Month: March 2024
The Gestational Surrogacy Process: A Comprehensive Guide

Gestational surrogacy is a life-changing option for couples or individuals who are unable to carry a pregnancy themselves. This remarkable process involves a gestational surrogate, who carries and gives birth to a baby on behalf of the intended parents. If you are considering gestational surrogacy, it is essential to understand the process, requirements, and potential challenges involved. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to the gestational surrogacy process, covering everything from finding a surrogate to post-birth arrangements.
1. Initial Consultation and Assessment
The first step in the gestational surrogacy process is to consult with a fertility specialist or reproductive endocrinologist who specializes in surrogacy. During this consultation, the intended parents will undergo a comprehensive medical evaluation to ensure they are suitable candidates for the process. The medical evaluation may include fertility testing, genetic screening, and a review of medical history.
2. Finding a Gestational Surrogate
Once the intended parents have been assessed and deemed suitable for gestational surrogacy, the next step is to find a gestational surrogate. There are several options for finding a surrogate, including:
– Known Surrogate: Some intended parents have a family member or close friend who is willing to be their surrogate. This is known as a known or altruistic surrogacy arrangement.
– Surrogacy Agency: Working with a surrogacy agency is a common option for finding a gestational surrogate. Agencies typically have a pool of pre-screened surrogates who have undergone thorough medical and psychological evaluations.
– Independent Search: Intended parents may choose to independently search for a gestational surrogate through online platforms, social media groups, or surrogacy support networks. It is essential to thoroughly vet any potential surrogates and ensure they meet the necessary criteria.
3. Legal and Financial Considerations
Legal and financial aspects play a crucial role in the gestational surrogacy process. It is essential to consult with an experienced reproductive attorney who specializes in surrogacy law to ensure all legal requirements are met and to establish clear agreements and contracts. The legal process typically involves:
– Surrogacy Agreement: This document outlines the rights, responsibilities, and expectations of all parties involved, including the intended parents and the gestational surrogate. It covers topics such as compensation, medical decisions, and post-birth arrangements.
– Parental Rights: Legal procedures are undertaken to establish the intended parents’ legal rights to the child born through surrogacy. This may involve pre-birth orders, post-birth adoptions, or other legal processes, depending on the jurisdiction and applicable laws.
– Financial Considerations: The gestational surrogacy process involves various financial aspects, including compensation for the gestational surrogate, medical expenses, legal fees, and insurance coverage. It is crucial to establish a clear financial plan and budget to ensure all costs are adequately covered.
4. Medical Procedures and IVF
Once the legal and financial aspects are in place, the medical procedures can commence. The gestational surrogacy process typically involves the following steps:
– Medical Synchronization: The menstrual cycles of the intended mother (or egg donor) and the gestational surrogate are synchronized using hormonal medications. This ensures that the surrogate’s uterus is prepared to receive the embryo.
– Ovarian Stimulation and Egg Retrieval: The intended mother (or egg donor) undergoes ovarian stimulation to produce multiple eggs. The eggs are then retrieved under sedation or anesthesia using a minimally invasive procedure known as follicular aspiration.
– Fertilization and Embryo Transfer: The retrieved eggs are fertilized with the intended father’s sperm or donor sperm in a laboratory through in vitro fertilization (IVF). The resulting embryos are then transferred into the gestational surrogate’s uterus through a minimally invasive procedure.
– Pregnancy Monitoring: Following the embryo transfer, the gestational surrogate will undergo regular monitoring to assess the progress of the pregnancy. This includes blood tests, ultrasounds, and other diagnostic procedures to ensure the health and well-being of the surrogate and the developing baby.
5. Pregnancy and Birth
During the gestational surrogacy process, the gestational surrogate assumes the role of carrying the pregnancy on behalf of the intended parents. The surrogate receives comprehensive prenatal care from her obstetrician, while the intended parents may participate in the pregnancy by attending appointments, ultrasounds, and supporting the surrogate emotionally.
When the time comes, the gestational surrogate will give birth to the baby. The intended parents may be present during the birth if agreed upon in the surrogacy agreement. After the birth, legal processes are followed to establish the intended parents’ legal rights to the child, ensuring a smooth transition to parenthood.
6. Post-Birth Arrangements and Support
Once the baby is born, the intended parents and the gestational surrogate may have agreed-upon post-birth arrangements. This can include the level of contact and involvement between the surrogate and the child, as well as ongoing support and communication.
It is important to establish open and honest communication and maintain a positive relationship between all parties involved. Surrogacy support groups, counseling, or therapy can be beneficial for both the intended parents and the gestational surrogate to navigate any emotional challenges that may arise post-birth.
The gestational surrogacy process is a complex but rewarding journey for intended parents and gestational surrogates alike. It involves careful consideration of medical, legal, and emotional aspects to ensure a successful and fulfilling experience. By understanding the various steps involved, finding a suitable gestational surrogate, addressing legal and financial considerations, undergoing medical procedures, and establishing post-birth arrangements, intended parents can embark on their path to parenthood with confidence and support. Seeking guidance from experienced professionals, such as fertility specialists, reproductive attorneys, and surrogacy agencies, is crucial to navigating the gestational surrogacy process smoothly and achieving the desired outcome of welcoming a healthy and happy baby into the world.
