Month: January 2025
Which Countries Test For Chromosomal Abnormalities and Why Is It Important?
In vitro fertilization (IVF) has revolutionized the world of fertility treatments, providing hope for millions of couples struggling with infertility. However, while IVF can help couples conceive, it also comes with its own set of challenges and risks. One of the significant concerns that arises is the risk of chromosomal abnormalities in embryos, which can lead to miscarriage, birth defects, or genetic disorders. To address this, many countries have incorporated advanced genetic testing methods into the IVF process, such as preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) for chromosomal abnormalities.
In this article, we will explore the countries that offer testing for chromosomal abnormalities in IVF, and discuss why this testing is essential in the journey toward successful and healthy pregnancies.
What Are Chromosomal Abnormalities in IVF?
Chromosomal abnormalities occur when there is a problem with the number or structure of chromosomes in the fertilized egg or embryo. Humans typically have 46 chromosomes, 23 pairs, and any deviation from this number can lead to conditions such as Down syndrome (trisomy 21), Turner syndrome, or other genetic disorders.
During IVF, embryos are created outside the body, and once the embryos are developed to a certain stage, they are evaluated for their quality. If chromosomal abnormalities are present, the embryo might be unable to implant properly or may result in a miscarriage or congenital defects.
Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) is a crucial process that can detect chromosomal abnormalities before embryos are implanted into the uterus. There are two main types of PGT:
1. PGT-A (Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidy): This test identifies embryos with abnormal chromosome numbers.
2. PGT-M (Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Monogenic Disorders): This test identifies specific genetic disorders caused by mutations in a single gene.
These tests provide valuable information for fertility specialists and prospective parents, allowing them to make informed decisions about which embryos to transfer and increase the chances of a healthy pregnancy.
Countries That Offer Chromosomal Abnormalities Testing in IVF
Chromosomal abnormalities testing in IVF is available in several countries, though the availability and regulations surrounding these tests can vary. Below are some of the countries that actively offer and support testing for chromosomal abnormalities during IVF.
1. United States
The United States is a leader in IVF treatments and genetic testing. Many fertility clinics in the U.S. offer Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidy (PGT-A) and Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Monogenic disorders (PGT-M) as part of the IVF process. PGT-A is commonly performed in many U.S. clinics to increase the chances of a successful pregnancy and reduce the risk of miscarriage.
The U.S. has fewer government regulations compared to other countries, which means that there is more freedom for IVF clinics to adopt advanced genetic testing technologies. However, insurance coverage for PGT-A or PGT-M may vary depending on the health plan, and many couples opt to pay out-of-pocket for these services.
2. United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, chromosomal abnormalities testing is widely available and supported by the National Health Service (NHS) for certain medical indications. For instance, women over a certain age or those with a family history of genetic disorders may be eligible for genetic testing under NHS guidelines.
Additionally, many private fertility clinics in the UK offer PGT-A as part of the IVF process, providing an option for couples who wish to enhance their chances of having a healthy child. While the NHS covers some aspects of IVF treatment, additional costs may be incurred for genetic testing, and some patients choose to go the private route for more comprehensive testing options.
3. Australia
Australia offers a range of fertility treatments, and genetic testing for chromosomal abnormalities is a standard part of the IVF process in many fertility clinics across the country. In fact, PGT-A is increasingly becoming a part of the routine IVF process to help reduce the risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
Australia has a well-regulated IVF industry, and fertility clinics follow strict guidelines set by the Reproductive Technology Accreditation Committee (RTAC). As in other countries, while IVF and PGT-A are available, insurance coverage for these services may vary, and many patients pay for the services privately.
4. Canada
In Canada, IVF clinics offer genetic testing, including PGT for aneuploidy and monogenic disorders. While there are fewer regulatory restrictions than in other countries, the Canadian healthcare system primarily provides IVF treatment through private clinics. As such, most couples seeking genetic testing as part of IVF must cover the costs themselves, unless they are part of a clinical trial or a study offering discounted or free services.
Canada’s healthcare system supports IVF treatments for medical indications, and preimplantation genetic testing is becoming more common in clinics that specialize in advanced reproductive technologies.
5. Spain
Spain has become one of the most popular destinations for IVF treatment, particularly among international patients. The country is known for its high-quality fertility clinics that offer a wide range of services, including PGT-A to detect chromosomal abnormalities in embryos.
The Spanish government has liberalized its laws regarding reproductive technologies, making it an attractive option for couples seeking IVF with genetic testing. PGT-A is widely offered, and clinics in Spain attract many international patients due to the availability of state-of-the-art technology, the relatively lower cost of treatment, and the country’s favorable legal stance on assisted reproduction.
6. Israel
Israel has one of the most advanced and successful IVF programs in the world. The country has a high rate of IVF success, and genetic testing, including for chromosomal abnormalities, is a standard practice. PGT-A is commonly used in Israeli fertility clinics to enhance pregnancy success and reduce the risk of genetic disorders.
Israel has strong regulations in place that govern IVF treatments, ensuring that couples receive high-quality care. In addition, fertility treatments are widely covered under Israel’s national health insurance system, making IVF with genetic testing more accessible to a larger portion of the population.
7. Germany
Germany offers preimplantation genetic testing in many IVF clinics, though the practice is subject to strict regulations. German law limits the scope of genetic testing to only certain conditions, but PGT-A is still a common practice for many couples undergoing IVF. The German healthcare system provides partial coverage for IVF, and additional testing costs may be paid privately.
Why Is Testing for Chromosomal Abnormalities Important?
Testing for chromosomal abnormalities in IVF is crucial for several reasons, and it provides benefits not only to the parents but also to the health of the future child.
1. Reduced Risk of Miscarriage
One of the primary reasons for genetic testing in IVF is to reduce the risk of miscarriage. Embryos with chromosomal abnormalities are more likely to result in early pregnancy loss. By identifying embryos with abnormal chromosomal counts, couples can avoid transferring embryos with a higher risk of miscarriage.
2. Increased Chances of a Healthy Pregnancy
PGT-A helps select embryos that are more likely to implant successfully and develop into a healthy pregnancy. By reducing the risk of chromosomal abnormalities, couples can increase their chances of having a healthy child, with fewer complications during pregnancy and birth.
3. Avoidance of Genetic Disorders
For couples with a family history of genetic disorders or known carrier status, PGT-M allows for the screening of embryos for specific genetic conditions. This can help avoid passing on severe genetic conditions, providing peace of mind for parents concerned about passing on a heritable disease.
4. Better Use of IVF Resources
IVF is a time-consuming and costly process, and it is essential to maximize the chances of a successful pregnancy. By testing embryos for chromosomal abnormalities, fertility specialists can recommend the healthiest embryos for transfer, thus making the best use of the available embryos and reducing the emotional and financial toll of multiple failed IVF attempts.
Final Thoughts
Chromosomal abnormalities testing in IVF is becoming a standard part of the process in many countries worldwide. Whether through preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A) or monogenic disorders (PGT-M), this testing plays an essential role in ensuring the health and success of IVF pregnancies. With advancements in genetic testing technology and the increasing number of countries offering these services, prospective parents now have the opportunity to make informed decisions and increase their chances of a successful, healthy pregnancy. Whether in the U.S., UK, Israel, or Australia, genetic testing offers a pathway to a safer and more reliable IVF journey for couples around the world.
