, you can transition to gently bathing your baby in a baby tub or sink. Remember to support their head and neck at all times.
3. Nail Care: Newborns’ nails can be sharp and may accidentally scratch their delicate skin. Use baby nail clippers or a soft file to carefully trim or file their nails while they are calm or asleep.
Sleeping and Soothing Your Newborn
1. Safe Sleep Environment: Ensure that your baby’s sleep environment is safe. Place your baby on their back in a crib or bassinet with a firm mattress and a fitted sheet. Avoid using loose bedding, pillows, stuffed animals, or crib bumpers, as they can pose suffocation risks.
2. Establishing a Sleep Routine: Newborns sleep for varying durations, typically 14-17 hours a day, waking up for feeding and diaper changes. Help establish a sleep routine by creating a calm and quiet environment during nighttime sleep and engaging in soothing activities, such as gentle rocking or singing lullabies.
3. Soothing Techniques: Newborns may experience fussiness or crying, which is their way of communicating their needs. Try different soothing techniques, such as gentle swaying, cuddling, or using a pacifier, to comfort and calm your baby. Skin-to-skin contact and carrying your baby in a baby carrier can also provide a sense of security.
Bonding and Developmental Stimulation
1. Skin-to-Skin Contact: Engage in regular skin-to-skin contact with your newborn. This practice helps regulate their body temperature, promotes bonding, and encourages breastfeeding.
2. Eye Contact and Talking: Make eye contact with your baby and talk to them frequently. Your voice and facial expressions are reassuring and stimulating for their development.
3. Tummy Time: Place your baby on their tummy for short periods several times a day while they are awake and supervised. Tummy time helps strengthen their neck, shoulder, and arm muscles and supports their motor development.
4. Play and Exploration: As your baby grows, engage in age-appropriate play and exploration activities. Provide toys with different textures, colors, and sounds to stimulate their senses and encourage their cognitive development.
Seeking Support and Care for Yourself
1. Reach Out for Support: It’s normal to feel overwhelmed or anxious as a new parent. Reach out to family, friends, or support groups for guidance, reassurance, and practical help. Share your concerns with your healthcare provider if you’re experiencing postpartum depression or anxiety.
2. Self-Care: Taking care of yourself is crucial for your well-being and ability to care for your newborn. Get sufficient rest, eat nutritious meals, and engage in activities that bring you joy and relaxation.
Caring for a newborn is a joyful and rewarding experience. By following these essential tips, you can ensure your baby’s health, happiness, and development. Remember to prioritize feeding and diaper changes, establish a safe sleep routine, and engage in bonding activities. Seek support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends when needed, and don’t forget to care for yourself as you embark on this wonderful journey of parenthood. Enjoy the precious moments with your newborn and cherish the milestones as they grow and thrive.
Medicines for Menopause Symptoms: Finding Relief for a Smooth Transition

Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman’s reproductive years. While it is a normal part of life, the hormonal changes associated with menopause can lead to a variety of uncomfortable symptoms. Hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, and vaginal dryness are just a few examples of the challenges many women face during this transition. Thankfully, there are medicines available to help alleviate these symptoms and improve the overall quality of life during menopause. In this article, we will explore the different medicines commonly used to manage menopause symptoms and provide insights on finding relief for a smooth transition.
Understanding Menopause Symptoms
Menopause occurs when a woman’s ovaries stop producing eggs, leading to a decline in estrogen and progesterone levels. This hormonal shift can cause various physical and emotional symptoms, including:
1. Hot Flashes and Night Sweats: Sudden feelings of intense heat, often accompanied by excessive sweating and rapid heartbeat.
2. Mood Swings and Irritability: Fluctuating hormone levels can impact mood, leading to irritability, anxiety, and depression.
3. Vaginal Dryness and Discomfort: Decreased estrogen levels can result in vaginal dryness, itching, and discomfort during intercourse.
4. Sleep Problems: Hormonal changes can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to insomnia or difficulties staying asleep.