How to Prevent Premature Birth
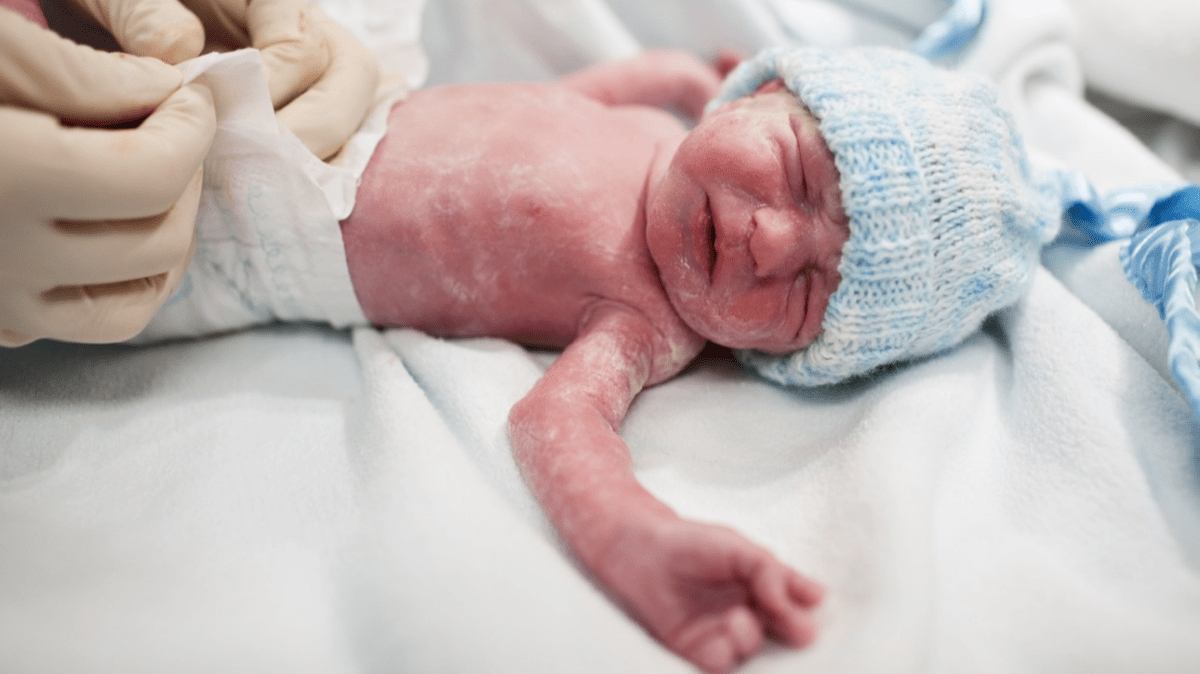
Premature birth, also known as preterm birth, is a serious concern that affects millions of babies and their families worldwide. It occurs when a baby is born before completing 37 weeks of gestation. Premature birth can lead to various health complications and developmental challenges for the baby. In some cases, it can even be life-threatening. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the causes and risk factors associated with premature birth and take proactive measures to prevent it. In this article, we will explore effective strategies to prevent premature birth and promote healthy pregnancies.
1. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle:
Taking care of your overall health is essential for a healthy pregnancy. Here are some lifestyle habits to adopt:
a) Eat a Balanced Diet: Ensure that your diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid processed foods, excessive caffeine, and sugary drinks.
b) Stay Active: Regular exercise during pregnancy can help reduce the risk of premature birth. Consult your healthcare provider for suitable exercises based on your health condition.
c) Avoid Smoking, Alcohol, and Drugs: These substances can significantly increase the risk of premature birth and have harmful effects on the baby’s development.
2. Get Prenatal Care:
Early and regular prenatal care plays a vital role in preventing premature birth. Prenatal visits allow healthcare providers to monitor the progress of your pregnancy, identify any potential complications, and provide appropriate interventions. Attend all scheduled appointments and follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations regarding tests and screenings.
3. Manage Chronic Conditions:
If you have any pre-existing medical conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or autoimmune disorders, it is crucial to manage them effectively during pregnancy. Work closely with your healthcare provider to monitor and control these conditions to minimize the risk of premature birth.
4. Avoid Infections:
Certain infections can increase the risk of premature birth. Take the following precautions to prevent infections:
a) Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently with soap and water. Avoid close contact with individuals who have contagious illnesses.
b) Get Vaccinated: Ensure that your vaccinations, such as flu and Tdap (tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis), are up to date before and during pregnancy.
c) Practice Safe Food Handling: Properly cook and store food to prevent food borne illnesses.
5. Manage Stress:
High levels of stress during pregnancy have been associated with an increased risk of premature birth. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques, seeking support from loved ones, and engaging in activities that bring you joy.
6. Avoid Environmental Hazards:
Exposure to certain environmental hazards can contribute to premature birth. Take the following precautions:
a) Limit Exposure to Chemicals: Avoid exposure to harmful chemicals, such as pesticides, solvents, and cleaning agents. Use natural and non-toxic alternatives whenever possible.
b) Minimize Radiation Exposure: Limit exposure to radiation from sources like X-rays and certain medical procedures. Inform your healthcare provider about your pregnancy before undergoing any tests or treatments.
7. Recognize the Signs of Preterm Labor:
Educate yourself about the signs and symptoms of preterm labor, such as regular contractions, lower back pain, pelvic pressure, and vaginal bleeding. If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
8. Seek Support:
Pregnancy can be a challenging time, both physically and emotionally. Surround yourself with a supportive network of family, friends, and healthcare professionals who can provide guidance, encouragement, and assistance when needed.
Remember, while these strategies can help reduce the risk of premature birth, they do not guarantee prevention in all cases. Sometimes, premature birth may occur due to factors beyond our control. If you have concerns about your pregnancy or the risk of premature birth, consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance.
In conclusion, preventing premature birth requires a combination of healthy lifestyle choices, proper prenatal care, and proactive management of existing health conditions. By adopting these strategies, expectant mothers can increase their chances of having a full-term, healthy pregnancy. Remember, every pregnancy is unique, and it is essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to ensure the best possible outcome for you and your baby.
Medication for Ovulation: Understanding Options and Treatment Strategies
Ovulation is a crucial process in a woman’s reproductive cycle, as it is the release of a mature egg from the ovary. However, some women may experience difficulties with ovulation, which can impact their fertility and ability to conceive. In such cases, medication for ovulation may be recommended to stimulate the release of eggs and increase the chances of pregnancy. In this article, we will explore the various medications available for ovulation induction, their mechanisms of action, and the treatment strategies associated with their use.
Understanding Ovulation and Ovulation Disorders
Before delving into medication options for ovulation, it is important to understand the process of ovulation and the potential disorders that can affect it. Ovulation typically occurs once a month when a mature egg is released from the ovary and travels through the fallopian tube, where it can be fertilized by sperm. Ovulation disorders can disrupt this process, leading to irregular or absent ovulation. Common ovulation disorders include polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), hypothalamic dysfunction, and premature ovarian insufficiency.
Medication Options for Ovulation Induction
1. Clomiphene Citrate (Clomid):
Clomiphene citrate, commonly known by its brand name Clomid, is a medication frequently prescribed for ovulation induction. It works by blocking estrogen receptors in the brain, which leads to an increase in follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) production. This, in turn, stimulates the ovaries to produce and release eggs. Clomid is typically taken orally for five consecutive days, starting on the third to fifth day of the menstrual cycle.
2. Letrozole (Femara):
Letrozole, also known by its brand name Femara, is an aromatase inhibitor that is primarily used in the treatment of breast cancer. However, it has also been found to be effective in stimulating ovulation. Letrozole works by inhibiting the production of estrogen, which leads to an increase in FSH production and subsequent ovulation. Like Clomid, letrozole is taken orally for five consecutive days, usually starting on the third to fifth day of the menstrual cycle.