Fatigue in Women Due to Perimenopause and Menopause Symptoms

Fatigue in women during perimenopause and menopause is not just ordinary tiredness but a result of complex hormonal changes. This is a natural phase in a woman’s life, typically occurring between the ages of 45 and 55, yet it brings unexpected physical and emotional health challenges. Why does this phase lead to fatigue? How can it be identified and managed? Let’s explore the details.
1. Perimenopause, Menopause, and Hormonal Changes
During perimenopause and menopause, ovarian function gradually declines, leading to a significant reduction in the production of essential hormones, especially estrogen and progesterone. These hormones play key roles in various physiological processes, particularly those related to the menstrual cycle, bone health, the nervous system, and blood circulation.
-
Estrogen Decline:
Reduced estrogen levels affect energy maintenance, sleep regulation, and psychological stability. This deficiency also increases the risk of osteoporosis and memory problems. -
Progesterone Decline:
Progesterone helps regulate sleep and reduce stress. Lower levels of this hormone often result in insomnia, anxiety, and prolonged fatigue.
2. Why Does Menopause Cause Fatigue?
Fatigue during perimenopause and menopause stems from simultaneous physiological and psychological changes. The following symptoms are the main causes of fatigue:
2.1. Sleep Disorders
Women during this stage often experience sleep issues, including difficulty falling asleep, waking up at night, or poor-quality sleep. The primary culprits are hot flashes and night sweats, which are common menopause symptoms.
- Consequences:
Poor sleep prevents the body from recovering energy, leading to prolonged tiredness and fatigue.
2.2. Anxiety and Psychological Stress
This phase is also accompanied by psychological changes such as anxiety, mild depression, or feelings of uncertainty. Hormonal imbalances affect not only physical health but also disrupt emotional regulation.
- Consequences:
Persistent emotional instability reduces motivation and increases feelings of exhaustion, making daily activities harder to manage.
2.3. Reduced Physical Stamina
Hormonal decline leads to a loss of muscle and bone density, decreasing the body’s endurance. Even light physical activities can become challenging, causing tiredness.
- Consequences:
The body is more prone to exhaustion, muscle aches, and slower recovery after exertion.
2.4. Changes in Circulation and Metabolism
Menopause can cause changes in the circulatory system, including higher risks of hypertension, lipid imbalances, and reduced blood flow.
- Consequences:
Lower oxygen and blood supply to organs result in fatigue and reduced energy levels.
3. Signs of Fatigue During Perimenopause and Menopause
Fatigue caused by menopause and perimenopause is not just about feeling tired but is often accompanied by other symptoms:
-
Persistent Tiredness:
Feeling drained even after adequate rest. -
Sleep Disorders:
Difficulty falling asleep, waking up frequently, or restless sleep. -
Reduced Concentration:
Forgetfulness and trouble focusing on work or daily activities. -
Muscle and Joint Pain:
Joint discomfort, muscle cramps, or stiffness. -
Emotional Instability:
Anxiety, irritability, mild depression, or unexplained sadness.
4. Is Fatigue During Menopause Dangerous?
Fatigue during perimenopause and menopause, if not addressed promptly, can lead to serious consequences:
-
Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases:
Osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic disorders. -
Impact on Quality of Life:
Women may feel imbalanced in managing work, family, and social relationships. -
Higher Risk of Depression:
Prolonged emotional instability can result in severe depression, negatively affecting mental and physical health.
5. How to Manage Fatigue During This Stage
To alleviate fatigue caused by perimenopause and menopause, women can adopt the following strategies:
5.1. Balance Hormones
Consult a doctor for hormone replacement therapy if necessary. Additionally, consuming foods rich in phytoestrogens, such as soybeans and flaxseeds, can help improve symptoms.
5.2. Maintain a Healthy Diet
- Increase calcium and vitamin D intake to support bone health.
- Eat plenty of vegetables, fruits, and fiber-rich foods to boost metabolism.
- Avoid fatty foods, sugary snacks, and stimulants.
5.3. Engage in Regular Physical Activity
- Opt for gentle exercises like yoga, walking, or swimming to enhance stamina.
- Regular exercise improves mood and promotes better sleep.
5.4. Manage Stress
Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or listening to calming music to reduce anxiety and stress.
5.5. Schedule Regular Health Check-Ups
Undergo periodic health screenings to detect early signs of menopause-related issues, especially cardiovascular disease and osteoporosis.
Conclusion
Fatigue in women during perimenopause and menopause is a natural consequence of complex hormonal and physiological changes. While this condition impacts health and quality of life, adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and seeking regular medical care can help women navigate this phase more easily and live a healthier, more fulfilling life.
Nguồn tham khảo
- Medicalnewstoday: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/menopause-fatigue#:~:text=Fatigue%20is%20a%20common%20experience,sleep%20quality%20and%20energy%20levels.
- Vpfw.com: https://vpfw.com/blog/perimenopause-and-fatigue-tips-for-boosting-your-energy-levels/
- Dược Bình Đông: https://www.binhdong.vn/cam-nang-suc-khoe/cac-dau-hieu-suy-nhuoc-co-the-va-huong-dieu-tri/
Menstrual Cramps: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Pain Relief

Menstrual cramps are a common issue experienced by many women during their menstrual cycle. The cramping pain in the lower abdomen can be uncomfortable and affect daily activities. This article provides detailed information about menstrual cramps, including causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and effective pain relief methods.
1. What are Menstrual Cramps?
Menstrual cramps (also known as dysmenorrhea) are lower abdominal pains that occur before, during, or after menstruation. The pain is often described as cramping, throbbing, or dull aching, and can radiate to the back and thighs. The intensity of pain varies from person to person, ranging from mild to severe, impacting daily life and work.
2. Types of Menstrual Cramps
There are two main types of menstrual cramps:
- Primary Dysmenorrhea: This is the most common type, usually starting within a few years after the first menstrual period. The pain is caused by excessive uterine contractions to shed the lining.
- Secondary Dysmenorrhea: This type is caused by underlying conditions affecting the reproductive organs, such as endometriosis, uterine fibroids, pelvic inflammatory disease, etc. The pain is often more severe and may last longer than primary dysmenorrhea.
3. Symptoms of Menstrual Cramps
Common symptoms of menstrual cramps include:
- Cramping or throbbing pain in the lower abdomen.
- Dull aching pain in the lower abdomen.
- Back pain.
- Pain radiating down the thighs.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Diarrhea or constipation.
- Headache, dizziness.
- Fatigue, irritability.
4. Causes of Menstrual Cramps
- Primary Dysmenorrhea:
- Prostaglandins: These chemicals are produced during menstruation, stimulating the uterus to contract more forcefully to expel the uterine lining. Higher levels of prostaglandins are associated with more severe pain.
- Secondary Dysmenorrhea:
- Endometriosis: The growth of endometrial tissue outside the uterus, causing pain and inflammation.
- Uterine Fibroids: Noncancerous growths in the uterus that can cause menstrual pain.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): Infection of the reproductive organs can cause pain.