5. Bone Loss and Osteoporosis: Estrogen helps maintain bone density, so its decline during menopause increases the risk of bone loss and osteoporosis.
Medicines for Menopause Symptoms
1. Hormone Therapy (HT): Hormone therapy involves the use of estrogen alone or estrogen combined with progesterone (in women with a uterus) to alleviate menopause symptoms. It is available in various forms, including pills, patches, creams, gels, and vaginal rings. Hormone therapy can effectively reduce hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and other symptoms. However, it is not suitable for everyone and carries some risks, so it should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
2. Non-Hormonal Prescription Medications: Certain prescription medications can help manage specific menopause symptoms. For example:
a. Antidepressants: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are commonly prescribed to alleviate hot flashes and improve mood.
b. Gabapentin: Originally used to treat seizures, gabapentin has been found to reduce hot flashes in some women.
c. Clonidine: Originally used to treat high blood pressure, clonidine can help reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes.
These medications should be prescribed and monitored by a healthcare provider, as they may have potential side effects and drug interactions.
3. Vaginal Estrogen: Vaginal estrogen is available in creams, tablets, or rings and is used to alleviate vaginal dryness and discomfort. It delivers a low dose of estrogen directly to the vaginal tissues, helping to restore moisture and elasticity. Vaginal estrogen is generally safe and effective, but it’s important to discuss any concerns or medical history with a healthcare provider.
4. Over-the-Counter (OTC) Remedies: Some women find relief from menopause symptoms using OTC remedies. These include:
a. Lubricants and Moisturizers: Over-the-counter lubricants and vaginal moisturizers can help alleviate vaginal dryness and discomfort during intercourse.
b. Herbal Supplements: Certain herbal supplements, such as black cohosh and evening primrose oil, have been used to manage menopause symptoms. However, their effectiveness varies, and it’s important to discuss their use with a healthcare provider to ensure safety and avoid potential interactions with other medications.
Finding the Right Treatment Approach
When it comes to managing menopause symptoms, there is no one-size-fits-all approach. Every woman’s experience with menopause is unique, and treatment options should be tailored to individual needs and preferences. Here are some factors to consider when finding the right treatment approach:
1. Symptom Severity: The severity of menopause symptoms can vary greatly among women. Mild symptoms may be managed effectively with lifestyle changes and OTC remedies, while more severe symptoms may require prescription medications or hormone therapy.
2. Personal Health History: It’s important to consider personal health history, including factors such as breast cancer, heart disease, blood clots, and stroke. Certain medications or treatments may not be suitable for women with specific health conditions or risk factors.
3. Individual Preferences: Every woman has her own preferences and comfort level when it comes to treatment options. Some may prefer natural or non-hormonal remedies, while others may find relief through hormone therapy. Open and honest communication with a healthcare provider is key to finding the best approach for each individual.
Lifestyle Changes for Menopause Symptom Management
In addition to medications, making certain lifestyle changes can help manage menopause symptoms:
1. Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes, improve mood, and promote overall well-being. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
2. Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can support overall health and help manage menopause symptoms. Limiting caffeine and alcohol intake may also alleviate hot flashes and sleep disturbances.
3. Stress Management: High stress levels can exacerbate menopause symptoms. Explore stress management techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies and activities that bring joy and relaxation.
4. Dressing in Layers: Wearing lightweight, breathable clothing and dressing in layers can help manage body temperature fluctuations associated with hot flashes.
Menopause is a natural phase in a woman’s life, and while it may come with its fair share of challenges, there are medicines and treatment options available to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. From hormone therapy to non-hormonal prescription medications and OTC remedies, various approaches can be tailored to individual needs. Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, stress management, and dressing in layers, can complement medication use and further alleviate symptoms. It’s important for women experiencing menopause to have open and honest discussions with their healthcare provider to explore the best treatment approach and find the right balance for a smoother transition into this new phase of life.