3. Gonadotropins:
Gonadotropins are injectable medications that directly stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. These medications contain follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), which are naturally produced by the pituitary gland. Gonadotropins are typically used in cases where Clomid or letrozole have not been effective or when a more controlled and closely monitored ovulation induction is required. They are administered via subcutaneous injections, and the dosage and timing are carefully adjusted based on the individual’s response.
4. Metformin:
Metformin is an oral medication commonly used to treat type 2 diabetes. However, it has also been found to be effective in treating ovulation disorders, particularly in women with PCOS. Metformin works by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing insulin resistance, which can help regulate hormone levels and restore normal ovulation. It is often used in combination with Clomid or letrozole to enhance their effectiveness.
Treatment Strategies for Ovulation Induction
1. Monitoring Ovulation:
During ovulation induction, it is essential to monitor the response to medication and determine the timing of ovulation. This is typically done through regular ultrasound examinations to monitor the growth of ovarian follicles and the thickness of the uterine lining. Blood tests may also be conducted to measure hormone levels and pinpoint the optimal time for intercourse or assisted reproductive techniques.
2. Timing Intercourse:
Ovulation induction aims to maximize the chances of conception, and timing intercourse is crucial in this process. Healthcare providers will provide guidance on the most fertile period based on the response to medication and monitoring. Intercourse is often recommended within a specific timeframe surrounding ovulation to optimize the chances of fertilization.
3. Assisted Reproductive Techniques:
In some cases, ovulation induction may be combined with assisted reproductive techniques such as intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF). These techniques involve the collection of eggs, their fertilization with sperm, and the transfer of resulting embryos into the uterus. Assisted reproductive techniques can be recommended when other methods of ovulation induction have not been successful or when there are additional fertility factors involved.
4. Side Effects and Risks:
Like any medication, ovulation induction medications can have side effects and risks. Common side effects include hot flashes, mood swings, breast tenderness, and bloating. In rare cases, there is a risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), a condition characterized by the overstimulation of the ovaries, which can lead to abdominal pain, swelling, and fluid retention. It is important to discuss potential side effects and risks with a healthcare provider and undergo regular monitoring to minimize complications.
Medication for ovulation induction can be a valuable tool for women experiencing ovulation disorders. Clomiphene citrate, letrozole, gonadotropins, and metformin are among the options available to stimulate ovulation and increase the chances of conception. Treatment strategies, such as monitoring ovulation, timing intercourse, and considering assisted reproductive techniques, play a vital role in the success of ovulation induction. It is crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate medication and treatment plan based on individual circumstances. With proper guidance and monitoring, medication for ovulation can significantly enhance the chances of achieving a successful pregnancy for women facing ovulation challenges.
IVF with Endometriosis: Understanding the Options and Success Rates

Endometriosis is a medical condition that affects many women of reproductive age. It occurs when the tissue that lines the uterus grows outside of it, causing inflammation, pain, and other complications. For women with endometriosis who are trying to conceive, in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be a viable option. In this article, we will explore the relationship between endometriosis and IVF, the potential challenges, and the success rates associated with this fertility treatment.
Endometriosis and Fertility
Endometriosis can have a significant impact on a woman’s fertility. The abnormal growth of endometrial tissue can lead to the formation of adhesions, ovarian cysts, and scarring, all of which can interfere with the natural conception process. Additionally, the inflammatory environment created by endometriosis can affect the quality of eggs and sperm, as well as impair embryo implantation.
IVF Treatment for Endometriosis
IVF is a fertility treatment option that involves the retrieval of eggs from the ovaries, fertilization of the eggs with sperm in a laboratory, and the transfer of resulting embryos into the uterus. IVF can bypass some of the challenges posed by endometriosis, as it allows for the direct placement of embryos into the uterus, bypassing any potential obstructions caused by the condition.
Benefits of IVF for Women with Endometriosis
1. Increased Fertilization Rates: The controlled environment of the IVF laboratory can optimize the conditions for fertilization, increasing the chances of successful fertilization compared to natural conception.
2. Monitoring and Stimulation: During the IVF process, women undergo hormonal stimulation to produce multiple eggs, which can increase the chances of obtaining viable embryos for transfer.
3. Embryo Selection: IVF allows for the selection of the highest quality embryos for transfer, which can improve the chances of successful implantation and pregnancy.
4. Endometrial Receptivity Assessment: Prior to the embryo transfer, an endometrial receptivity assessment can be performed to ensure that the uterine lining is optimal for implantation.
Success Rates of IVF with Endometriosis
The success rates of IVF for women with endometriosis can vary depending on various factors, including the severity of endometriosis, the age of the woman, and the quality of the embryos. While endometriosis can pose challenges to fertility, studies have shown that IVF can be an effective treatment option for women with endometriosis.
According to research, women with endometriosis who undergo IVF have comparable success rates to women without endometriosis. However, it is important to note that success rates can vary significantly from person to person. Factors such as the stage of endometriosis, the presence of other fertility factors, and the overall health of the individual can influence the outcome.
Challenges and Considerations
While IVF can be a promising option for women with endometriosis, there are some challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
1. Response to Ovarian Stimulation: Women with endometriosis may have a reduced ovarian reserve, which can affect the response to ovarian stimulation during the IVF process. This may result in a lower number of eggs retrieved for fertilization.
2. Quality of Eggs and Embryos: Endometriosis can impact the quality of eggs and embryos, making it important to discuss the potential impact with a healthcare professional. Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) may be recommended to select embryos with the highest chances of success.
3. Risk of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS): Ovarian stimulation during IVF carries a risk of OHSS, a condition characterized by enlarged ovaries and fluid accumulation. Women with endometriosis may be at a higher risk of developing OHSS.
4. Recurrence of Endometriosis: IVF does not cure endometriosis, and there is a possibility of its recurrence after treatment. It is important to discuss with a healthcare professional about managing endometriosis symptoms and potential future fertility options.
IVF can be a viable option for women with endometriosis who are struggling to conceive naturally. While endometriosis can pose challenges to fertility, IVF offers the possibility of overcoming these challenges and achieving pregnancy. It is important to consult with a fertility specialist to discuss the individual circumstances and determine the most appropriate treatment plan. While success rates can vary, IVF with endometriosis has shown promising results, providing hope for women with this condition who dream of starting a family. With the right support and guidance, many women with endometriosis can fulfill their desire to become parents through IVF.