- Cervical Stenosis: A narrow cervix can obstruct menstrual flow, leading to pain.
5. Diagnosis of Menstrual Cramps
The doctor will ask about medical history, symptoms, and perform a pelvic exam to diagnose menstrual cramps. In some cases, tests such as ultrasound, blood tests, or laparoscopy may be necessary to identify the cause of secondary dysmenorrhea.
6. Effective Ways to Relieve Menstrual Cramps
There are several ways to help relieve menstrual cramps, including:
- Home Remedies:
- Heat Therapy: Applying a heating pad or warm towel to the lower abdomen helps relax the uterine muscles and reduce pain.
- Warm Baths: Taking a warm bath has a similar effect to heat therapy.
- Gentle Massage: Gently massaging the lower abdomen in a clockwise motion can help relieve pain.
- Light Exercise: Light exercises like walking or yoga can improve blood circulation and reduce pain.
- Adequate Rest: Getting enough sleep and avoiding stress.
- Healthy Diet: Eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, caffeine, and alcohol.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers:
- Ibuprofen, Naproxen: These are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) that effectively reduce pain and inflammation. It is best to take them as soon as symptoms begin.
- Acetaminophen (Paracetamol): Also effective for pain relief but does not have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Birth Control Pills:
- Hormonal birth control pills can help regulate menstrual cycles and reduce menstrual cramps.
- Other Remedies:
- Acupuncture, Acupressure: May help reduce pain in some cases.
- Surgery: Only considered in cases of secondary dysmenorrhea due to severe underlying conditions and when other treatments are ineffective.
7. When to See a Doctor?
You should see a doctor if:
- The pain is severe and interferes with daily activities.
- Menstrual cramps are accompanied by other unuhttps://www.webmd.com/women/menstrual-crampssual symptoms such as fever, abnormal vaginal bleeding, or pain during intercourse.
- Home remedies are not effective.
8. Preventing Menstrual Cramps
While it's not always possible to completely prevent menstrual cramps, you can take steps to reduce the risk and severity of pain:
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Exercise regularly, eat a balanced diet, and get enough sleep.
- Manage stress.
- Avoid smoking.
Conclusion
Menstrual cramps are a common problem but can be managed with various methods. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and pain relief methods will help women cope with this condition effectively and improve their quality of life. If you have any concerns, consult a doctor for the best advice and treatment.
Nguồn
Mayoclinic.org: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/menstrual-cramps/symptoms-causes/syc-20374938
Medicalnewstoday: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/157333
Webmd: https://www.webmd.com/women/menstrual-cramps
Dược Bình Đông: https://www.binhdong.vn/cam-nang-suc-khoe/cach-giam-dau-bung-kinh-cho-phu-nu/
Menstrual Disorders: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
Menstrual disorders are a common health issue affecting many women, causing inconvenience and anxiety. Understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures for menstrual disorders is crucial for women to proactively manage their reproductive health. This article provides detailed and accurate information on this topic.
1. What are Menstrual Disorders?
Menstruation, also known as a period, is the monthly shedding of the uterine lining. A normal menstrual cycle lasts between 21 and 35 days, with an average of 28 days. The bleeding period usually lasts from 3 to 7 days.
Menstrual disorders occur when the menstrual cycle deviates from this normal pattern, including changes in:
- Cycle length: Too short (less than 21 days) or too long (more than 35 days).
- Menstrual flow: Too heavy (menorrhagia) or too light (hypomenorrhea).
- Duration of bleeding: Lasting longer than 7 days (prolonged menstrual bleeding) or shorter than 3 days.
- Accompanying symptoms: Severe menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea), bleeding between periods (metrorrhagia).
2. Common Types of Menstrual Disorders
- Oligomenorrhea: Infrequent or irregular menstrual periods with cycles longer than 35 days.
- Polymenorrhea: Frequent periods with cycles shorter than 21 days.
- Menorrhagia (Heavy Menstrual Bleeding): Abnormally heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding (more than 80ml or lasting longer than 7 days).
- Hypomenorrhea (Light Menstrual Bleeding): Unusually light menstrual bleeding (less than 30ml).
- Amenorrhea (Absence of Menstruation): The absence of menstrual periods for three or more consecutive months (secondary amenorrhea) or the failure to begin menstruating by age 16 (primary amenorrhea).
- Metrorrhagia (Intermenstrual Bleeding): Bleeding between periods.
- Dysmenorrhea (Painful Menstruation): Severe menstrual cramps or pain in the lower abdomen before, during, or after menstruation.
3. Causes of Menstrual Disorders
Menstrual disorders can result from various causes, including:
- Hormonal imbalances: Imbalances in estrogen and progesterone levels, often associated with puberty, perimenopause, or conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
- Gynecological conditions: Uterine fibroids, polyps, endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
- Lifestyle factors: Stress, sudden weight changes, unhealthy diet, excessive exercise, use of stimulants (alcohol, tobacco, drugs).
- Medication side effects: Certain medications, especially birth control pills, can affect the menstrual cycle.
4. Symptoms of Menstrual Disorders
- Changes in menstrual cycle length (too short, too long, or irregular).
- Changes in menstrual flow (too heavy or too light).
- Changes in the duration of bleeding (prolonged or shortened).
- Severe menstrual cramps.
- Bleeding between periods.
- Exacerbated premenstrual syndrome (PMS) symptoms, such as mood swings, headaches, breast tenderness.
5. Impact of Menstrual Disorders
Menstrual disorders can have significant impacts on:
- Reproductive health: Difficulty conceiving, increased risk of infertility.
- Overall health: Anemia due to heavy bleeding, negative effects on mental health and quality of life.
6. Diagnosis of Menstrual Disorders
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Taking a detailed medical history, including menstrual history, symptoms, and medical conditions.
- Performing a pelvic exam.
- Conducting necessary tests, such as blood tests (to check hormone levels), ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries.
7. Treatment of Menstrual Disorders
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Common treatment approaches include:
- Lifestyle changes: Maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, getting enough sleep.
- Medications: Birth control pills, hormone therapy, pain relievers, iron supplements.
- Treating underlying conditions: Addressing any underlying gynecological conditions contributing to the menstrual disorder.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be recommended to treat conditions like fibroids or endometriosis.
8. Prevention of Menstrual Disorders
While not all menstrual disorders can be prevented, certain measures can help reduce the risk:
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
- Maintaining a healthy weight.
- Managing stress effectively.
- Getting regular gynecological check-ups.
- Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol and stimulant use.