Choosing the Sex of Your Baby: Exploring Methods and Considerations

The desire to choose the sex of a baby has been a topic of interest for many couples. While natural conception does not provide a guaranteed method for selecting the sex of a baby, there are various techniques and approaches that claim to offer a higher chance of conceiving a child of a specific sex. In this article, we will explore the methods of choosing the sex of your baby, discuss the scientific basis behind these methods, and highlight important considerations for couples contemplating this decision.
Methods of Choosing the Sex of Your Baby
1. Timing of Intercourse: One method of attempting to influence the sex of a baby is by timing intercourse in relation to the woman’s ovulation cycle. The Shettles Method suggests that having intercourse closer to ovulation may increase the chances of conceiving a boy, while having intercourse a few days before ovulation may increase the chances of conceiving a girl.
2. Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD): Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis is a technique used in conjunction with in vitro fertilization (IVF). It involves the selection and transfer of embryos of a desired sex based on their genetic characteristics. This method offers a higher degree of accuracy but is more invasive and costly.
3. Sperm Sorting: Sperm sorting techniques, such as MicroSort, involve separating sperm based on their chromosomal content. This method aims to increase the likelihood of conceiving a baby of a desired sex. However, the success rates and accuracy of sperm sorting techniques vary, and they are not widely available.
Scientific Basis and Considerations
1. Chromosomal Differences: The sex of a baby is determined by the combination of chromosomes received from both parents. Women have two X chromosomes (XX), while men have one X and one Y chromosome (XY). The sperm carries either an X or a Y chromosome, determining the sex of the baby.
2. Natural Variability: It is important to note that natural conception and reproductive processes involve natural variability. Even when following specific methods or timing intercourse, there is no guarantee of conceiving a baby of a desired sex. The chance of conceiving a baby of a specific sex is typically around 50% for each pregnancy.
3. Ethical Considerations: The desire to choose the sex of a baby raises ethical considerations. Some argue that it may reinforce gender stereotypes or lead to a preference for one sex over another, potentially leading to gender imbalance in certain societies. It is essential to consider the ethical implications and personal values when contemplating choosing the sex of a baby.
4. Emotional Preparedness: Choosing the sex of a baby should not overshadow the importance of a healthy and well-supported pregnancy. Couples should prioritize their emotional preparedness for parenting, regardless of the baby’s sex. It is crucial to embrace and nurture the child, regardless of whether they align with the desired sex.
Choosing the sex of a baby is a topic that intrigues many couples. While various methods and techniques claim to increase the chances of conceiving a baby of a specific sex, it is important to approach this topic with caution and realistic expectations. Natural conception does not provide a guaranteed method for selecting the sex of a baby, and the accuracy of alternative methods such as timing intercourse, preimplantation genetic diagnosis, or sperm sorting techniques may vary. Considering the scientific basis, ethical implications, and emotional preparedness are vital when contemplating choosing the sex of a baby. Ultimately, embracing and loving the child, regardless of their sex, is of utmost importance in building a strong and healthy family.
Sexuality After Hysterectomy: Exploring the Physical and Emotional Aspects

A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the uterus. It can be performed for various reasons, such as treating certain gynecological conditions or preventing the spread of certain diseases. While a hysterectomy can have significant health benefits, it also brings about changes in a woman’s body, including potential effects on her sexuality. Understanding and addressing the physical and emotional aspects of sexuality after a hysterectomy is crucial for women to maintain a healthy and fulfilling sex life. In this article, we will explore the impact of a hysterectomy on sexuality, discuss common concerns and challenges, and provide guidance for navigating this aspect of post-hysterectomy life.
Physical Changes and Challenges
1. Vaginal Dryness: Following a hysterectomy, some women may experience vaginal dryness. This can be attributed to hormonal changes, particularly a decrease in estrogen levels. Vaginal dryness can cause discomfort during sexual activity and may require the use of lubricants to enhance comfort and pleasure.