Creating an Effective Pumping Schedule for Breastfeeding Success
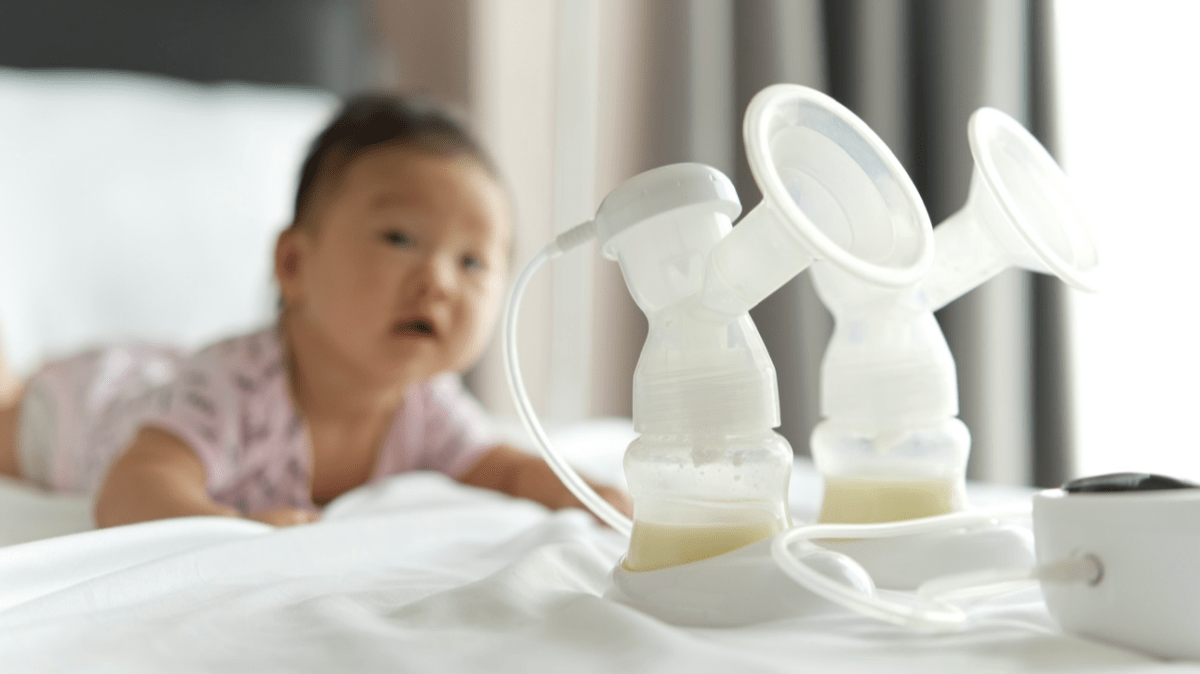

Breastfeeding is a beautiful and natural way to nourish your baby, providing them with essential nutrients and building a strong bond between mother and child. However, there may be times when you need to be away from your baby or want to build up a supply of breast milk for future use. This is where pumping comes in. By using a breast pump, you can express breast milk and store it for later use. To maximize the benefits of pumping while maintaining a successful breastfeeding relationship, it’s important to establish an effective pumping schedule. In this article, we will discuss how to create a pumping schedule that works for you and your baby, all while optimizing your milk supply and breastfeeding journey.
1. Understand Your Baby’s Feeding Patterns:
Before creating a pumping schedule, it’s important to understand your baby’s feeding patterns. Newborns typically feed every 2-3 hours, so you’ll want to aim to pump around the same frequency to mimic their natural feeding routine. As your baby grows, their feeding patterns may change, so stay attuned to their cues and adjust your pumping schedule accordingly.
2. Start Pumping Early:
If you plan to introduce bottle feeding or need to build up a supply of breast milk, it’s a good idea to start pumping early. Experts recommend waiting until breastfeeding is well established, usually around 3-4 weeks postpartum, before introducing pumping. This allows your baby to establish a good latch and your milk supply to stabilize.
3. Pump in Between Feedings:
To create a pumping schedule that complements breastfeeding, try pumping in between your baby’s feedings. This can help you build up a supply of breast milk without interfering with your baby’s demand for nursing. Pumping in the morning when milk supply is typically higher can also yield more milk.
4. Consider Power Pumping:
If you’re struggling with low milk supply or want to increase your milk production, power pumping may be beneficial. Power pumping involves pumping for shorter, more frequent sessions to stimulate milk production. A typical power pumping session consists of pumping for 20 minutes, resting for 10 minutes, pumping for another 10 minutes, resting for 10 minutes, and pumping for a final 10 minutes. Incorporate power pumping into your schedule a few times a week to boost milk supply.
5. Establish a Consistent Routine:
Consistency is key when it comes to pumping. Try to establish a regular pumping routine by pumping at the same times each day. This helps signal your body to produce milk during those specific times, making pumping more efficient and effective. Set reminders or use a pumping app to stay on track with your schedule.
6. Utilize Hands-On Pumping Techniques:
To enhance milk flow and maximize output, incorporate hands-on pumping techniques. Before and during your pumping session, massage your breasts gently to stimulate let-down and encourage milk flow. You can also use breast compressions while pumping to empty the breasts more effectively.
7. Find a Comfortable Pumping Environment:
Creating a comfortable and relaxing pumping environment can significantly impact your pumping experience. Find a quiet and private space where you can focus on pumping without distractions. Use a comfortable chair, play soothing music, or practice relaxation techniques to help stimulate let-down and make pumping a more enjoyable experience.
8. Be Mindful of Hydration and Nutrition:
Maintaining proper hydration and nutrition is essential for milk production. Drink plenty of water throughout the day and consume a well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Some lactation consultants also recommend certain galactagogue foods or supplements that can help support milk production.
9. Store and Label Expressed Milk Properly:
When pumping, it’s important to store and label your expressed milk properly. Use clean, sterilized bottles or breast milk storage bags to store your milk. Label each container with the date and time of expression to ensure freshness. Follow guidelines for proper storage, including refrigeration or freezing, to maintain the quality of your breast milk.
10. Involve Your Partner or Support System:
Creating a pumping schedule can be challenging, especially when juggling other responsibilities. Involve your partner or support system in the process. They can help with feedings, handle bottle preparation, or assist with other tasks to give you the time and space you need to pump effectively.
11. Seek Support and Guidance:
If you’re struggling with establishing a pumping schedule or have concerns about your milk supply, don’t hesitate to seek support and guidance. Reach out to a lactation consultant or breastfeeding support group for personalized advice and assistance. They can help troubleshoot any issues, provide tips, and offer encouragement along your breastfeeding and pumping journey.