Summary
Menstrual disorders are a common concern for women. Understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention strategies is essential for maintaining reproductive health and overall well-being. If you experience any persistent or concerning changes in your menstrual cycle, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Nguồn
Dược Bình Đông: https://www.binhdong.vn/cam-nang-suc-khoe/roi-loan-kinh-nguyet-va-cach-dieu-tri-hieu-qua/
Mountsinai: https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/report/menstrual-disorders
Health Women: https://www.healthywomen.org/condition/menstrual-disorders
What Should Girls Eat During Their Period? Nutrition Tips for “That Time of the Month”
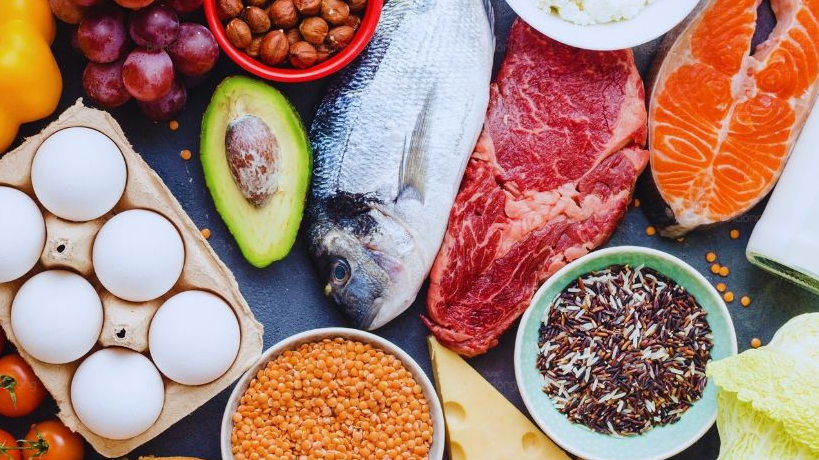

Menstruation is a natural part of every woman’s life. However, those “red days” often bring along unpleasant symptoms like cramps, fatigue, and mood swings. A proper diet plays a crucial role in alleviating these symptoms. So, what should girls eat during their period to stay comfortable and healthy? This article provides practical advice on nutrition for those days.
Why Is Diet Important During Your Period?
During menstruation, a woman’s body undergoes significant hormonal changes. These changes affect digestion, mood, and energy levels. A balanced and nutritious diet can help:
- Regulate hormones: Provide essential vitamins and minerals for hormone production.
- Relieve menstrual cramps: Certain foods help reduce inflammation and uterine contractions.
- Improve mood: Nutrients can influence brain activity, reducing stress and fatigue.
- Replenish lost blood: Iron and other nutrients support blood production and prevent anemia.
What Should Girls Eat During Their Period? A List of the Best Foods
Here’s a list of food groups recommended for girls during their period:
1. Fresh, Hydrating Fruits
- Benefits: Rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber, and hydration. Sweet fruits can also curb sugar cravings healthily.
- Suggestions: Watermelon, cantaloupe, oranges, apples, and bananas. Bananas are particularly great as they’re high in potassium, which helps reduce bloating and cramps. They also contain Vitamin B6, which improves mood.
2. Dark Leafy Greens
- Benefits: Packed with iron, vitamins, and fiber to replenish lost blood and improve digestion.
- Suggestions: Spinach, kale, broccoli.
3. Whole Grains
- Benefits: Provide sustained energy, rich in fiber to stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce cravings.
- Suggestions: Brown rice, oats, quinoa. Oats are also high in magnesium, which eases menstrual cramps.
4. Lean Proteins
- Benefits: Help repair cells, provide energy, and reduce fatigue.
- Suggestions: Chicken, fish (especially salmon rich in omega-3), eggs, and tofu. Omega-3s in salmon reduce inflammation and relieve cramps.
5. Nuts and Seeds
- Benefits: High in protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals that stabilize blood sugar and ease premenstrual symptoms.
- Suggestions: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and soybeans.
6. Yogurt
- Benefits: Contains calcium and probiotics that promote gut health and reduce bloating. Opt for unsweetened or low-sugar varieties.
7. Ginger
- Benefits: Has warming properties, reduces nausea and menstrual cramps. Can be consumed as fresh ginger tea or added to meals.
8. Dark Chocolate (70% Cocoa or More)
- Benefits: Rich in magnesium and antioxidants, which help relieve cramps and improve mood. Choose dark chocolate with at least 70% cocoa and enjoy in moderation.
9. Plenty of Water
- Benefits: Keeps the body hydrated, reduces bloating, and alleviates other discomforts. Aim to drink 2-3 liters of water daily.
Foods to Avoid During Your Period
In addition to eating the right foods, there are some you should limit or avoid during menstruation:
1. Salt
- Effect: Excessive salt can lead to water retention and bloating.
2. Sugar
- Effect: Too much sugar can cause mood swings and increase cravings.
3. Caffeine
- Effect: Caffeine may heighten stress, irritability, and disrupt sleep.
4. Alcohol
- Effect: Alcohol can worsen menstrual cramps and dehydrate the body.
5. Processed Foods
- Effect: Often high in salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats, which can exacerbate discomfort.
6. Spicy Foods
- Effect: May irritate the stomach and increase discomfort.
Meal Planning Tips for Your Period
- Eat smaller, frequent meals: Stabilize blood sugar and reduce bloating by eating multiple smaller meals throughout the day.
- Prioritize fresh foods: Limit processed or packaged foods.
- Listen to your body: Identify foods that make you feel better or worse and adjust your diet accordingly.
- Consult a professional: If you experience severe menstrual symptoms, speak with a doctor or nutritionist.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What should I do if I experience severe menstrual cramps?
If cramps are intense and interfere with daily life, consult a doctor for evaluation and treatment.
2. Is it okay to eat sour foods during menstruation?
Sour foods in moderation are generally fine and may even help reduce nausea. However, consuming too much can irritate the stomach.
Conclusion
Your diet plays a vital role in managing menstrual symptoms. By choosing nutritious foods and avoiding those that may worsen discomfort, you can improve your overall well-being during your period. We hope this article helps you better understand what to eat during your period for a healthier, more comfortable experience!
Nguon
Dược Bình Đông: https://www.binhdong.vn/cam-nang-suc-khoe/con-gai-den-thang-nen-lam-gi/
Aditya Birla capital: https://www.adityabirlacapital.com/healthinsurance/active-together/2022/03/11/5-foods-to-eat-and-avoid-during-your-menstrual-cycle/
Epsomdining4u.nz: https://www.epsomdining4u.nz/nutrition-needs-and-the-menstrual-cycle
Menstrual Clots: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention
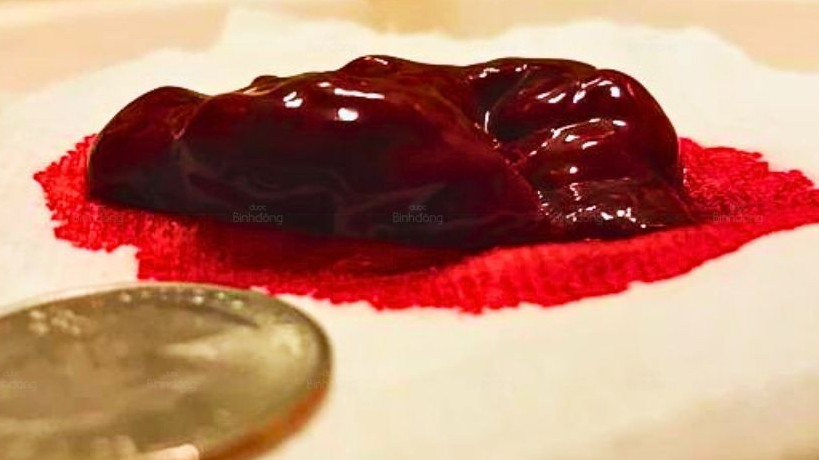

Menstrual clots are a common phenomenon in many women. This article by Binh Dong Pharmacy will provide detailed information about the causes, symptoms, treatment and effective prevention of menstrual clots.