2. Loss of Libido: For some women, a hysterectomy may lead to a decrease in sexual desire or a temporary loss of libido. Hormonal changes, emotional factors, and physical discomfort can contribute to this change. It is important to communicate openly with your partner and healthcare provider to address any concerns and explore ways to regain sexual desire.
3. Changes in Orgasm: Some women may notice changes in their ability to achieve orgasm or changes in the intensity of orgasm after a hysterectomy. These changes can be influenced by hormonal factors, emotional well-being, and alterations in pelvic anatomy. Exploring different sexual techniques and communication with your partner can help navigate these changes and find new sources of pleasure.
4. Pelvic Floor Dysfunction: Following a hysterectomy, some women may experience pelvic floor dysfunction, which can manifest as urinary incontinence, pelvic pain, or discomfort during sexual activity. Pelvic floor exercises, also known as Kegel exercises, can help strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and improve these symptoms. Consult with a healthcare provider or a pelvic floor physical therapist for guidance on specific exercises.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
1. Body Image and Self-Esteem: A hysterectomy may bring about changes in body image and self-esteem. The removal of the uterus can lead to feelings of loss or a sense of femininity. It is important to address these emotions and seek support from loved ones, support groups, or mental health professionals to help navigate these changes and cultivate a positive body image.
2. Emotional Well-Being: Hormonal changes, physical discomfort, and the stress of undergoing surgery can impact emotional well-being. Feelings of sadness, anxiety, or a sense of loss are not uncommon after a hysterectomy. Openly discussing your emotions with a healthcare provider, counselor, or support group can help in coping with these feelings and promoting emotional well-being.
3. Communication with Partner: A hysterectomy can potentially affect intimate relationships. Open and honest communication with your partner about your concerns, desires, and physical changes is essential. Exploring new ways of intimacy, such as non-penetrative sexual activities or focusing on emotional connection, can help maintain a fulfilling and satisfying sex life.
Tips for Navigating Sexuality After Hysterectomy
1. Education and Open Communication: Educate yourself about the changes that may occur after a hysterectomy and discuss them openly with your healthcare provider, partner, or support groups. Understanding the physical and emotional aspects can help alleviate concerns and foster open communication.
2. Self-Exploration: Take time to explore your body and rediscover what brings you pleasure. This may involve self-pleasure or engaging in sexual activities with your partner. Experimenting with different techniques, positions, or incorporating sex toys can enhance sexual pleasure and build confidence.
3. Lubrication: Vaginal dryness can be managed with the use of water-based lubricants. Experiment with different brands and types of lubricants to find one that suits your needs and enhances comfort during sexual activity.
4. Pelvic Floor Exercises: Regularly practicing pelvic floor exercises can strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, improve blood flow to the pelvic area, and enhance sexual pleasure. Consult with a healthcare provider or a pelvic floor physical therapist for guidance on performing these exercises correctly.
5. Emotional Support: Seek emotional support from loved ones, support groups, or mental health professionals who can provide guidance and understanding during the post-hysterectomy period. Sharing your concerns and experiences with others who have gone through similar situations can be comforting and reassuring.
6. Professional Help: If you are experiencing significant emotional distress, difficulties in maintaining intimate relationships, or persistent physical challenges, consider seeking help from a therapist or counselor who specializes in sexual health or women’s health issues.
Sexuality after a hysterectomy can be influenced by both physical and emotional factors. Understanding the potential changes and challenges that may arise can help women navigate this aspect of their lives with confidence and resilience. By addressing concerns openly, seeking support from healthcare providers and loved ones, and exploring different techniques and strategies, women can maintain a healthy and fulfilling sex life after a hysterectomy. Remember, every woman’s experience is unique, and it is important to be patient and compassionate with yourself as you adapt to these changes.