Creating an effective pumping schedule is crucial for breastfeeding success and maintaining a healthy milk supply. By understanding your baby’s feeding patterns, starting pumping early, and establishing a consistent routine, you can optimize your pumping sessions while supporting your breastfeeding goals. Remember to prioritize self-care, seek support when needed, and enjoy the special bonding moments that breastfeeding and pumping provide.
What is VMS Menopause: Understanding and Managing Menopausal Symptoms

Menopause is a natural stage in a woman’s life that marks the end of her reproductive years. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 55, although the timing can vary from woman to woman. During this time, the body goes through hormonal changes that can result in various physical and emotional symptoms. One common symptom experienced by many women is VMS menopause, which stands for Vasomotor Symptoms. In this article, we will delve into what VMS menopause entails, explore the symptoms associated with it, and discuss strategies for managing these symptoms effectively.
What is VMS Menopause?
VMS menopause refers to a specific set of symptoms that occur as a result of hormonal fluctuations during menopause. These symptoms primarily revolve around the body’s regulation of temperature and can include hot flashes, night sweats, and flushing. Vasomotor symptoms are experienced by the majority of women going through menopause, with studies suggesting that around 75% of menopausal women experience hot flashes to some degree.
Understanding Vasomotor Symptoms
1. Hot Flashes: Hot flashes are the most common vasomotor symptom experienced during menopause. They are characterized by a sudden feeling of intense heat, often accompanied by sweating, flushing of the face and neck, and an increased heart rate. Hot flashes can last anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes and can occur multiple times throughout the day or night.
2. Night Sweats: Night sweats are essentially hot flashes that occur during sleep, leading to excessive sweating and disrupted sleep patterns. Waking up drenched in sweat and having to change clothing or bedding can be a common occurrence for women experiencing night sweats.
3. Flushing: Flushing refers to the sudden reddening of the skin, usually on the face and neck. This symptom is often associated with hot flashes and can be accompanied by a sensation of warmth or heat.
Managing VMS Menopause Symptoms
While VMS menopause symptoms can be bothersome and disruptive, there are various strategies and treatments available to help manage them effectively. Here are some approaches that women can consider:
1. Lifestyle Modifications:
– Dressing in layers: Wearing lightweight, breathable clothing that can be easily adjusted can help regulate body temperature during hot flashes.
– Managing stress: Stress can trigger or worsen vasomotor symptoms. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises may help alleviate symptoms.
– Regular exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help regulate hormonal balance and reduce the frequency and severity of VMS menopause symptoms.
– Maintaining a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can contribute to the severity of vasomotor symptoms. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help manage these symptoms.
2. Natural Remedies:
– Black cohosh: This herbal supplement has been used traditionally to alleviate menopausal symptoms, including hot flashes and night sweats.
– Soy: Foods rich in soy, such as tofu and soy milk, contain isoflavones that mimic estrogen in the body. Some women find that increasing their intake of soy can help reduce VMS menopause symptoms.
– Flaxseed: Flaxseed is a good source of lignans, which are compounds that can have estrogen-like effects in the body. Adding flaxseed to your diet may help alleviate hot flashes and other vasomotor symptoms.
3. Hormone Therapy:
Hormone therapy involves the use of medications that contain estrogen and/or progesterone to supplement the declining levels of these hormones during menopause. Hormone therapy can effectively manage vasomotor symptoms in many women, but it’s important to discuss the risks and benefits with a healthcare provider before considering this option.
4. Non-Hormonal Medications:
There are non-hormonal medications available that can help manage VMS menopause symptoms. These medications include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), and gabapentin. These medications are primarily used to treat other conditions but have been found to be effective in reducing the frequency and severity of hot flashes.
5. Complementary Therapies:
– Acupuncture: Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body. Some studies suggest that acupuncture may help reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes.
– Mind-body techniques: Techniques such as relaxation exercises, meditation, and mindfulness have been shown to help reduce vasomotor symptoms in some women.
It’s important to note that what works for one woman may not work for another. It may take some trial and error to find the most effective management strategies for VMS menopause symptoms. Consulting with a healthcare provider or menopause specialist can provide personalized guidance and recommendations based on individual needs and preferences.
VMS menopause refers to vasomotor symptoms experienced by women during the menopausal transition. Hot flashes, night sweats, and flushing are common symptoms that can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life. By implementing lifestyle modifications, considering natural remedies, exploring hormone therapy or non-hormonal medications, and trying complementary therapies, women can effectively manage VMS menopause symptoms and navigate this transitional phase with greater ease and comfort. Remember to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable approach for your individual needs.
Male Fertility and Age: Understanding the Impact on Reproductive Health

When it comes to fertility and reproductive health, much of the focus is often on women. However, it’s important to recognize that male fertility also plays a significant role in the ability to conceive. While age-related decline in female fertility is widely acknowledged, the impact of age on male fertility is often overlooked or misunderstood. In this article, we will explore the relationship between male fertility and age, shedding light on the factors that can affect a man’s reproductive health as he gets older.
1. The Basics of Male Fertility:
Before delving into the impact of age on male fertility, it’s crucial to understand the basics. Male fertility is determined by the quality and quantity of sperm. Healthy sperm have the ability to swim, penetrate an egg, and fertilize it successfully. Factors that can affect male fertility include sperm count, motility (movement), morphology (shape), and overall sperm health.
2. The Prime Reproductive Years:
Like women, men also have a prime reproductive age range. Generally, men are considered to have optimal fertility in their late teens to early 30s. During this time, sperm production is at its peak, and the quality of sperm is generally high. However, it’s essential to note that every individual is different, and fertility can vary.
3. Age-Related Decline in Sperm Quality:
As men age, there is a gradual decline in sperm quality. Studies have shown that sperm count, motility, and morphology can decrease with advancing age. This decline in sperm health can affect a man’s ability to conceive naturally with their partner. It’s important to understand that while the decline may be gradual, it can still have a significant impact on fertility over time.
4. Increased Risk of Genetic Abnormalities:
Advanced paternal age has been linked to an increased risk of genetic abnormalities in offspring. As men age, the risk of chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome, and certain genetic disorders, such as autism and schizophrenia, also increases. This is because the DNA in sperm can accumulate mutations over time, leading to potential health risks for future children.
5. Impact on Time to Conception:
Studies have shown that advanced paternal age can affect the time it takes for couples to conceive. As men get older, the chances of experiencing prolonged time to pregnancy increase. This can be attributed to factors such as decreased sperm quality and quantity, which can lead to reduced fertility potential.