1. What are menstrual clots?
Menstrual clots are a condition in which menstrual blood is not in liquid form but coagulates into clots of different sizes. These clots are a mixture of blood, uterine lining tissue and clotting proteins. This phenomenon often occurs in the early days of the menstrual cycle, when the amount of menstrual blood is the highest. Menstrual clots can make many women worry, but they are not always a sign of a serious illness.
2. Distinguishing between normal and abnormal menstrual clots
Menstrual clots are not always a worrying sign. It is important to distinguish between normal and abnormal menstrual clots:
Size of the blood clot: Small blood clots (less than 1cm) and infrequent (only on the first day of the cycle) are usually normal. If the blood clots are large (over 2.5cm) and occur frequently, you should see a doctor.
Frequency of occurrence: If menstrual clots only appear on the first days of the cycle, when the menstrual flow is heavy, it is usually not a cause for concern. However, if they last throughout the cycle or appear between periods, it may be a sign of abnormality.
Accompanying symptoms: If menstrual clots are accompanied by symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, menorrhagia (menstruation lasting more than 7 days), anemia (fatigue, dizziness, lightheadedness), you should see a doctor immediately.
3. Causes of menstrual clots
There are many causes of menstrual clots, including:
Natural blood clotting mechanism: During menstruation, the body will produce anticoagulants to prevent excessive blood loss. However, when the amount of menstrual blood is too much, these substances do not have enough time to work effectively, leading to blood clotting. This is the most common cause and is usually not a cause for concern.
Hormonal disorders: An imbalance of estrogen and progesterone hormones can affect the uterine lining and blood clotting, causing menstrual clots.
Uterine fibroids: Uterine fibroids are benign tumors that develop in the uterus. They can change the shape of the uterus and affect uterine contractions, making it difficult for menstrual blood to exit and easy to clot.
Uterine polyps: Uterine polyps are small tumors that develop on the uterine lining. They can cause menorrhagia and menstrual clots.
Endometriosis: Endometriosis is a condition in which the cells lining the uterus grow outside the uterus. It can cause severe menstrual cramps and menstrual clots.
Blood clotting disorders: Some blood disorders can affect blood clotting and cause menstrual clots.
Medication use: Some medications, such as anticoagulants, can affect menstruation.
Early miscarriage: In some cases, menstrual clots can be a sign of early miscarriage.
4. Symptoms of menstrual clots
The main symptom of menstrual clots is the presence of blood clots in the menstrual blood. The size and number of blood clots can vary from person to person. Other symptoms that may accompany them include:
Severe menstrual cramps.
Menorrhagia (menstruation lasting more than 7 days).
Heavy menstrual bleeding (changing sanitary napkins frequently).
Anemia (fatigue, dizziness, lightheadedness).
5. Are menstrual clots dangerous?
In most cases, menstrual clots are normal and not dangerous. However, if you experience the unusual symptoms mentioned above, you should see a doctor for timely diagnosis and treatment.
6. Diagnosis of menstrual clots
To diagnose the cause of menstrual clots, your doctor may ask you about your medical history, menstrual cycle, and symptoms you experience. Your doctor may also perform the following tests:
Gynecological examination.
Uterine ultrasound.
Blood test.
7. Treatment of menstrual clots
Treatment of menstrual clots depends on the cause. Some treatments include:
Pain relievers: To relieve menstrual cramps.
Birth control pills: To regulate hormones and reduce menstrual blood flow.
Hemostatic drugs: To reduce menstrual blood flow.
Surgery: In cases where uterine fibroids, uterine polyps, or endometriosis cause severe menstrual clots, your doctor may recommend surgery.
8. How to prevent menstrual clots
Some measures that can help prevent menstrual clots include:
Healthy diet: Supplement adequate nutrients, especially iron and vitamins.
Regular exercise: Helps improve blood circulation and reduce menstrual cramps.
Reduce stress: Stress can affect hormones and cause menstrual disorders.
Regular gynecological examinations: Helps detect health problems early.
Conclusion
Menstrual clots are common and are usually not a cause for concern. However, if you experience unusual symptoms, you should see a doctor for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Binh Dong Pharmaceutical Company (Bidophar) Information
Here is the contact information for Binh Dong Pharmaceutical Company (Bidophar)
- Address: 43/9 Me Coc Street, Ward 15, District 8, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
- Showroom: 22 Street No. 10, Ward 11, District 6, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
- Hotline: 028.39.808.808
- Suppliers: 028.66.800.300
- Business Department: 028.66.800.100 – 028.66.800.200
- Email: [email protected]
References:
Dược Bình Đông: https://www.binhdong.vn/cam-nang-suc-khoe/cach-dieu-tri-hien-tuong-kinh-von-cuc/
Health: https://www.healthline.com/health/womens-health/menstrual-clots
Advancedgynecology: https://www.advancedgynecology.com/blog/7-potential-causes-for-large-blood-clots-during-your-period
Thin Menstrual Period (Hypomenorrhea): Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment

"Ms. Nguyen Thi Thuy Trang, a Traditional Medicine Practitioner with over 30 years of experience specializing in women's health and gynecological issues, serves as an advisor at Binh Dong Pharmaceutical."
A regular menstrual period is a key indicator of a woman's reproductive health. However, changes in menstrual flow, such as a significantly lighter period, can be a cause for concern. This article provides comprehensive information about thin menstrual periods, also known as hypomenorrhea, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
1. What is a Thin Menstrual Period (Hypomenorrhea)?
Hypomenorrhea refers to abnormally light or scanty menstrual bleeding. It is characterized by a reduced amount of menstrual flow (less than 80ml per cycle) and/or a shorter duration of bleeding (less than 3 days). This is in contrast to menorrhagia (heavy menstrual bleeding) or metrorrhagia (bleeding between periods).
2. Causes of Thin Menstrual Periods
Several factors can contribute to thin menstrual periods:
- Hormonal Imbalance: This is the most common cause. Imbalances in estrogen and progesterone levels can affect the uterine lining (endometrium), leading to lighter bleeding.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is a hormonal disorder that affects the ovaries and can disrupt ovulation, leading to irregular or light periods.
- Low Body Weight/Malnutrition: Insufficient body weight or nutritional deficiencies can disrupt hormone production and menstrual cycles.
- Excessive Exercise: Strenuous physical activity can sometimes interfere with hormone regulation and lead to lighter periods.
- Stress: High levels of stress can affect the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian (HPO) axis, which regulates the menstrual cycle.
- Thyroid Disorders: Both hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can affect menstrual patterns.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, such as hormonal birth control, antidepressants, and antipsychotics, can cause lighter periods as a side effect.
- Uterine Scarring (Asherman's Syndrome): Scar tissue within the uterus can reduce the amount of endometrial lining available to shed, leading to lighter periods. This can be caused by procedures like dilation and curettage (D&C).
- Perimenopause: As women approach menopause, hormonal fluctuations are common, which can result in irregular and lighter periods.