Welcome to Sistapedia!! 🎉

Hi there! Here's how to create a video post 😍
Bloating During Pregnancy: Causes, Remedies, and Management

Pregnancy is a beautiful and transformative time in a woman’s life. However, along with the joy and anticipation, it can also bring about various physical discomforts. One common discomfort experienced by many pregnant women is bloating. Bloating during pregnancy is a result of hormonal changes, increased blood volume, and the growing uterus. While bloating can be uncomfortable, understanding the causes and implementing effective remedies and management strategies can help alleviate this symptom. In this article, we will explore the causes of bloating during pregnancy, discuss remedies for relief, and provide tips for managing bloating throughout this special journey.
Causes of Bloating During Pregnancy
1. Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy can affect digestion and slow down the movement of food through the digestive tract. This can lead to a build-up of gas and contribute to bloating.
2. Increased Progesterone: Progesterone, a hormone essential for maintaining pregnancy, can cause relaxation of the muscles in the digestive system. This relaxation can slow down digestion and contribute to bloating and discomfort.
3. Increased Blood Volume: During pregnancy, blood volume increases to support the growing baby. This can cause water retention and contribute to bloating.
4. Pressure on the Digestive Organs: As the uterus expands to accommodate the growing baby, it can put pressure on the digestive organs, such as the stomach and intestines. This pressure can lead to a feeling of fullness and bloating.
Remedies for Bloating Relief
1. Eat Small, Frequent Meals: Instead of consuming large meals, opt for smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day. This helps to prevent overloading the digestive system and promotes better digestion.
2. Avoid Trigger Foods: Identify and avoid foods that tend to cause bloating or discomfort. Common culprits include carbonated beverages, greasy or fried foods, spicy foods, and foods high in fiber. Pay attention to your body’s responses and adjust your diet accordingly.
3. Slow Down While Eating: Take your time to chew food thoroughly and eat at a slower pace. Eating too quickly can lead to swallowing air, which contributes to bloating.
4. Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help maintain proper hydration and promote healthy digestion. Avoid carbonated beverages and sugary drinks, as they can worsen bloating.
5. Exercise Regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity can help promote healthy digestion and alleviate bloating. Activities such as walking, swimming, or prenatal yoga can be beneficial. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine appropriate exercises for your specific stage of pregnancy.
6. Wear Comfortable Clothing: Opt for loose-fitting, comfortable clothing that doesn’t constrict your abdomen. Tight clothing can put pressure on the digestive organs and worsen bloating.
7. Probiotics: Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help improve digestion and reduce bloating. Consult with your healthcare provider about incorporating probiotic-rich foods or supplements into your diet.
Management Tips for Bloating During Pregnancy
1. Practice Good Posture: Maintaining good posture can help alleviate pressure on the digestive organs and promote healthy digestion. Sit or stand up straight, and avoid slouching.
2. Get Sufficient Fiber: While high-fiber foods can contribute to bloating, it is important to maintain a balanced intake of fiber. Choose fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Gradually increase your fiber intake to allow your body to adjust.
3. Relaxation Techniques: Stress and anxiety can contribute to bloating. Engaging in relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or prenatal yoga can help reduce stress levels and promote healthy digestion.
4. Consult with Your Healthcare Provider: If bloating becomes persistent, severe, or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider. They can evaluate your symptoms, rule out any underlying conditions, and provide appropriate guidance and support.
Bloating during pregnancy is a common discomfort experienced by many women. Understanding the causes and implementing effective remedies and management strategies can help alleviate bloating and promote a more comfortable pregnancy experience. By adopting healthy eating habits, staying hydrated, engaging in regular exercise, practicing good posture, and incorporating relaxation techniques, women can manage bloating and promote healthy digestion. Remember, each pregnancy is unique, and it is important to listen to your body, make adjustments as needed, and consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
How to Announce the Sex of a Baby in Different Religions: Celebrating with Cultural Sensitivity

The announcement of the sex of a baby is a joyous occasion that brings excitement and anticipation to expectant parents and their loved ones. In various religious and cultural traditions, the announcement of a baby’s sex holds special significance and is celebrated in unique ways. These customs and practices reflect the beliefs and values of different religions and provide an opportunity to honor and embrace cultural diversity. In this article, we will explore how to announce the sex of a baby in different religions, highlighting the traditions and practices that accompany these joyous announcements.