6. Role of Lifestyle Factors:
While age is a significant factor in male fertility, it’s important to acknowledge that lifestyle factors also play a role. Certain habits, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, drug use, poor diet, obesity, and exposure to environmental toxins, can further impact sperm health and fertility. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for optimizing reproductive health at any age.
7. Seeking Medical Assistance:
If you and your partner have been actively trying to conceive without success, it may be beneficial to seek medical assistance. A fertility specialist can evaluate both partners’ reproductive health, including a comprehensive semen analysis for the male partner. They can provide guidance, identify any potential issues, and recommend appropriate treatments or interventions.
8. Options for Assisted Reproductive Technologies:
In cases where natural conception is not possible or challenging due to age-related fertility issues, assisted reproductive technologies (ART) can offer alternative pathways to parenthood. Techniques such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), and sperm retrieval methods can help overcome certain fertility obstacles and increase the chances of conception.
9. Importance of Open Communication:
Navigating the challenges of male fertility and age requires open and honest communication between partners. It’s crucial to discuss concerns, expectations, and any potential fertility issues early on in the journey. This can help reduce stress, promote understanding, and facilitate informed decision-making regarding family planning options.
10. Future Directions in Male Fertility Research:
While much is known about the impact of female age on fertility, research on male fertility and age is still evolving. Scientists are continuously studying the factors that contribute to age-related decline in male fertility and exploring potential interventions. Stay updated on the latest research and advancements in the field to make informed decisions regarding reproductive health.
In conclusion, male fertility and age are interlinked, and understanding the impact is crucial for individuals and couples planning to start a family. While men generally have a longer fertility window compared to women, age-related decline in sperm quality and an increased risk of genetic abnormalities should be considered. By being aware of these factors and seeking appropriate medical guidance, couples can make informed decisions and take proactive steps towards achieving their reproductive goals.
Navigating Sexual Intimacy with Endometriosis: Tips and Strategies for a Fulfilling Relationship

Endometriosis is a chronic condition that affects millions of women worldwide. It occurs when the tissue that normally lines the uterus grows outside of it, leading to various symptoms such as pelvic pain, heavy periods, and infertility. Alongside the physical challenges, endometriosis can also impact a woman’s sexual intimacy and relationships.
Navigating sexual intimacy with endometriosis can be a complex and sensitive topic. It requires open communication, understanding, and a willingness to adapt to the unique needs and limitations that may arise. In this article, we will discuss some strategies and tips to help individuals with endometriosis and their partners navigate sexual intimacy in a supportive and fulfilling way.
1. Educate Yourself: The first step in navigating sexual intimacy with endometriosis is to educate yourself about the condition. Understand the symptoms, triggers, and treatment options available. This will help you approach the topic with empathy and knowledge.
2. Open Communication: Communication is key when it comes to navigating any aspect of a relationship, including sexual intimacy. Be open and honest with your partner about your symptoms, pain levels, and any concerns or fears you may have. Discuss what feels comfortable and what doesn’t, and explore alternative ways to experience intimacy.
3. Manage Pain: Endometriosis can cause significant pelvic pain, which can make sexual intercourse uncomfortable or even unbearable. It’s essential to find ways to manage pain and make sexual intimacy more enjoyable. This may include trying different positions, using lubricants, or exploring non-penetrative forms of intimacy.
4. Timing: Endometriosis symptoms can fluctuate throughout the menstrual cycle. Some women may experience increased pain and discomfort during their periods, while others may have more relief. Understanding your body’s patterns can help you plan intimate moments during times when you’re feeling better.
5. Foreplay and Emotional Connection: Sexual intimacy is not just about intercourse. Focus on building emotional connection and engaging in extended foreplay to enhance pleasure and intimacy. Take the time to explore each other’s bodies and find what feels good without putting pressure on penetration.
6. Seek Professional Help: If endometriosis significantly affects your sexual intimacy and relationship, consider seeking professional help. A healthcare provider who specializes in endometriosis can provide guidance, suggest treatments, or refer you to a pelvic floor physical therapist who can help with pain management and improving sexual function.
7. Self-Care and Support: Living with endometriosis can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. It’s crucial to prioritize self-care and seek support from loved ones or support groups. Taking care of your overall well-being can positively impact your sexual intimacy.
8. Experiment and Adapt: Every person with endometriosis is unique, and what works for one may not work for another. Be open to experimentation and adapt your approach based on your individual needs and preferences. Try different positions, techniques, or sexual aids to find what brings pleasure and minimizes discomfort.
9. Manage Stress: Stress can worsen endometriosis symptoms and affect sexual intimacy. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in regular exercise, or seeking therapy. Taking steps to reduce stress can improve overall well-being and enhance sexual intimacy.
10. Use Lubrication: Endometriosis can cause vaginal dryness, making sexual intercourse uncomfortable. Using a water-based lubricant can help reduce friction and make intimacy more pleasurable. Experiment with different brands and types of lubricants to find one that works best for you.
11. Explore Non-Sexual Intimacy: Sexual intimacy is not limited to penetration. Explore other forms of intimacy that can bring you and your partner closer together. This can include cuddling, kissing, massage, or simply spending quality time together.
12. Patience and Understanding: Navigating sexual intimacy with endometriosis requires patience and understanding from both partners. It’s essential to acknowledge and validate each other’s feelings and experiences. Remember that some days may be better than others, and it’s okay to take breaks or adjust your expectations accordingly.
13. Consider Alternative Methods: If traditional sexual intercourse is too painful or uncomfortable, consider exploring alternative methods of sexual pleasure. This can include using sex toys, engaging in oral sex, or focusing on mutual masturbation. Find what works best for you and your partner’s comfort levels.
14. Take Breaks When Needed: Endometriosis can be physically and emotionally exhausting. It’s important to listen to your body and take breaks when needed. Don’t push yourself beyond your limits and communicate your needs to your partner. It’s okay to prioritize self-care and rest.
15. Support Each Other: Remember that endometriosis can impact both partners in a relationship. Offer support and understanding to each other as you navigate the challenges of sexual intimacy. Seek couples therapy if necessary to strengthen your relationship and address any issues that may arise.
Navigating sexual intimacy with endometriosis can be challenging, but with open communication, patience, and a willingness to adapt, it is possible to maintain a fulfilling and satisfying intimate relationship. Remember to prioritize self-care, seek professional help when needed, and support each other throughout the journey.