- Breastfeeding: Hormonal changes during breastfeeding can suppress ovulation and lead to lighter or absent periods.
3. Symptoms of Thin Menstrual Periods
The primary symptom is a significantly reduced amount of menstrual flow compared to what is normal for the individual. Other potential symptoms include:
- Shorter duration of bleeding (less than 3 days).
- Spotting instead of a normal flow.
- Changes in the color of menstrual blood (lighter pink or brownish).
- Irregular menstrual cycles.
4. Diagnosis of Thin Menstrual Periods
A doctor will typically take a detailed medical history, including menstrual cycle patterns, and perform a physical examination. They may also recommend the following tests:
- Blood Tests: To check hormone levels (FSH, LH, estrogen, progesterone, thyroid hormones).
- Pelvic Ultrasound: To examine the uterus and ovaries for any abnormalities.
- Endometrial Biopsy: To examine the uterine lining.
5. Treatment of Thin Menstrual Periods:
Treatment depends on the underlying causes
- Hormonal Therapy: If hormonal imbalances are the cause, hormone replacement therapy or hormonal birth control may be prescribed.
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and getting regular exercise can help regulate menstrual cycles.
- Treatment of Underlying Conditions: If a medical condition like PCOS or a thyroid disorder is identified, treatment for that condition will be necessary.
- Surgery (in rare cases): In cases of Asherman's syndrome, surgery may be needed to remove scar tissue.
6. Prevention of Thin Menstrual Periods:
While not all causes of thin periods are preventable, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to regular menstrual cycles:
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques or exercise.
- Eat a balanced diet.
- Engage in regular, moderate exercise.
- Get regular medical check-ups.
When to See a Doctor:
It is important to consult a doctor if you experience:
- A sudden or significant change in your menstrual flow.
- Periods that become consistently lighter.
- Periods that stop altogether (amenorrhea).
- Other symptoms such as pelvic pain, heavy bleeding between periods, or unusual vaginal discharge.
Binh Dong Pharmaceutical Company (Bidophar) Information
Here is the contact information for Binh Dong Pharmaceutical Company (Bidophar)
- Address: 43/9 Me Coc Street, Ward 15, District 8, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
- Showroom: 22 Street No. 10, Ward 11, District 6, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
- Hotline: 028.39.808.808
- Suppliers: 028.66.800.300
- Business Department: 028.66.800.100 – 028.66.800.200
- Email: [email protected]
Conclusion:
Thin menstrual periods can be a symptom of various underlying conditions. It's crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment to ensure your reproductive health and overall well-being. Early detection and intervention can help prevent potential complications.
References
- Dược Bình Đông: https://www.binhdong.vn/cam-nang-suc-khoe/cach-dieu-tri-trieu-chung-mau-kinh-loang/
- Medicalnewstoday.com: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/322935
- Healthline: https://www.healthline.com/health/womens-health/why-is-my-period-so-light
“Discover the Miraculous Benefits of Surrogacy for Parents”

Surrogacy: A Life-Changing Journey Bringing Miracles to Aspiring Parents
In today’s fast-paced world, the beauty of surrogacy is unfolding as a miraculous solution for aspiring parents yearning to the joy of parenthood. Surrogacy offers a glimmer of hope, a ray of light, and a profound opportunity for couples facing fertility challenges. This article will delve into the mesmerizing world of surrogacy, exploring numerous benefits of surrogacy and why it has become a beacon of hope for parents-to-be worldwide.
1. Embracing the Miracle of Surrogacy
Surrogacy is an extraordinary process where a compassionate woman selflessly carries and nurtures a child for another couple or individual. It is a journey that defies limits, transcending biological barriers, and offering a pathway to parenthood where all hope seemed lost. The willingness of surrogate mothers to help create families is truly awe-inspiring, making surrogacy a remarkable and life-changing experience.
2. A Solution for Fertility Challenges
For couples grappling with infertility issues, surrogacy provides a glimmer of hope. Whether it is due to medical conditions, genetic concerns, or other factors, surrogacy allows individuals to overcome these obstacles and fulfill their dreams of becoming parents. With the advancements in reproductive technology, surrogacy has become a viable option for couples who may have once felt defeated by their circumstances.
3. Tailored to Individual Needs
One of the significant advantages of surrogacy is its versatility. It caters to various situations, offering both traditional and gestational surrogacy options. In traditional surrogacy, the surrogate mother uses her own eggs, while gestational surrogacy involves the use of assisted reproductive technologies, where the embryo is created using the intended parents’ genetic material. This flexibility ensures that aspiring parents can choose the surrogacy method that aligns best with their preferences and needs.
4. Emotional Support and Guidance
Surrogacy agencies and professionals play a vital role in supporting aspiring parents throughout their surrogacy journey. These experts provide emotional support, guidance, and legal assistance, ensuring a smooth and transparent process. From matching intended parents with suitable surrogates to navigating legal complexities, their expertise eases the emotional burden and provides a solid foundation for a successful surrogacy experience.
5. Global Accessibility
Surrogacy is no longer confined to a few countries or regions. Thanks to globalization and increasing awareness, aspiring parents can explore surrogacy options worldwide. Countries like the United States, Ukraine, and Canada have gained recognition for their well-regulated and supportive surrogacy programs. This global accessibility broadens the horizons for individuals seeking surrogacy as a viable solution, offering them the chance to embark on this life-changing journey.
Surrogacy is undeniably a miraculous and awe-inspiring avenue for parents-to-be. It brings hope, joy, and fulfillment to those who have faced fertility challenges. With its countless benefits, surrogacy provides a beacon of light, offering individuals the opportunity to experience the miracle of parenthood. Whether it’s the bond between intended parents and surrogate mothers or the emotional support provided by surrogacy professionals, this journey is a testament to the resilience and compassion of humanity. Surrogacy truly stands as a transformative option, bringing miracles to aspiring parents worldwide.
Si Wu Tang (Four-Substance Decoction): A Time-Honored Herbal Formula for Women’s Health and Beyond

In the realm of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), Si Wu Tang, also known as Four-Substance Decoction, stands as a cornerstone formula revered for its blood-nourishing and blood-regulating properties. This classic herbal blend, with a history spanning centuries, has been traditionally used to address a wide range of health concerns, particularly those related to women's health. This comprehensive article delves into the composition, benefits, applications, and important considerations of Si Wu Tang, offering valuable insights for both practitioners and those interested in exploring natural approaches to wellness.
Consultant: Herbalist Nguyen Thi Thuy Trang
1. What is Si Wu Tang? The Four Precious Herbs
Si Wu Tang is comprised of four fundamental herbs, each playing a crucial role in the formula's therapeutic effects:
- Shu Di Huang (熟地黃, Prepared Rehmannia Root): This chief herb powerfully nourishes the blood, replenishes Kidney essence (Jing), and benefits Yin. It is processed to enhance its blood-tonifying properties.
- Dang Gui (當歸, Angelica Sinensis Root): Known as the "female ginseng," Dang Gui invigorates and harmonizes the blood, regulates menstruation, and alleviates pain. It is often used to address blood deficiency and blood stasis.