1. Christianity:
a. Baptismal Announcement: In Christian traditions, the announcement of the baby’s sex can be made during a baptismal ceremony. The parents may choose to reveal the sex of the baby during the baptism, incorporating prayers and blessings for the child’s future.
b. Church Announcement: Another common practice is to announce the baby’s sex during a church service. The parents may share the news with the congregation, who can then offer prayers and blessings for the baby and the family.
c. Dedication Ceremony: Some Christian families opt to announce the sex of the baby during a dedication ceremony. This is a special event where the parents publicly dedicate the child to God and seek the support and prayers of the community.
2. Islam:
a. Aqiqah Celebration: In Islamic tradition, the announcement of the baby’s sex can be made during the Aqiqah celebration. This is a joyous event that takes place a few days after the baby’s birth. The parents may reveal the baby’s sex while sharing a meal with family and friends, who offer prayers and blessings for the child’s well-being.
b. Mosque Announcement: Some Muslim families choose to announce the baby’s sex during a visit to the mosque. They may share the news with the congregation during a prayer gathering, where the community offers congratulations and prayers for the baby’s future.
c. Naming Ceremony: The announcement of the baby’s sex can be made during the naming ceremony, which typically takes place within a few days of the baby’s birth. The parents reveal the baby’s sex while choosing a name that holds significance in Islamic culture.
3. Hinduism:
a. Godh Bharai Ceremony: In Hindu tradition, the announcement of the baby’s sex can be made during the Godh Bharai ceremony. This is a baby shower-like celebration where the mother is showered with gifts and blessings. The parents may reveal the baby’s sex during the ceremony, and the event is filled with prayers, songs, and cultural rituals.
b. Puja and Prayer: Another common practice is to announce the baby’s sex during a puja (prayer) ceremony. The parents may invite family and friends to participate in the puja, where prayers and blessings are offered for the baby’s well-being and future.
c. Astrological Consultation: Some Hindu families consult astrologers to determine the baby’s sex and to seek guidance on auspicious dates and times for the announcement. The astrologer may conduct a horoscope reading and provide insights into the baby’s future based on the alignment of celestial bodies.
4. Judaism:
a. Brit Milah or Simchat Bat: In Jewish tradition, the announcement of the baby’s sex can be made during the Brit Milah (circumcision) for boys or the Simchat Bat (naming) for girls. These ceremonies typically take place within the first few weeks of the baby’s life. The parents may reveal the baby’s sex during the ceremony, which is filled with prayers, blessings, and joyful celebrations.
b. Synagogue Announcement: Some Jewish families choose to announce the baby’s sex during a visit to the synagogue. They may share the news with the congregation during a prayer service, where the community offers congratulations and prayers for the baby’s future.
c. Kiddush Celebration: The announcement of the baby’s sex can be made during a Kiddush celebration. This is a festive gathering held on Shabbat or other special occasions, where the parents reveal the baby’s sex while offering blessings and sharing the joyous news with family and friends.
Announcing the sex of a baby is an important milestone in the journey of parenthood, and it holds special significance in different religious traditions. By honoring and embracing cultural diversity, families can celebrate this joyful occasion with cultural sensitivity and respect. Whether through baptismal ceremonies, mosque visits, naming ceremonies, or synagogue gatherings, the announcement of the baby’s sex becomes a moment of shared joy, prayers, and blessings within the religious and cultural context. It is important to remember that each family’s traditions may vary, and it is essential to consult with religious leaders, family members, and community members for guidance and support in planning and executing these announcements. Ultimately, the announcement of a baby’s sex in different religions allows families to celebrate their faith, heritage, and the future of their child with love, gratitude, and cultural unity.