Menopause and Itchy Skin: Understanding the Connection and Relief Options
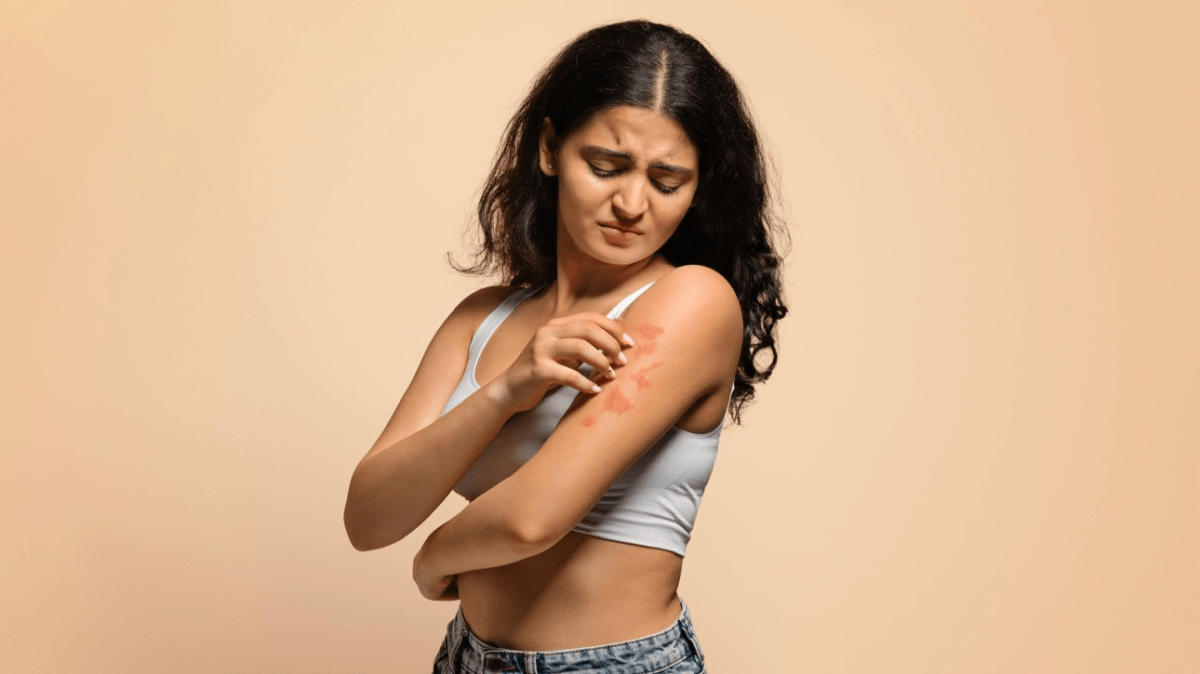
Menopause is a natural stage in a woman’s life when her menstrual periods cease, typically occurring in her late 40s or early 50s. Along with the hormonal changes that occur during menopause, many women experience a range of physical and emotional symptoms. One common symptom that can accompany menopause is itchy skin. In this article, we will explore the connection between menopause and itchy skin, the potential causes, and effective relief options.
Understanding Menopause and Hormonal Changes
During menopause, a woman’s body undergoes significant hormonal changes. The ovaries produce less estrogen and progesterone, leading to various physical and emotional symptoms. These hormonal fluctuations can affect the skin, leading to dryness, sensitivity, and itching.
Causes of Itchy Skin during Menopause
Several factors contribute to itchy skin during menopause. These include:
1. Estrogen Deficiency: Estrogen plays a vital role in maintaining healthy skin. As estrogen levels decline during menopause, the skin may become drier and more prone to itching.
2. Declining Collagen Levels: Collagen is a protein that provides structure and elasticity to the skin. With age and hormonal changes, collagen levels naturally decrease, leading to thinner and less resilient skin, which can contribute to itching.
3. Reduced Sebum Production: Sebum is the skin’s natural oil that helps to moisturize and protect it. During menopause, sebum production decreases, leading to dryness and itchiness.
4. Changes in Blood Flow: Hormonal changes during menopause can affect blood circulation, potentially leading to reduced blood flow to the skin. This can contribute to dryness and itchiness.
5. Skin Conditions: Menopause can exacerbate pre-existing skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis, leading to increased itching and discomfort.
Relief Options for Itchy Skin during Menopause
While itchy skin during menopause can be bothersome, there are several relief options that can help alleviate the discomfort:
1. Moisturize Regularly: Keeping the skin well-hydrated is essential for relieving dryness and itchiness. Use a moisturizer that is specifically formulated for dry or sensitive skin, and apply it regularly, especially after bathing or showering.
2. Avoid Hot Showers or Baths: Hot water can further dry out the skin and worsen itching. Opt for lukewarm water instead, and limit your bathing time to avoid stripping the skin of its natural oils.
3. Choose Gentle, Fragrance-Free Products: Harsh soaps, detergents, and skincare products can irritate the skin and exacerbate itching. Opt for gentle, fragrance-free options that are specifically formulated for sensitive skin.
4. Wear Breathable Fabrics: Synthetic fabrics can trap heat and moisture, leading to increased itchiness. Choose breathable, natural fabrics such as cotton or linen to allow the skin to breathe.
5. Use a Humidifier: Dry indoor air can worsen skin dryness and itching. Use a humidifier to add moisture to the air and improve overall skin hydration.
6. Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid potential triggers that worsen itching, such as certain fabrics, perfumes, or environmental factors like extreme heat or cold.
7. Practice Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate menopausal symptoms, including itchy skin. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, meditation, or yoga to help manage stress levels and promote overall well-being.
8. Seek Medical Advice: If your itchy skin is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms, it is advisable to seek medical advice. A healthcare professional can evaluate your symptoms, provide a proper diagnosis, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Medical Treatment Options
In some cases, over-the-counter or prescription medications may be necessary to alleviate severe or persistent itching. These may include:
1. Topical Steroids: Topical corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and relieve itching. They are available in various strengths and formulations, and should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
2. Antihistamines: Oral antihistamines can help reduce itching by blocking histamine receptors in the body. However, they can cause drowsiness, so it is important to choose non-drowsy formulations if daytime use is required.
3. Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Hormone replacement therapy, which involves taking estrogen and progesterone supplements, can help relieve menopausal symptoms, including itchy skin. However, HRT is not suitable for everyone, and its use should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
Itchy skin is a common symptom experienced by many women during menopause. The hormonal changes and age-related factors that occur during this stage can contribute to dryness, sensitivity, and itching. By understanding the causes and implementing effective relief options, women can alleviate the discomfort associated with itchy skin during menopause. Remember to moisturize regularly, choose gentle skincare products, avoid triggers, and seek medical advice if the itching is severe or persistent. With proper care and attention, women can navigate through menopause with greater comfort and well-being.