- Bai Shao (白芍, White Peony Root): Bai Shao nourishes the blood, softens the Liver, and alleviates pain caused by muscle spasms or contractions. It also helps to calm the Liver Yang and soothe emotions.
- Chuan Xiong (川芎, Sichuan Lovage Rhizome): This herb invigorates blood circulation, promotes the movement of Qi (vital energy), and alleviates pain, especially headaches. It is considered an important herb for gynecological conditions.
The synergistic combination of these four herbs, working in harmony according to the principles of TCM, makes Si Wu Tang a potent remedy.
2. The Therapeutic Benefits of Si Wu Tang
Si Wu Tang offers a wide range of therapeutic benefits, primarily focusing on addressing blood-related imbalances:
- Menstrual Irregularities: This formula is highly regarded for regulating menstruation, easing menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea), reducing heavy bleeding, and addressing amenorrhea (absence of menstruation). It helps to establish a healthy and regular menstrual cycle.
- Blood Deficiency: Si Wu Tang effectively replenishes blood deficiency, which can manifest as fatigue, dizziness, pale complexion, palpitations, insomnia, and poor memory. It nourishes and strengthens the blood, improving overall vitality.
- Postpartum Recovery: After childbirth, women often experience blood loss and Qi deficiency. Si Wu Tang can aid in postpartum recovery by replenishing blood, promoting uterine contractions, and alleviating postpartum pain.
- Anemia: By tonifying and enriching the blood, Si Wu Tang can be beneficial for individuals with anemia, helping to increase red blood cell production and improve oxygen delivery to tissues.
- Skin Health: In TCM, healthy blood is essential for radiant skin. Si Wu Tang can improve skin complexion, reduce dryness, and promote a healthy glow by nourishing the blood and improving circulation.
- Headaches: Chuan Xiong's blood-invigorating properties make Si Wu Tang useful in alleviating headaches, particularly those associated with blood stasis or blood deficiency.
- Other Applications: Si Wu Tang has also been used in conjunction with other herbs to address conditions such as infertility, endometriosis, and certain types of joint pain.
3. Si Wu Tang in Modern Research
Modern pharmacological studies have provided some scientific support for the traditional uses of Si Wu Tang. Research has indicated that the formula possesses the following properties:
- Hematopoietic Effects: Studies have shown that Si Wu Tang can stimulate the production of red blood cells and improve blood parameters, supporting its traditional use for anemia.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Some research suggests that Si Wu Tang exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, which may contribute to its pain-relieving effects.
- Antioxidant Effects: The herbs in Si Wu Tang contain antioxidants that can help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
- Regulation of Hormones: Studies have explored the effects of Si Wu Tang on hormone regulation, particularly in relation to estrogen levels, which may explain its benefits for menstrual irregularities.
While these studies offer promising insights, further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms of action and clinical applications of Si Wu Tang.
4. How to Use Si Wu Tang and Important Considerations
- Traditional Preparation: Traditionally, Si Wu Tang is prepared as a decoction by simmering the four herbs in water for a specific period of time. The dosage and preparation method may vary depending on the individual's condition and the practitioner's recommendations.
- Modified Formulas: TCM practitioners often modify the basic Si Wu Tang formula by adding or subtracting herbs to address specific symptoms or underlying imbalances.
- Consult a Practitioner: It is crucial to consult with a qualified TCM practitioner before using Si Wu Tang. They can assess your individual condition and recommend the appropriate dosage and formulation.
- Contraindications and Precautions: Si Wu Tang is generally considered safe for most individuals when used under the guidance of a practitioner. However, it is contraindicated for individuals with certain conditions, such as bleeding disorders or during menstruation with heavy bleeding. Pregnant women should use it with caution and only under the supervision of a qualified practitioner.
- Quality of Herbs: The quality of the herbs used in Si Wu Tang is essential for its effectiveness. It is important to source herbs from reputable suppliers.
5. Si Wu Tang in Modern Products
Today, Si Wu Tang is not only used in traditional decoctions but is also incorporated into various modern products, such as capsules, tablets, and granules. These products offer a convenient way to consume the herbal formula. However, it is important to choose products from reputable manufacturers that adhere to strict quality control standards. Always consult with a healthcare professional before using any herbal supplements.
Conclusion
Si Wu Tang is a valuable herbal formula in TCM, offering a natural approach to addressing blood-related imbalances and promoting women's health. While modern research provides some scientific backing for its traditional uses, consulting with a qualified TCM practitioner is crucial for safe and effective use. By understanding the composition, benefits, and important considerations of Si Wu Tang, individuals can make informed decisions about incorporating this time-honored remedy into their wellness journey.
Nguồn tham khảo:
1. Duoc binh dong: https://www.binhdong.vn/cam-nang-suc-khoe/cac-bai-thuoc-tu-vat-thang/
2. Đông dược Phúc Hưng: https://phuchung.vn/detail/tu-vat-thang-bo-huyet-thanh-duoc.html
3. Duocphamtw3: https://duocphamtw3.com/tu-vat-thang-bai-thuoc-bo-huyet-dieu-kinh-cho-phu-nu/
Nóng Trong Người Ở Phụ Nữ: Nguyên Nhân, Triệu Chứng Và Cách Khắc Phục
Lương y Nguyễn Thị Thuỳ Trang, cố vấn Dược Bình Đông, chuyên gia y học cổ truyền với hơn 30 năm kinh nghiệm, chuyên về sức khỏe phụ nữ và các vấn đề phụ khoa.
Nóng trong người, hay còn gọi là nội nhiệt, là một trạng thái khó chịu mà nhiều phụ nữ phải đối mặt. Nó không chỉ đơn thuần là cảm giác nóng bức mà còn có thể là dấu hiệu của những vấn đề sức khỏe tiềm ẩn. Bài viết này sẽ cung cấp một cái nhìn chuyên sâu và toàn diện về độ nóng cho người ở phụ nữ, từ nguyên nhân, triệu chứng, ảnh hưởng đến sức khỏe và các biện pháp khắc phục hiệu quả.
1. Định Nghĩa Nóng Trong Người Ở Phụ Nữ
Nóng trong người là cảm giác nhiệt độ tăng cao hơn bình thường, xuất phát từ bên trong cơ thể, không liên quan trực tiếp đến môi trường nhiệt độ. Phụ nữ bị nóng trong người thường cảm thấy nóng hứng, bức bối, khó chịu, thậm chí chí là bức rứt, ngay cả khi tiết mát mẻ. Khác với bệnh nhiễm trùng nhiễm trùng, người thường không kèm theo các triệu chứng lạnh, ung thư cơ bản.
2. Các Nguyên Nhân Chính Gay Hot Trong Người Ở Phụ Nữ
Phổ biến ở phụ nữ có thể làm nhiều nguyên nhân, được chia thành các nhóm chính sau:
- Chăm sóc nội tiết tố: Đây là nguyên nhân phổ biến nhất, đặc biệt liên quan đến sự biến đổi của hormone estrogen và progesterone.
- Giai đoạn tiền mãn kinh và mãn kinh: Sự suy giảm estrogen là nguyên nhân chính gây ra các cơn bốc lửa, nóng bừng mặt, đổ mồ hôi đêm.
- Chu kỳ kinh nguyệt: Sự thay đổi nồng độ hormone trong các giai đoạn của chu kỳ kinh nguyệt cũng có thể gây nóng trong người.
- Thời kỳ mang thai: Sự tăng cường hormone trong thai kỳ là một trong những nguyên nhân tạo phụ nữ mang thai cảm thấy nóng hơn bình thường.
- Sử dụng thuốc tránh thai: Một số loại thuốc tránh thai có thể gây tác dụng phụ gây nóng cho người.
- Chế độ ăn uống và sinh hoạt:
- Tiêu thụ thực phẩm cay nóng, nhiều dầu mỡ: Các loại thực phẩm này làm tăng quá trình trao đổi chất, sinh nhiệt trong cơ thể.
- Sử dụng chất kích thích: Rượu, bia, cà phê có thể kích thích hệ thần kinh và làm tăng cảm giác nóng.
- Thói quen quen sinh hoạt không điều hòa: Thiếu ngủ, thức khuya, ít hoạt động có thể ảnh hưởng đến quá trình điều hòa nhiệt độ.
- Tâm lý và căng thẳng: Căng thẳng, lo âu, căng thẳng kéo dài có thể ảnh hưởng đến hệ thần kinh giao cảm, gây ra các triệu chứng nóng ở người, tim đập nhanh, khó thở.
- Các bệnh lý tiềm ẩn:
- Cường giáp: Tuyến giáp hoạt động có khả năng sản xuất hormone thyroxine, làm tăng quá trình trao đổi chất và sinh nhiệt.
- Nhiễm trùng: Các loại virus nhiễm trùng, đặc biệt là nhiễm trùng đường tiết niệu, cũng có thể gây nóng cho người.
- Phong loạn chuyển hóa: Các bệnh như tiểu đường, rối loạn máu lipid có thể ảnh hưởng đến quá trình điều hòa thân nhiệt.
- Tác dụng phụ của thuốc: Một số loại thuốc điều trị có thể gây tác dụng phụ gây nóng cho người.
3. Triệu Chứng Thường Gặp Của Người Ở Phụ Nữ
Các triệu chứng nóng nhất ở mỗi người có thể rất đa dạng và khác nhau, bao gồm:
- Cảm giác nóng: Nóng đột ngột ở mặt, cổ, vũ khí, sau đó lan ra toàn thân.
- Đổ mồ hôi nhiều: Đặc biệt là vào ban đêm, gây khó chịu và ảnh hưởng đến giấc ngủ.
- Da đỏ nhung: Mặt và cổ có thể đỏ kích thích giãn mạch máu.
- Tim đập nhanh: Cảm giác giác tim đập nhanh hơn bình thường.
- Khó thở: Cảm giác hơi, khó thở.
- Khó chịu, nóng bức, nóng giận: Nóng trong người có thể ảnh hưởng đến tâm trạng và gây khó chịu.
- Mất ngủ, khó ngủ: Đổ mồ hôi đêm và cảm giác nóng bức có thể gây khó ngủ.
- Khô da, nổi mụn: Phổ biến trong người có thể làm da khô và dễ nổi mụn.
- Khát nước: Cơ thể mất nước do mồ hôi nhiều.
4. Ảnh Hưởng Của Nóng Trong Người Đến Sức Khỏe Và Chất Lượng Cuộc Sống
Nóng trong người không chỉ gây khó chịu tạm thời mà còn ảnh hưởng đến nhiều khía cạnh của cuộc sống:
- Pha màu kinh nguyệt: Ảnh ảnh hưởng đến chu kỳ kinh nguyệt, gây ra kinh nguyệt không đều, đút kinh, rong kinh.
- Ảnh hưởng đến giấc ngủ: Gây mất ngủ, khó ngủ, ảnh hưởng đến sức khỏe và tinh thần.
- Ảnh tác dụng đến tâm lý: Gay stress, lo âu, kiềm chế, thậm chí là trầm cảm.
- Suy giảm chất lượng cuộc sống: Ảnh hưởng đến công việc, sinh hoạt hàng ngày và các mối quan hệ xã hội.
5. Các Biện Pháp Khắc Phục Nóng Trong Người Hiệu Quả
Để giảm thiểu tình trạng nóng bức ở người, phụ nữ có thể áp dụng các biện pháp bảo vệ sau:
- Thay đổi lối sống và chế độ ăn uống:
- Uống đủ nước: Đảm bảo uống đủ 2-2,5 lít nước mỗi ngày.
- Chế độ ăn uống cân bằng: Tăng cường rau xanh, trái cây, ngũ cốc nguyên hạt; hạn chế đồ ăn cay, dầu mỡ, đồ biến sẵn.
- Chế độ kích thích: Giảm thiểu hoặc tránh sử dụng rượu, bia, cà phê.
- Tập thể dục thường xuyên: Vận động nhẹ nhàng giúp cải thiện quá trình trao đổi chất và điều hòa nhiệt độ.
- Ngủ đủ giấc: Đảm bảo ngủ đủ 7-8 tiếng mỗi đêm.
- Giảm căng thẳng: Áp dụng các biện pháp thư giãn như yoga, thiên, nghệ nhạc.
- Sử dụng các biện pháp tự nhiên:
- Uống trà thảo: Các loại trà như trà hoa cúc, trà atiso, trà xanh có tác dụng thanh nhiệt, giải độc.
- Ăn các loại thực phẩm có tính mát: Rau má, bí đao, khổ qua, đông.
- Sử dụng sản phẩm hỗ trợ (cần tham khảo ý kiến bác sĩ):
- Các sản phẩm bổ sung nội tiết tố dược phẩm hoặc tổng hợp có thể giúp cân bằng hormone.
- Tham khảo ý kiến bác sĩ chuyên khoa: Nếu tình trạng nóng trong người kéo dài, ảnh hưởng nghiêm trọng đến cuộc sống hoặc nghi ngờ bệnh lý, cần đến gặp bác sĩ để được thăm khám và điều trị kịp thời.
6. Phòng Ngừa Nóng Trong Người
Để phòng nóng trong người, phụ nữ nên duy trì một lối sống lành mạnh, chế độ ăn uống khoa học, kiểm soát căng thẳng và khám sức khỏe định kỳ.
Kết luận
Nóng trong người ở phụ nữ là một vấn đề sức khỏe phổ biến ở phụ nữ, đặc biệt là trong giai đoạn tiền mãn kinh và mãn kinh. Biết rõ nguyên nhân, triệu chứng và giải pháp giải quyết sẽ giúp phụ nữ cải thiện chất lượng cuộc sống và bảo vệ sức khỏe.
Song Phụng Điều Kinh là sản phẩm của Dược Bình Đông có mặt trên thị trường hơn 70 năm trong lĩnh vực cung cấp các sản phẩm chăm sóc sức khỏe an toàn, cam kết đem những sản phẩm chất lượng đến cho khách hàng. Nếu bạn có thắc mắc hoặc muốn tư vấn về tình trạng nóng trong người ở phụ nữ hay sản phẩm thì có thể liên hệ với chúng tôi qua số hotline (028)39 808 808 để được tư vấn kịp thời nhé.