Is it Safe to Lift Weights During Pregnancy?
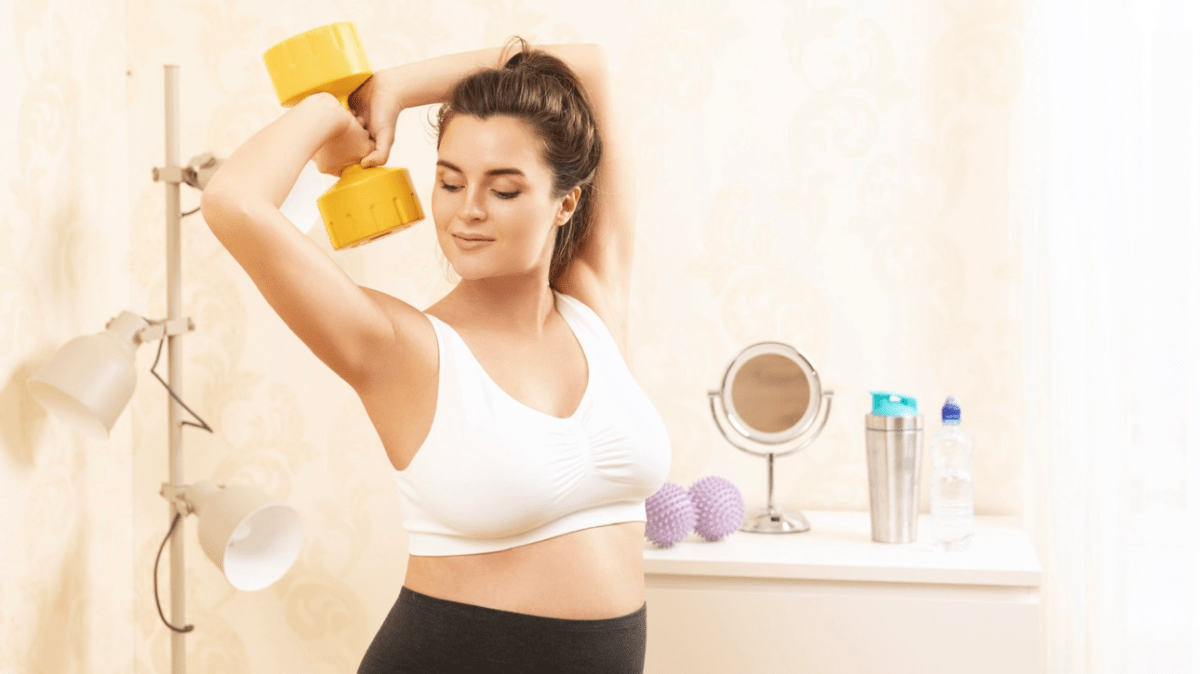

Pregnancy is a time of significant physical and emotional changes for women. It is common for expectant mothers to have concerns about their exercise routines and whether certain activities, such as weightlifting, are safe during pregnancy. The good news is that, in most cases, lifting weights can be a beneficial and safe form of exercise during pregnancy. However, there are certain considerations and precautions that should be taken to ensure the well-being of both the mother and the baby. In this article, we will explore the topic of weightlifting during pregnancy and provide valuable insights for expectant mothers.
The safety of lifting weights during pregnancy largely depends on the individual’s health, pre-pregnancy fitness level, and the stage of pregnancy. In general, if you have a healthy pregnancy and were physically active before getting pregnant, weightlifting can be safe and beneficial. However, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider before starting or continuing any exercise routine during pregnancy. They can assess your specific situation and provide personalized recommendations based on your health and any potential risks.
Benefits of Weightlifting During Pregnancy
Engaging in weightlifting exercises during pregnancy offers several benefits for expectant mothers, including:
1. Improved Strength and Endurance: Weightlifting helps strengthen and tone muscles, which can be particularly beneficial during pregnancy when your body undergoes significant changes and additional strain.
2. Enhanced Posture and Stability: Pregnancy can affect your posture and balance. Weightlifting exercises, when performed with proper form and technique, can help improve posture and stability, reducing the risk of common pregnancy-related discomforts, such as lower back pain.
3. Increased Energy Levels: Regular exercise, including weightlifting, can boost energy levels and combat pregnancy-related fatigue.
4. Better Mood and Mental Well-being: Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood boosters. Weightlifting can help reduce stress, anxiety, and symptoms of depression, promoting overall mental well-being during pregnancy.
Considerations for Safe Weightlifting During Pregnancy
While weightlifting can be safe during pregnancy, it is important to keep the following considerations in mind:
1. Seek Professional Guidance: If you are new to weightlifting or have never done it before, consider seeking guidance from a certified prenatal fitness specialist or a qualified personal trainer experienced in working with pregnant women. They can help create a safe and effective exercise program tailored to your needs.
2. Modify Your Routine: As your pregnancy progresses, your body undergoes changes that may require modifications to your weightlifting routine. Avoid exercises that put excessive strain on your abdomen or require lying flat on your back, especially after the first trimester. Focus on exercises that promote strength, stability, and overall body conditioning.
3. Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how your body feels during and after each weightlifting session. If you experience any pain, dizziness, shortness of breath, or other discomforts, stop exercising and consult your healthcare provider.
4. Stay Hydrated: It is crucial to stay hydrated before, during, and after your weightlifting workouts. Drink plenty of water to avoid dehydration, which can pose risks during pregnancy.
5. Use Proper Form and Technique: Maintain proper form and technique during weightlifting exercises to minimize the risk of injury. Avoid heavy lifting that could strain your muscles and joints.
6. Don’t Overexert Yourself: Pregnancy is not the time to set personal records or push yourself to the limits. Respect your body’s limits and focus on maintaining fitness rather than pursuing significant strength gains.
7. Monitor Your Heart Rate: Pay attention to your heart rate during exercise. Aim for a moderate intensity level and avoid prolonged periods of high-intensity exercise that could elevate your heart rate excessively.
In most cases, lifting weights can be safe and beneficial during pregnancy, provided you have a healthy pregnancy and receive clearance from your healthcare provider. Weightlifting offers numerous advantages, including improved strength, endurance, posture, stability, energy levels, and mood. However, it is crucial to follow the necessary precautions, seek professional guidance, modify your routine as needed, and listen to your body throughout the process. By doing so, you can enjoy the benefits of weightlifting while ensuring the safety and well-being of both you and your baby.
